Introduction
To implement Deque employing a circular array we should track 2 pointer front and rear within the array, all the operations are on these 2 pointers.
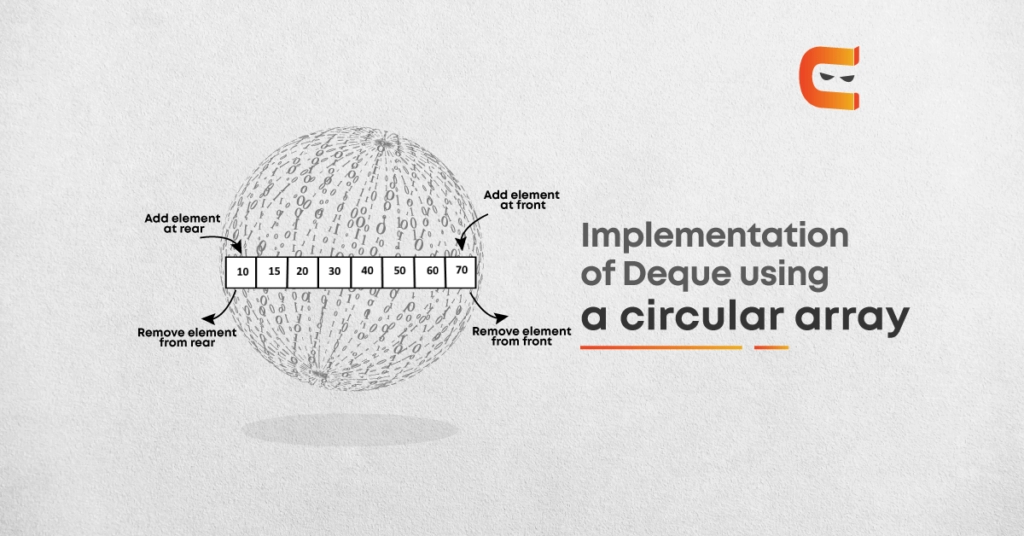
The which means of circular array will be understood by the image below.
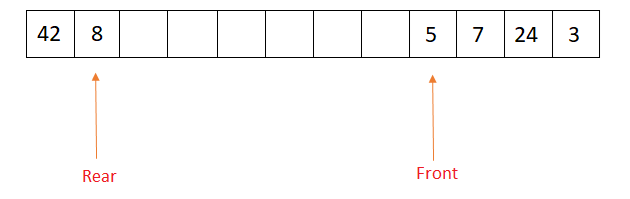
In this image the rear is behind the front, that’s once rear was at the top of the array and there have been some empty slots within the beginning of the array, thus the insertion of part at the rear would cause the rear to return at position zero, this can be as a result of the circular array is circular in nature.
Create an associate array of size n, wherever n is that the most size of Deque and initialize front and rear as -1, before any operation on the Deque. because the array is circular increment front or rear once they are a gift at the top of the array can take them to the start line and equally decrementing front and rear once they are at the start line can take them to the top of the array.
Learn one of the most powerful and portable programming languages C++ and become eligible to apply for the positions at Google, Microsoft, Facebook, Amazon etc.
insertFront(x)
- If the array is full, the component can’t be inserted.
- If there are not any components within the Deque(or array) it means the front is equal to -1, increment front and rear, and set arr[front] as x.
- Else decrement front and set arr[front] as x.
Time Complexity = O(1)
insertRear()
- If the array is already full then it not possible to insert more elements.
- If there are not any elements within the Deque, that is rear which is equal to -1, increase front and rear and set arr[rear] as x.
- Else increment rear and set arr[rear] as x.
Time Complexity = O(1)
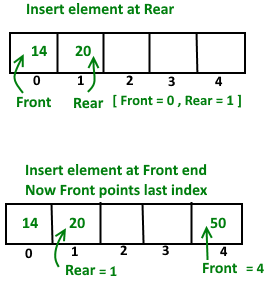
deleteFront()
- If the Deque is empty, return.
- If there is only one element in the Deque, that is, front equals rear, set front and rear as -1.
- Else increment front by 1.
Time Complexity = O(1)
deleteRear()
- If the Deque is empty, return.
- If there’s just one component within the Deque, that is, rear equals front, set front and rear as -1.
- Else decrement rear by one.
Time Complexity = O(1)

getFront()
- If the Deque is empty, return.
- Else come arr[front].
Time Complexity = O(1)
getRear()
- If the Deque is empty, return.
- Else come arr[rear].
Time Complexity = O(1)
isEmpty()
If front is equals to -1 the Deque is empty, else it’s not.
Time Complexity = O(1)
isFull()
If (rear + 1) % n equals to the front then the Deque is full, else it’s not. Here n is that the most size of Deque.
Time Complexity = O(1)
Implementation of Deque using circular array in Java:
class ImplementationOfDequeUsingCircularArray {
// Maximum size of Deque
private static final int MAXIMUM SIZE = 100;
// Array to implement Deque
private static int deque[];
// Variables for representing the front and rear of dequeue
private static int front = -1;
private static int rear = -1;
private static void insertFront(int x) {
// if array is not full
if (!isFull()) {
// case 1 : If the array is empty of there is no element
// increase the front and rear and add element at arr[front]
if (front == -1) {
front = rear = 0;
deque[front] = x;
}
// else, decrement front circularly and add the
// new element at arr[front]
else {
if (front == 0) {
front = MAXIMUM SIZE - 1;
} else {
front--;
}
deque[front] = x;
}
}
}
private static void insertRear(int x) {
// if array is not full
if (!isFull()) {
// Then we have to check if we are inserting first element in the array
// Now increase the front and rear and add element at arr[rear]
if (rear == -1) {
front = rear = 0;
deque[rear] = x;
}
// else increment rear circularly and add
// new element at arr[rear]
else {
if (rear == MAXIMUM SIZE - 1) {
rear = 0;
} else {
rear++;
}
deque[rear] = x;
}
}
}
private static void deleteFront() {
// if array is not empty
if (!isEmpty()) {
// if there is only 1 element
// make front and rear as -1
if (front == rear) {
front = rear = -1;
}
// else increment front circularly
else {
if (front == MAXIMUM SIZE - 1) {
front = 0;
} else {
front++;
}
}
}
}
private static void deleteRear() {
// if array is not empty
if (!isEmpty()) {
// if there is only 1 element
// make front and rear as -1
if (front == rear) {
rear = front = -1;
}
// else decrement rear circularly
else {
if (rear == 0) {
rear = MAXIMUM SIZE - 1;
} else {
rear--;
}
}
}
}
private static int getFront() {
// if array is not empty return arr[front]
if (!isEmpty()) {
return deque[front];
}
return -1;
}
private static int getRear() {
// if array is not empty return arr[rear]
if (!isEmpty()) {
return deque[rear];
}
return -1;
}
private static boolean isEmpty() {
// if front is equal to -1 it means dequeue is empty
if (front == -1) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
private static boolean isFull() {
// if front element is 1 ahead of rear element then
// deque is full
if ((rear + 1) % MAXIMUM SIZE == front) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
deque = new int[MAXIMUM SIZE];
// Example
insertFront(5);
insertRear(10);
insertRear(11);
insertFront(19);
System.out.println(getFront());
System.out.println(getRear());
System.out.println(isFull());
deleteRear();
System.out.println(getRear());
deleteFront();
System.out.println(getFront());
System.out.println(isEmpty());
}
}
Time Complexity: As the per all the operations performed we have found that time complexity of all operations like insertfront(), insertlast(), deletefront(), deletelast()is O(1).
Also see, Rabin Karp Algorithm






