Introduction
This blog will discuss the implementation of std::queue in C++. We will discuss two different approaches to the implementation of queues in C++. But before discussing the different approaches to implementing the queue, we should look at what a queue is.
A queue is a Data Structure that follows the principle of FIFO (First In First Out), which means that the element that enters first will exit first.
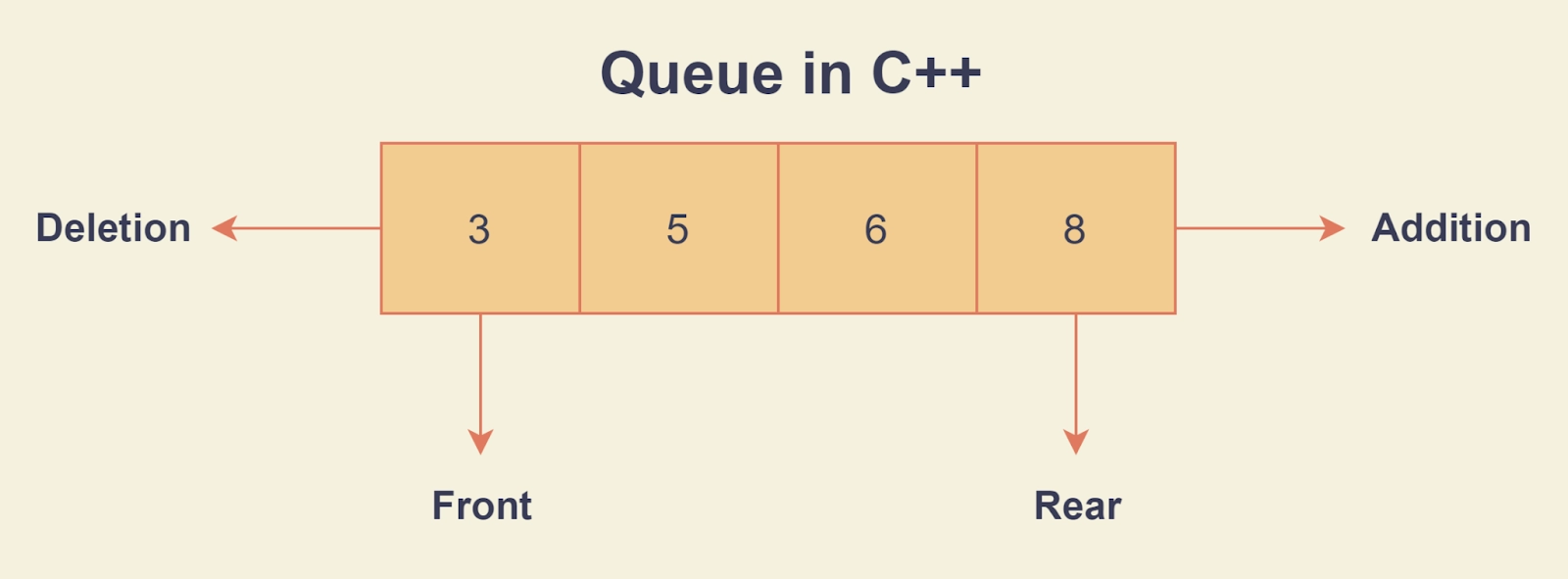
Now that we have seen what exactly a queue is. It is time to implement the queue in C++.
We will implement the queue using two methods:
- Implementation of queue using an array
- Implementation of queue using a linked list
Implementation of queue using an array
// C++ program to implement a queue using an array
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Queue {
int front, rear, size;
int * queue;
Queue(int c) {
front = rear = 0;
size = c;
queue = new int;
}
~Queue() {
delete[] queue;
}
// to insert an element in the queue
void enqueue(int element) {
if (size == rear) {
cout << "Queue is full" << endl;
return;
} else {
cout << "Element inserted" << endl;
queue[rear] = element;
rear++;
}
return;
}
// function to delete an element from the queue
void dequeue() {
// to check if the queue is empty
if (front == rear) {
cout << "Queue is empty" << endl;
return;
}
// shift all the elements from index 1 till the last element to the left by 1
else {
for (int i = 0; i < rear - 1; i++) {
queue[i] = queue[i + 1];
}
cout << "Element deleted" << endl;
// decrement the rear
rear--;
}
return;
}
// function to print the elements of the queue
void printQueue() {
// to check if queue is empty
if (front == rear) {
cout << "Queue is Empty" << endl;
return;
}
// traverse front to rear and print elements
cout << "The queue is: ";
for (int i = front; i < rear - 1; i++) {
cout << queue[i] << " <-- ";
}
cout << queue[rear - 1] << endl;
return;
}
// print the front of the queue
void getFront() {
// to check if the queue is empty
if (front == rear) {
cout << "Queue is Empty" << endl;
return;
}
cout << "Front element is: " << queue[front] << endl;
return;
}
};
// Driver code
int main() {
// To create a queue of size 5
Queue queue(5);
// print the queue elements
queue.printQueue();
// inserting elements in the queue
queue.enqueue(7);
queue.enqueue(4);
queue.enqueue(9);
queue.enqueue(6);
// print the queue elements
queue.printQueue();
// insert the element in the queue
queue.enqueue(1);
// print the queue elements
queue.printQueue();
// deletion of the front element from the queue
queue.dequeue();
// print the queue elements
queue.printQueue();
// deletion of the front element from the queue
queue.dequeue();
// print Queue elements
queue.printQueue();
// print the front element of the queue
queue.getFront();
return 0;
}
Output:
Queue is Empty
Element inserted
Element inserted
Element inserted
Element inserted
The queue is: 7 <-- 4 <-- 9 <-- 6
Element inserted
The queue is: 7 <-- 4 <-- 9 <-- 6 <-- 1
Element deleted
The queue is: 4 <-- 9 <-- 6 <-- 1
Element deleted
The queue is: 9 <-- 6 <-- 1
Front element is: 9
In the above approach we are using four different functions to implement the queue the functions are: insert(), delete(), print() and getFront().
1. Insertion of the element in the queue
void enqueue(int element) {
// to check if queue is full or not
if (size == rear) {
cout << "Queue is full" << endl;
return;
}
// to insert an element at the rear of the queue
else {
cout << "Element inserted" << endl;
queue[rear] = element;
rear++;
}
return;
}
If the queue is full, we will print the queue is full; else we increment the rear index and store the new element at the rear index.
2. Deletion of the element from the queue
void dequeue() {
// to check if the queue is empty
if (front == rear) {
cout << "Queue is empty" << endl;
return;
}
// shift all the elements from index 1 till the last element to the left by 1
else {
for (int i = 0; i < rear - 1; i++) {
queue[i] = queue[i + 1];
}
cout << "Element deleted" << endl;
// decrement the rear
rear--;
}
return;
}
In this function, we are first checking if the queue is empty or not. If the queue is empty then we are printing the queue is empty. Else, we shift all the elements from the first index to the last index to the left by 1. Here we ignore the element's value at index 0 because we have to remove the element at index 0.
3. Printing the whole queue
void printQueue() {
// to check if queue is empty
if (front == rear) {
cout << "Queue is Empty" << endl;
return;
}
// traverse from front to rear and print the elements
cout << "The queue is: ";
for (int i = front; i < rear - 1; i++) {
cout << queue[i] << " <-- ";
}
cout << queue[rear - 1] << endl;
return;
}
In this function, we are first checking if the queue is empty or not. If the queue is empty then we are printing the queue is empty else we are simply printing all the elements of the queue.
4. Displaying the front element of the queue
void getFront() {
// to check if the queue is empty
if (front == rear) {
cout << "Queue is Empty" << endl;
return;
}
cout << "Front element is: " << queue[front] << endl;
return;
}
In this function, we are first checking if the queue is empty or not. If the queue is empty then we are printing the queue is empty else we are just printing the front element by using the front variable which is keeping the index of the front variable.
Implementation of queue using a linked list
// C++ program to implement a queue using a linked list
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// Node for linked list
struct Node {
int data;
Node * next;
};
struct Queue {
Node * front, * rear;
Queue() {
front = rear = NULL;
}
// to insert an element in the queue
void enqueue(int element) {
Node * q;
q = new Node;
q -> data = element;
q -> next = NULL;
if (front == NULL) {
front = rear = q;
} else {
cout << "Element inserted" << endl;
rear -> next = q;
rear = q;
}
}
// function to delete element from the queue
void dequeue() {
Node * temp;
if (front == NULL) {
cout << "Queue is Empty" << endl;
} else {
cout << "Element deleted" << endl;
temp = front;
front = front -> next;
delete temp;
}
return;
}
// function to print the elements of the queue
void printQueue() {
Node * temp;
temp = front;
cout << "The queue is: ";
while (temp -> next != NULL) {
cout << temp -> data << " <-- ";
temp = temp -> next;
}
cout << temp -> data << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
Queue queue;
// inserting the elements in the queue
queue.enqueue(4);
queue.enqueue(3);
queue.enqueue(1);
// print the queue elements
queue.printQueue();
// deletion of the front element from the queue
queue.dequeue();
// print the queue elements
queue.printQueue();
// insert the element in the queue
queue.enqueue(9);
// print the queue
queue.printQueue();
// delete the queue elements
queue.dequeue();
// print the queue
queue.printQueue();
}
Output:
Element inserted
Element inserted
The queue is: 4 <-- 3 <-- 1
Element deleted
The queue is: 3 <-- 1
Element inserted
The queue is: 3 <-- 1 <-- 9
Element deleted
The queue is: 1 <-- 9
In the above approach, we are using three different functions to implement the queue the functions are: insert(), delete(), and print().
1. Insertion of the element in the queue
void enqueue(int element) {
Node * q;
q = new Node;
q -> data = element;
q -> next = NULL;
if (front == NULL) {
front = rear = q;
} else {
cout << "Element inserted" << endl;
rear -> next = q;
rear = q;
}
return;
}
In this function, we are first checking whether the element we are inserting in the queue is the first element or not. If it is the first element, we assign a value to the front node. Else, we are assigning value to the next node of the linked list.
2. Deletion of the element from the queue
void dequeue() {
Node * temp;
if (front == NULL) {
cout << "Queue is Empty" << endl;
} else {
cout << "Element deleted" << endl;
temp = front;
front = front -> next;
delete temp;
}
return;
}
In this function, we are first checking if the queue is empty or not. If the queue is empty then we are printing queue is empty else, we are storing the node in another node named temp, and we are shifting the current node that is front to front->next.
3. Printing the whole queue
void printQueue() {
Node * temp;
temp = front;
cout << "The queue is: ";
while (temp -> next != NULL) {
cout << temp -> data << " <-- ";
temp = temp -> next;
}
cout << temp -> data << endl;
}
In this function, we are printing all the elements of the queue.
You can try by yourself with the help of online C++ Compiler.