Introduction
In this blog, we will look into the features of Flutter.
Flutter is a cross-platform software development framework first introduced by Google in 2015 and released in 2017. Flutter has steadily matured and expanded its capabilities to include mobile development for iOS and Android and web and desktop applications. Let's look at the issue and see why it's so popular nowadays.
If you are new to Flutter and are yet to set up your environment for the language, you can check out this article.
We'll go over the entire architecture and features in the following paragraphs.
Characteristics of Flutter
Let’s now look at some of the characteristics of Flutter.
Dart: the language used by Flutter
Before we begin analysing the Flutter framework, let's look at the Dart programming language utilised to create it. Dart is an object-oriented programming language that Google introduced in 2011. Dart has steadily evolved since then by delivering new features. The "dart2native" capability allows it to be compiled as a desktop programme for Windows, Linux, and macOS. The desktop solution is not yet in production as of the writing of this article, but the prognosis appears positive. Aside from that, the Dart programme can be turned to JavaScript or made into a self-contained executable file. The last one is particularly noteworthy since, by compiling to JavaScript, you can run Dart programmes in any modern web browser.

Dart Logo
Dart is a simple language to learn in general. Its syntax is comparable to those of Java, Swift, and Kotlin. Furthermore, the Dart software development kit (SDK) comes with a standalone Dart Virtual Machine (VM) that allows users to build programs in a command-line interface (CLI) environment. If you are unfamiliar with CLI, you can try out Dart on DartPad. DartPad is a web-based editor that allows you to use Dart's API and compile Dart code.
Flutter Framework
As previously stated, Google first announced the Flutter framework in 2015. It used the Android operating system and had the codename "Sky." On December 4, 2018, the Dart SDK version 2.18 and Flutter version 1.17 were released, offering a build with Metal API integration.
The framework is developed in C, C++, and Dart, and the user interface is rendered using Google's Skia Graphics Engine. Google Chrome, Chrome OS, Chromium OS, Mozilla Firefox, Mozilla Thunderbird, Android, Firefox OS, and now Flutter all use this graphics engine.

Flutter logo
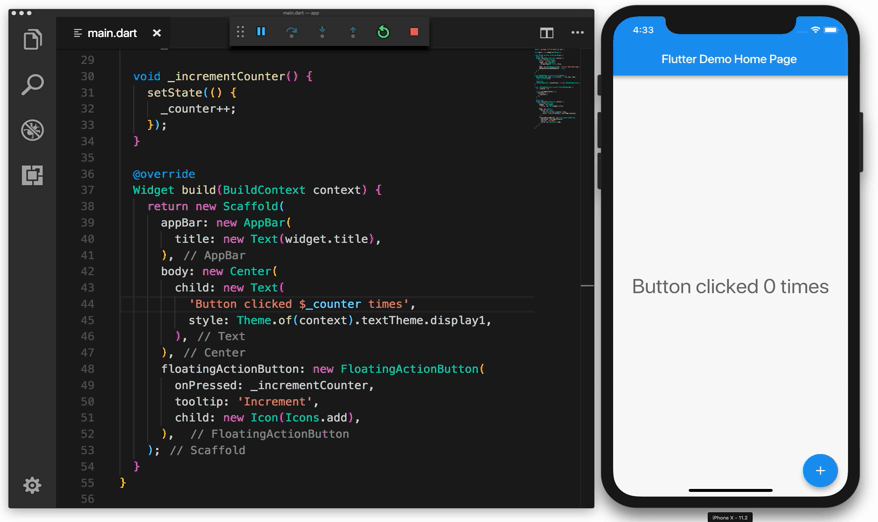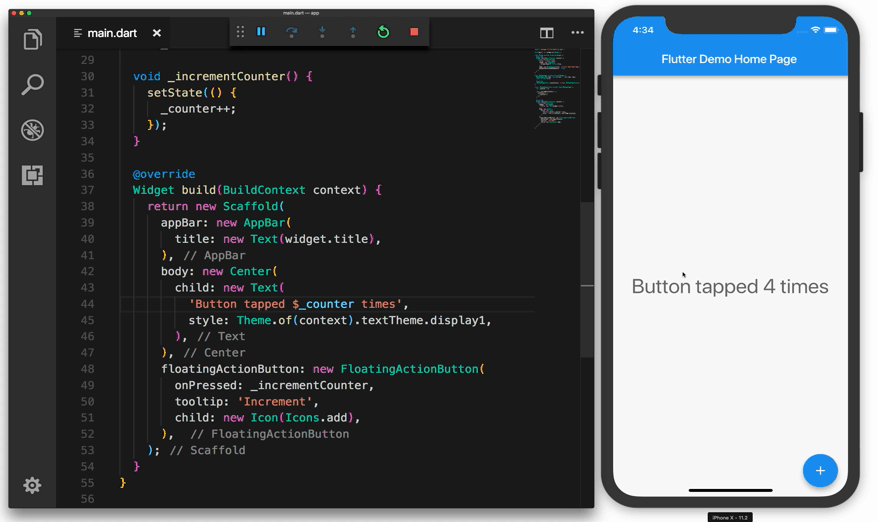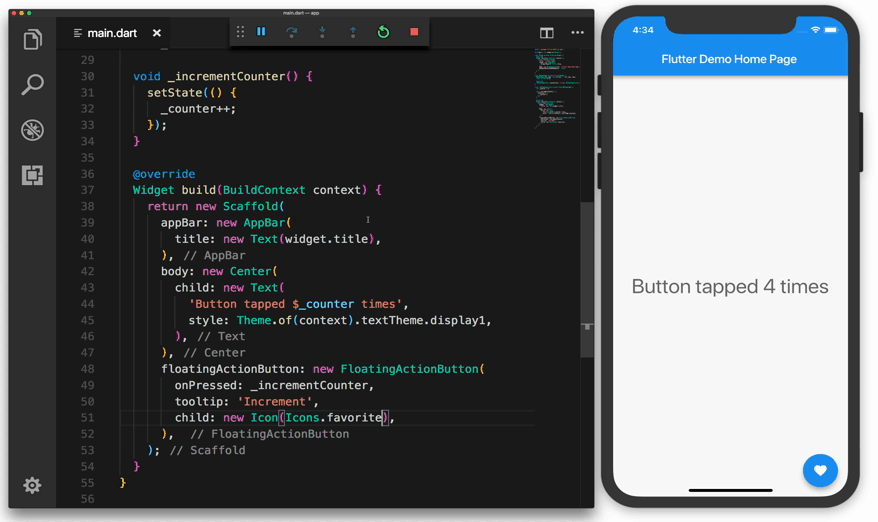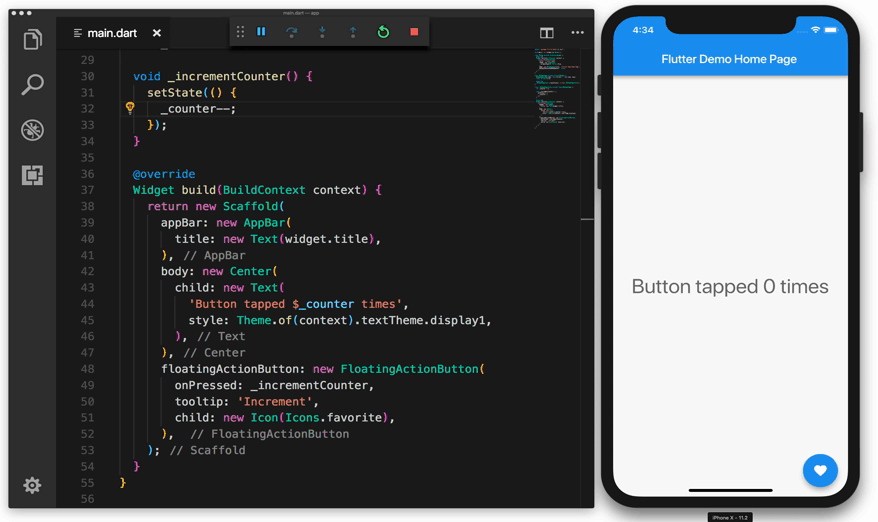
Flutter runs on the Windows, Linux, and macOS operating systems via the Dart virtual machine (VM). The Dart VM employs just-in-time (JIT) code compilation, allowing development time savings such as hot-reloading. The JIT compilation injects new code into the running programme as the developer writes and debugs the mobile application. It has a stateful hot-reload functionality that allows source code changes to be instantaneously reflected in the running application without a restart or any loss of state. This saves the developers a significant amount of time in the long run.
The Flutter framework was created using various principles that should be discussed in detail. These are the ideas "Everything is a widget," "Composition > Inheritance," and "Widget tree."
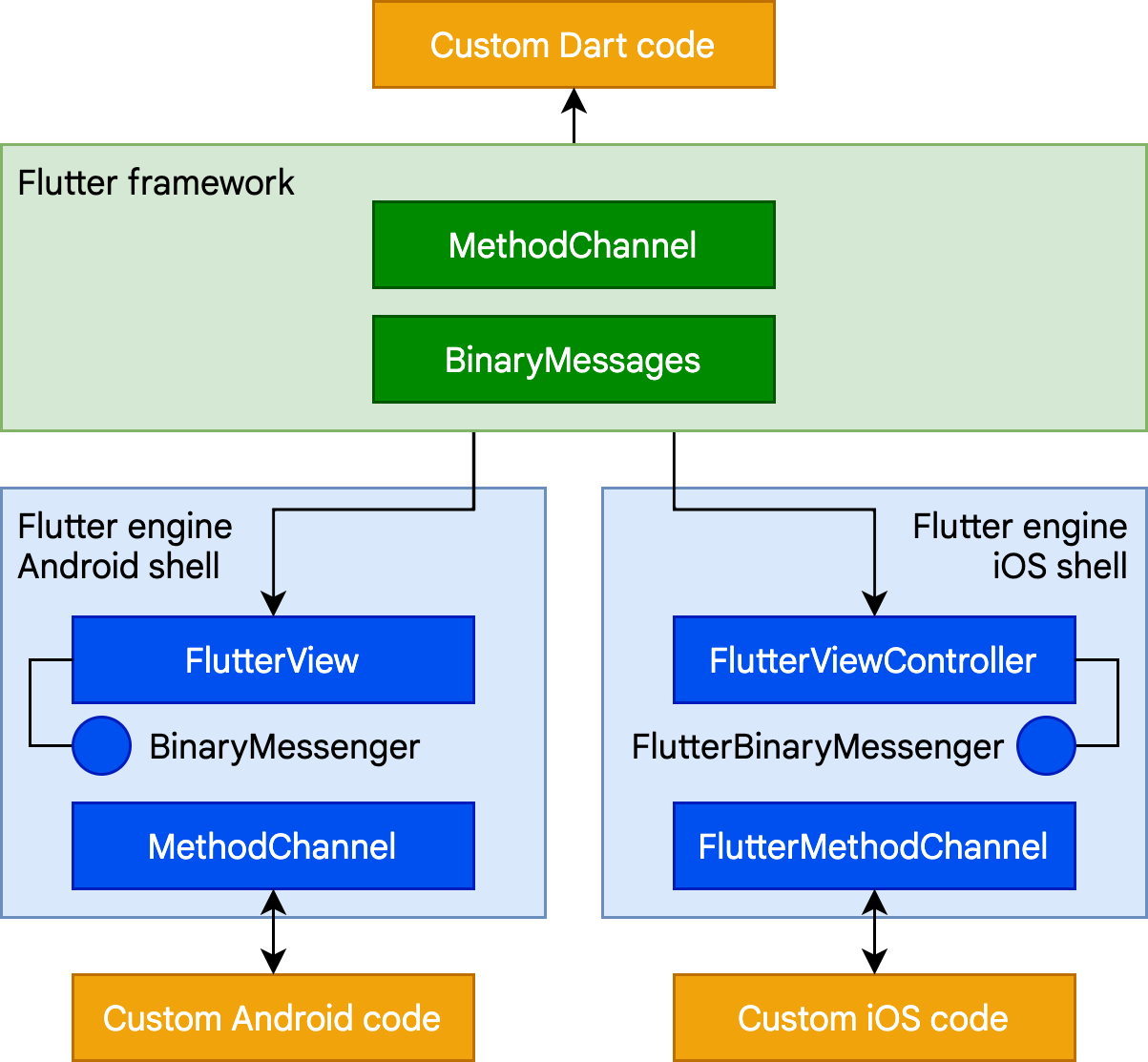
Flutter System Architecture,
Source: flutterdocumentation.com
Flutter Architecture
Apart from the previously mentioned essential ideas, Flutter provides the basic architecture that you may use to apply to your application and simply manage its state. The Business Logic Component architecture(BLOC) is used in Flutter. It's a state-based method that allows you to initiate events and handle state changes resulting from them. The BLOC is an excellent strategy for separating business logic from the user interface and testing important business logic points. The BLOC architecture was designed with simplicity, versatility, and testability in mind, and all of these aims were met. However, this is a different topic that we may discuss later.

Flutter architecture