We're on the verge of a massive AR app explosion.
Since Apple's high-profile launch of augmented reality applications, the entire industry has anticipated a deep integration of AR technology and practical scenarios. Despite the lack of a large-scale application at this time, numerous local and international manufacturers and e-commerce platforms are developing AR services on a regular basis.
These apps are primarily used for display, trial, and other purposes. For example, IKEA's AR software allows users to see how IKEA's furniture products will look when installed in their own spaces on a smartphone screen. Users can quickly move and rotate furniture on the screen to see if it matches the table in their hall.
There are also numerous AR uses, such as lipstick and garment trials. Ali and JD have created their e-commerce AR applications in China, allowing consumers to experience the thrill of virtual purchasing.
With the maturation of software and hardware technology, it is realistic to expect AR applications to grow increasingly popular. It is expected to become the next big thing in mobile Internet apps.
AI Enterprise Layout
Apple and Google, two global IT behemoths, have long been involved in the field of augmented reality. Apple, for example, unveiled its AR applications and the ARKit development framework. Google also announced the ARCore platform, built on the Android operating system, allowing developers, software developers, and device makers to collaborate and create a massive AR ecosystem.
While the smartphone market approaches saturation, all major manufacturers are looking for the next growth opportunity. All parties are looking in the direction of augmented reality. Global software, hardware, and artificial intelligence companies are prepared to take power. We're in the hours leading up to the AR explosion.
Behind AR: Data Labeling Service
The three essential elements of AI are data, algorithms, and processing. The starting point is data.
Training data service providers with extensive project experience are needed to aid traditional organizations with intelligent transformation and technology enterprises to sort out data labeling instructions and obtain more appropriate data. Utilizing high-quality data in specific scenarios shortens the research and development cycle, speeds up the implementation process, and enables businesses to execute smarter transformations faster and more effectively.
In the process of in-depth industrial landing, there is still a gap between artificial intelligence technology and company needs. Enterprise users' main goal is to leverage artificial intelligence technologies to help them build their businesses. In reality, artificial intelligence technology alone will not be able to meet all of a company's needs. It must develop goods and services that can be deployed broadly in response to specific business circumstances and objectives.
As a result, artificial intelligence solutions have gradually agreed on how to supply high-quality AI data for various scenarios and purposes.
Labeling Types in AR/VR Industry
- Semantic Understanding
- Object Detection
- Object Recognition
- Video Annotation
- Sentiment Recognition
ByteBridge.io, a Human-Powered and ML-powered Data Annotation Platform
Machine learning training data is provided by ByteBridge, a data labeling tooling platform with real-time workflow management.
Accuracy Guarantee
- By automatically pre-labeling data, ML-assisted capacity can help eliminate human errors.
- As the consensus process is added to assure correctness, real-time QA and QC are included in the labeling procedure.
- Assign the same task to numerous workers, and the proper solution is the one that emerges from the majority of the responses.
- The machine and human personnel thoroughly check and inspect all work outcomes.
ByteBridge can thus confirm that our data acceptance and accuracy rate is greater than 98 percent.
Communication Cost Saving
Developers can start labeling projects using the labeling instruction template on ByteBridge's SaaS dashboard and receive results instantaneously.
Thanks to online setting labeling briefing and expert help, instruction communication is no longer difficult.
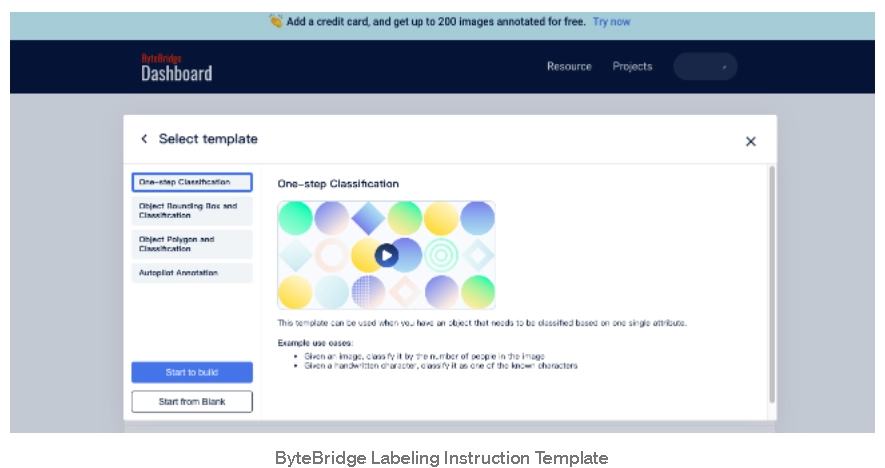
source
Configure Your Own Annotation Project
- Developers can specify labelling rules directly on ByteBridge's dashboard and monitor the ongoing process on a pay-per-task approach with a precise anticipated time and price.
- It provides an API for data transfer and allows developers to manage and monitor the complete data labeling process as a fully managed platform. Users can also participate in the quality control process using the platform.
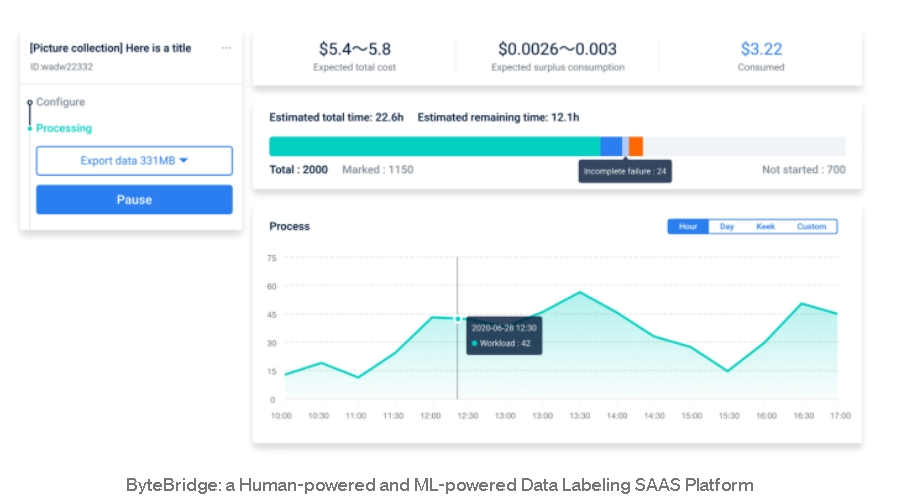
source
Image Classification, 2D Boxing, Polygon, and Cuboid are all labeling tools already available on the dashboard.
According to the customer's needs, we can supply bespoke annotation tools and services.
Cost-effective
Compared to the traditional market, a partnership of human labor with AI algorithms ensures a 50% reduced pricing.
Also Read - Image Sampling
Frequently Asked Questions
What is image labelling?
The process of recognizing and labelling distinct aspects of an image is known as image labelling. Image labeling comes in handy when it comes to automating creating metadata or offering recommendations to consumers based on details in their photographs.
What is Labelling in image processing?
ABSTRACT. CCL (Connected Component Labelling) is a fundamental image processing approach used in practically every object detection application. It collects pixels from the same related component and clusters them together (e.g., object).
What is image labelling in deep learning?
Drawing a tight shape around a picture with a label or labels is known as image labelling.
What are labels used for?
Labels can be used for various purposes, including identification, information, warnings, usage directions, environmental advice, and advertising. Stickers, permanent or temporary labels, and printed packaging are examples.
How accurate is a LiDAR?
LiDAR sensors have a range accuracy of 0.5 to 10mm relative to the sensor, as well as a mapping accuracy of up to 1cm horizontal (x, y) and 2cm vertical (x, y) (z). This makes them particularly suitable for mobile mapping as a remote sensing tool.
Conclusion
So that's the end of the article Image Labelling.
After reading about the Image Labelling, are you not feeling excited to read/explore more articles on the topic of machine learning? Don't worry; Coding Ninjas has you covered.
Upskill yourself in Data Structures and Algorithms, Competitive Programming, JavaScript, System Design, and more with our Coding Ninjas Studio Guided Path! If you want to put your coding skills to the test, check out the mock test series and enter the contests on Coding Ninjas Studio! If you're just getting started and want to know what questions big giants like Amazon, Microsoft, and Uber ask, check at the difficulties, interview experiences, and interview bundle for placement preparations.
However, you may want to pursue our premium courses to give your job an advantage over the competition!
Please vote for our blogs if you find them valuable and exciting.
Happy studying!






