Why is it needed?
- Identity and Access Management (IAM) technology can create, capture, record, and manage user identities and access rights.
- With its ever-expanding set of features such as biometrics, behavioral analytics, and AI, IAM is well adapted to the rigors of the modern security landscape.
- IAM aids in the prevention of identity-based threats and data breaches caused by privilege escalation (when an unauthorized user has too much access to data).
Benefits of IAM
-
Security Benefits
IAM technologies assist in the identification and management of security issues. IAM allows us to identify policy violations and revoke incorrect access privileges without exploring the various distributed systems. You can also use IAM to ensure that security measures meet regulatory and audit needs.
-
Ease of use
IAM optimizes the signup, sign-in, and user management processes for app owners, end-users, and administrators. It makes all easy to offer and manage access, which increases user happiness.
-
Cost Cutting in Security
IAM services can help us to reduce operating costs. When using identity and access services, you no longer need local identities for external purposes, simplifying application administration. Cloud-based Identity access management services can eliminate the requirement for on-premise infrastructure purchases and maintenance.
-
Easy Automation
Automating IAM systems enables businesses to function more effectively by minimizing the effort, time, and money necessary to manage network access manually.
-
Managing Rules and Guidelines
IAM systems assist firms in better complying with regulatory rules by allowing them to demonstrate that company information is not being exploited. Companies can also demonstrate that any data required for audits is readily available.
Tools and Technologies
IAM technologies are intended to make user provisioning and account setup smoother. These solutions should minimize the time it takes to execute these procedures by implementing a controlled workflow that reduces errors and the possibility of abuses while permitting automated account fulfilment. An IAM system should also enable administrators to view and modify changing access roles and permissions in real-time.
These systems should recognize the difference between the speed and automation of their processes and the control required by administrators to monitor and change access rights. As a result, to manage access requests, the central directory requires an access rights system that connects employees' job descriptions, business unit identities, and locations to the appropriate authority levels.
Multiple review levels can ensure that individual requests are properly checked. This simplifies establishing suitable review processes for higher-level access and makes it easier to assess existing rights to prevent privilege creep, which is the steady accumulation of access rights beyond what users require to execute their tasks.
Digital Authentication
When a user attempts to access your organization's network and other resources, authentication occurs. For security reasons, the user must authenticate their identity before being authorized to access. The most frequent way of authentication is to enter credentials at a login prompt.
Types of Digital Authentication
-
User Password
The unique password is the most frequent method of digital authentication. Some organizations require longer or more complicated passwords that include a combination of characters, symbols, and numbers to make passwords safer. Users often find remembering unique passwords inconvenient unless they can automatically aggregate their collection of passwords behind a single sign-on entry point.
-
Pre-shared key
A PSK is a sort of digital authentication in which the password is shared among users who are permitted to access the same resources – think of it as a College Wifi Access password. Individual passwords are more secure than this method of authentication. One issue with shared passwords, such as PSK, is that they must be changed regularly, which can be difficult.
-
Behavioral Authentication
A person is identified via behavioral biometric authentication based on distinctive patterns displayed when they interact with a device such as a PC, Mobile Phone, or Tablet (including mouse and keyboard). Everything from finger pressure on the TouchPad to the angle you hold your Cell Phone is considered.
-
Biometrics
Biometric authentication includes using some aspect of your physical character to verify your identity. This might be a fingerprint, an iris scan, a retina scan, or any other physical feature. It is possible to use a single or several qualities.
Is There Any Security Risk in IAM?
As previously stated, biometrics raises security problems, including data theft. That danger is reduced by collecting and retaining only the required information. Organizations must understand what biometric data they have, what they require, how to get rid of what they do not need, and how and where it is stored.
When user account provisioning and de-provisioning are not managed effectively, there are too many insecure inactive allocated user accounts, and there is sprawl in admin accounts, cloud-based IAM can be a worry. To prevent malicious users from getting access to user identities and passwords, organizations must establish lifecycle control over all modules of cloud-based IAM.
FAQs
Why do we need identity and access management?
IAM enables you to implement the security principle of least privilege, allowing you to grant only the essential access to your resources while preventing unauthorized access to other resources. IAM enables you to meet compliance clauses relating to the separation of duties.
What is identity and access management (IAM) in cloud computing?
IAM is a cloud service that manages user permissions and access to cloud resources. IAM policies are authorization policies linked to users or cloud resources to control what they can access and do with them.
What is the goal of IAM?
IAM ensures that the right employees and job responsibilities in your business have access to the tools required to accomplish their tasks. Identity management and access systems allow your organization to manage employee apps without checking in as an administrator to each app.
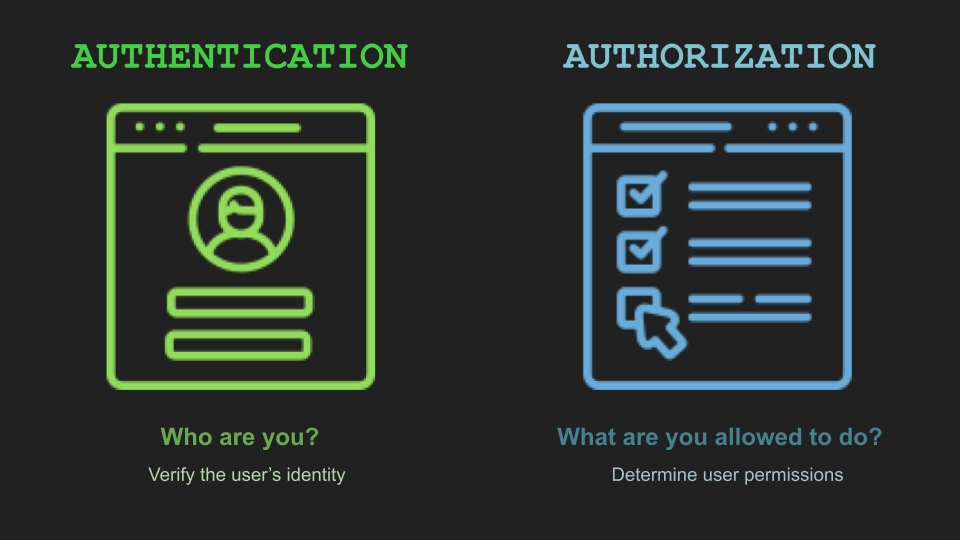
What is the distinction between identity and access management?
One of the most common misconceptions in the IT world is that identity management and access management are the same things. Identity management is concerned with authenticating users. It is all about creating user identity and controlling attributes. Access management is concerned with authorizing users. It is about analyzing qualities based on policies and making access grant/restrict decisions.
Conclusion
In this article, we have extensively discussed the IAM security standard. We started with a brief introduction to Identity Access management, and then discussed various Tools and technologies.
To read more about Cloud Computing you can read Introduction to Cloud Computing, Cloud Management, License and their management, and XASS .
Refer to our guided paths on Coding Ninjas Studio to learn more about DSA, Competitive Programming, JavaScript, System Design, etc. Enrol in our courses, refer to the mock test and problems; look at the interview experiences and interview bundle for placement preparations.
Do upvote our blog to help other ninjas grow.
Happy Learning!