History of Google Cloud Platform
GCP was initially made available online in 2008 when App Engine was introduced. Google released a preview version of App Engine in April 2008; this developer tool lets users run their web applications on Google infrastructure. (For context, this was two years after Amazon first introduced EC2 and S3 cloud storage as part of its cloud computing business.)
App Engine was made accessible to 10,000 developers to gather the feedback required to improve this preview edition. With 500 MB of storage, 200 million megacycles of CPU processing per day, and 10 GB of bandwidth per day, these early adopter developers were able to launch apps.
By the end of 2011, Google had taken App Engine out of beta and turned it into a fully supported, official Google product. Since then, Google has added new services and products and made acquisitions to improve the user interface of its cloud platform. One of the world's leading providers of public clouds nowadays is the Google Cloud Platform.
Various Elements of Google Cloud Platform
As you can see, the Google cloud platform is composed of a variety of components that benefit individuals in various ways. We will discuss a few of these components that are included in the Google Cloud in the section that follows.
-
Google Compute Engine: This computing engine was introduced together with Google's IaaS service, which in essence offers virtual machines (VMs) similar to Amazon EC2.
- Google Cloud App Engine: The PaaS service is available through the app engine for correctly hosting applications. This is a really potent and significant platform that aids in the creation of various mobile and online applications.
- Google Cloud Container Engine: This specific component is advantageous because it enables the user to execute the docker containers that are currently active on the Google Cloud Platform and are actually started by Kubernetes.
- Google Cloud Storage: It's crucial to have the capacity to store data and valuable resources on the cloud platform. The Google cloud platform is well-liked among storage providers because it enables users to backup or store data on cloud servers that can be accessed from anywhere at any time.
- Google Cloud Endpoints: The customers of the Google Cloud Platform can create and manage secure application program interfaces with the aid of this specific functionality.
Google Cloud resources
Virtual machines (VMs) and other physical and virtual resources housed in Google's data centers across the world make up the Google Cloud. Physical resources include computers and hard drives. Every data center site is located in an area. Asia, Australia, Europe, North America, and South America all have regions available. Every region is made up of zones that are separate from one another inside the region. Each zone has a name that comprises a letter identification and the region's name. Zone A in the East Asia region, for instance, is designated as Asia-east1-a.
Because the resources are spread out, there is redundancy in case of failure, and there is less latency because the resources are closer to the clients. Additionally, this release presents a few guidelines for combining resources.
Google Cloud Platform infrastructure, regions, and zones
There are presently 24 sites across the world where Google Cloud Platform resources are made available as part of Google's worldwide infrastructure. Regions are the first component of a location, and availability zones are found there. There is no single point of failure in these zones. Some resources, like the HTTP global load balancer, are accessible from any Google edge site or region since they are global resources.
Regional resources can include things like storage. For redundancy, the storage is split up among several zones in an area. Finally, only one unique zone within one specific region is available for zonal resources, including computing instances. You must choose the locations for application deployment on GCP in accordance with your organization's demands for performance, reliability, scalability, and security.
Google Cloud Platform services
A certain category of services is provided by each GCP region. Certain services are only available in certain areas. The Google Cloud Platform's primary services include:
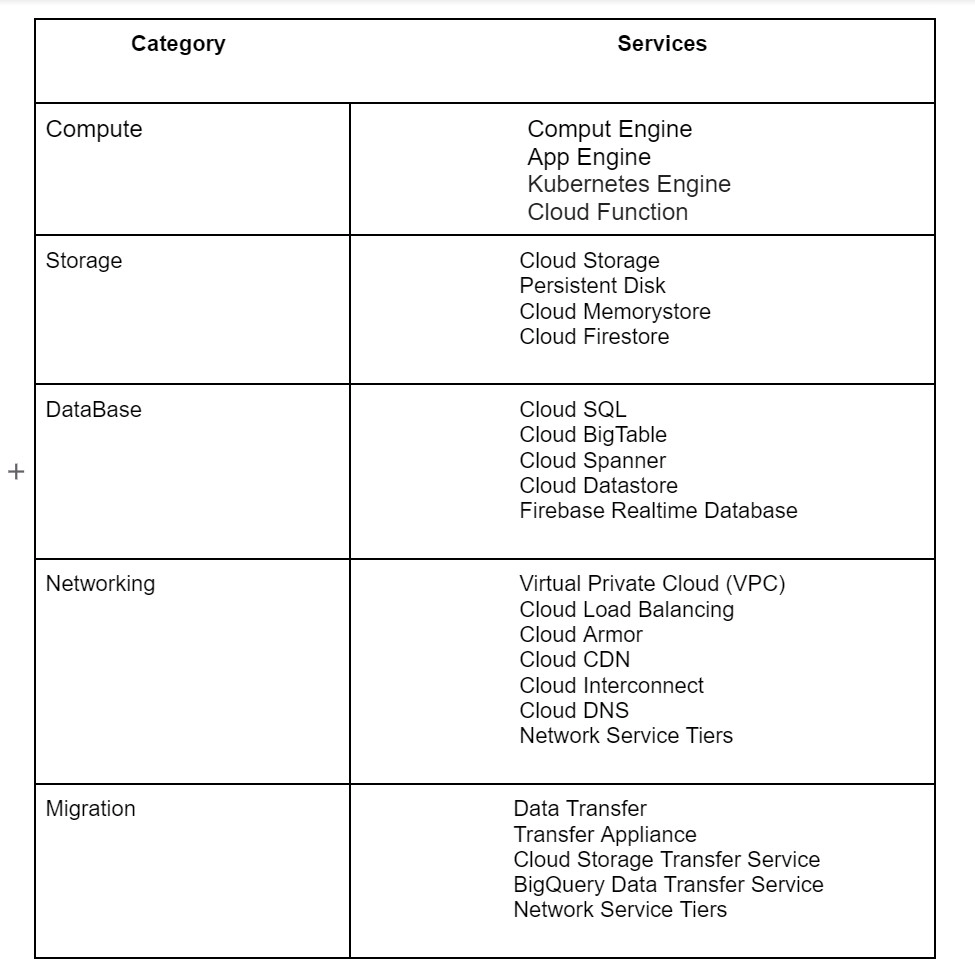
Google Cloud Platform pros
My preferred cloud is Google. My personal experience is that it resembles building structures out of LEGOs. Each service has a specific use case and was created to be compatible with the next service and its clear rules of engagement.
- The documentation for the Google Cloud Platform is unrivaled in terms of its strengths. (Reading documents can change your career, by the way.) How Google puts the actions within the docs of GCP is a favorite among users. They are split into two sections: an overview and a hands-on portion that guides the reader through using the feature or service.
- The global backbone network of GCP, which uses cutting-edge software-defined networking and edge-caching services to ensure quick, reliable, and scalable performance, is another point of strength. Yes, employing a virtual private cloud (VPC) to develop architectures that automatically route traffic on a global network does cost a little bit extra, but in my opinion, it is worth it.
Google Cloud Platform cons
- The Google Cloud Platform contains significantly fewer services than those provided by AWS and Azure if I were to point out a drawback to GCP.
- Additionally, GCP has an opinionated usage model for their cloud services that are targeted toward software engineers.
The key point is that Google is spending money on GCP rather than pursuing market expansion or dominance. My opinion is that Google finds it difficult to prioritize GCP over the company's larger revenue generators, like as search, ads, and YouTube.
Frequently Asked Questions
On what model does the Google Cloud Platform rely on?
Similar to other public cloud services, the majority of Google Cloud services operate on a pay-as-you-go basis, where customers only pay for the cloud resources they actually utilize.
What distinguishes the Google Cloud from the Google Cloud Platform?
A variety of online services that are part of Google Cloud can assist businesses in going digital. A component of Google Cloud is the Google Cloud Platform, which offers public cloud infrastructure for hosting web-based applications and is the subject of this blog article.
What are the four types of cloud storage?
The four types of cloud storage are private cloud storage, private cloud storage, hybrid cloud storage, and community cloud storage.
How many products does Google Cloud have?
The Google Cloud range includes more than 100 products.
Conclusion
In this article, we have discussed the google cloud platform. We hope this article helps you to learn something new. And if you're interested in learning more, see our posts on AWS vs. Azure and Google Cloud, Google BigQuery, AWS Vs Azure Vs Google Cloud: The Platform of Your Choice?, Java knowledge for your first coding job.
Visit our practice platform Coding Ninjas Studio to practice top problems, attempt mock tests, read interview experiences, and much more. Thank you for reading this post. Feel free to upvote and share this article if it has been useful for you.








