Introduction
In this blog, we will discuss hub and switch. Both hub and switch are network connecting devices. Network devices are various hardware devices that are used to connect computers, printers, etc., to a network. These are also referred to as Networking hardware or Network equipment. These devices help to transfer data quickly, securely, and correct way over the same or different network. Each of these devices consists of a specific purpose. For any machine to connect to the network, it first needs a network interface card or a wifi card. The network interface card is also known as ethernet card, network card, LAN card, network adapter card, network interface unit or terminal access point. It is a physical and data link layer device used by computers to connect and communicate with other devices on the LAN. A wifi card is used to connect any device to the local network wirelessly.
Network Interface Card
Source: hmhub
Also see, Message Switching in Computer Networks and Basic Networking Commands
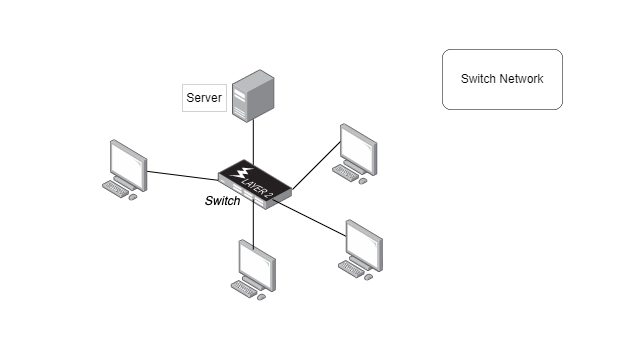
Hub

The main purpose of a hub is to connect all present network devices together on a predefined internal network. Hub is a device consisting of multiple ports that accept ethernet connections from network devices. Hub is not considered to be an intelligent one because it doesn't filter any data present or has no intelligence to assume as to where the data is actually supposed to be sent, and that’s the reason because the only thing a hub knows is that when a device is actually connected to one of its ports. So whenever a data packet arrives at one of the ports, it is copied to all the other ports. So all the devices present on that hub see that data packet. So again, when a data packet comes into one port, the hub will just rebroadcast that data to every port that has a device connected to it.
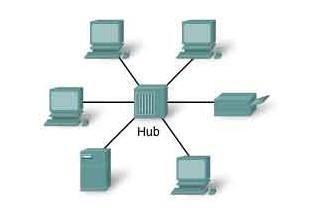
Source: hub
So, even if only two computers among the entire group want to communicate, the other computers will also receive the data, even though it was not actually intended for them. So whenever this happens, it not only creates security concerns, but it also creates unnecessary traffic on the network, which wastes bandwidth.
Pros:
- Ability to connect to the network using various physical devices.
- Cheaper compared to other devices.
- Causes a minimum delay.
- Does not affect the network’s performance.
Cons:
- Does not filter the data, hence wastage of bandwidth.
- Makes the network insecure by sharing data to all devices present in the network.
- Involves flooding of data.
- Cannot connect token ring.
Application:
- In small home networks.
- Used to monitor various networks.
- Used in computer laboratories for connectivity.
- Helps in visibility of peripherals throughout.