Introduction
QuickSort is a sorting algorithm that is widely used in the industry. It is fast, efficient, and powerful. It uses the divide-and-conquer technique to divide the array into sub-arrays, sort them, and then recursively sort the larger arrays.

In this article, we will read quicksort python in detail. We will code it in both Python2 and Python3. Let's get started!
Must Recommended Topic, Floor Division in Python, Swapcase in Python
Also See, Divmod in Python
What is QuickSort in Python?
Quicksort is a widely used sorting algorithm that follows the divide and conquer principle. This sorting algorithm works with large data sets but varies from scenario to scenario. The algorithm takes an array as input, and in the quick sort algorithm, you select a pivot element which is nothing but a random number in an array. This number plays a vital role in the performance of the algorithm. Once you select the pivot elements, the elements smaller than pivot are moved toward the left, and numbers greater than the pivot are moved to the right. This process continues by dividing the array into subarrays. In the last, the array is sorted.
Also see, Python Operator Precedence
Quick Sort Algorithm
Let's take a look at the quick sort algorithm.
- Choose a pivot element - it can be any element. It is preferable that the element is chosen so that roughly half of the elements are smaller than it, and roughly half are bigger than it.
- Rearrange the elements of the array such that all the elements smaller than the pivot are on its left, and all the elements larger than the pivot are on its right. The pivot is now in its correct position in the sorted array. This is called the partition step.
- Recursively call quick sort on the elements on the left side of the pivot, and do the same for the elements on the right side of the pivot element.
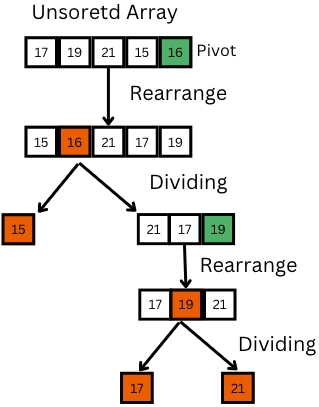
You can also read about Multilevel Inheritance in Python, Fibonacci Series in Python
Coding QuickSort in Python
We will code quicksort in Python 3 as well as in Python 2. Coding quicksort in Python, or any other language involves applying the concepts we studied above in the language.
QuickSort in Python 3
# The partition function, which returns the position of the pivot element.
def partition(nums:list[int],start:int,end:int)->int:
#the pivot element. We are taking the end element as pivot.
pivot:int = nums[end];
# i, which will help us find the final position of the pivot element.
i:int = start-1;
for j in range(start,end):
#if the current element is smaller than the pivot
if (nums[j]<pivot):
# increment i
i=i+1;
#swap elements at i and j
nums[j],nums[i]=nums[i],nums[j];
# finally move the pivot element to its correct position
i=i+1;
nums[end],nums[i]=nums[i],nums[end];
#return the final position of the pivot element
return i;
#the recursive function that performs quicksort in python 3
#start is the start index of the subarray to sort
#end is the end index of the subarray to sort
def quicksort(nums:list[int],start:int,end:int):
# if start is not less than end, it means the subarray has 0 or 1 elements, and doesn't need
# to be sorted.
if (start<end):
# find the position of the pivot element
pivot:int = partition(nums,start,end);
#recursively sort left and right subarrays for pivot
quicksort(nums,start,pivot-1);
quicksort(nums,pivot+1,end);
#utility function to call quick sort
def sortArray(nums:list[int])->list[int]:
quicksort(nums,0,len(nums)-1)
arr = [5,3,2,6,1,4]
sortArray(arr)
print(arr)QuickSort in Python 2
# The partition function, which returns the position of the pivot element.
def partition(nums,start,end):
#the pivot element. We are taking the end element as pivot.
pivot = nums[end];
# i, which will help us find the final position of the pivot element.
i = start-1;
for j in range(start,end):
#if the current element is smaller than the pivot
if (nums[j]<pivot):
# increment i
i=i+1;
#swap elements at i and j
nums[j],nums[i]=nums[i],nums[j];
# finally move the pivot element to its correct position
i=i+1;
nums[end],nums[i]=nums[i],nums[end];
#return the final position of the pivot element
return i;
#the recursive function that performs quicksort in python 2
#start is the start index of the subarray to sort
#end is the end index of the subarray to sort
def quicksort(nums,start,end):
# if start is not less than end, it means the subarray has 0 or 1 elements, and doesn't need
# to be sorted.
if (start<end):
# find the position of the pivot element
pivot = partition(nums,start,end);
#recursively sort left and right subarrays for pivot
quicksort(nums,start,pivot-1);
quicksort(nums,pivot+1,end);
#utility function to call quick sort
def sortArray(nums):
quicksort(nums,0,len(nums)-1)
arr = [5,3,2,6,1,4]
sortArray(arr)
print(arr)Output:
You can practice by yourself with the help of online python compiler.
Time and Space complexity of Quicksort
Time Complexities
Let's discuss the worst, best, and average time complexities of the quicksort algorithm in Python.
Worst Case Complexity is O(n2)
Base Case Complexity is O(nlogn)
Average Case Complexity O(nlogn)
Space Complexity
The space complexity for quicksort is O(1) because it is an in-place algorithm. Recursion stack space is not counted here. If we count the stack space, the time complexity will be O(logn) in the average case and O(n) in the worst case.
Also see, Convert String to List Python





