Introduction
Hello Ninja!!! Welcome to yet another on RESTful web services. But before going directly to RESTful web service do we know what exactly is a web service? A web service is any piece of software that is accessible through the internet and makes use of a standardised XML message system. All communications to a web service are encoded in XML.

Web services are self-contained, modular, distributed, dynamic programmes that can be specified, published, found, and invoked across a network to construct goods, processes, and supply chains. These apps can be distributed, local, or web-based. TCP/IP, HTTP, Java, HTML, and XML are all open standards on which web services are constructed. Now let's start with our main topic which is RESTful web service.
RESTful Web Service
Restful Web Services is a REST-based service that is lightweight, maintainable, and scalable. Restful Web Service exposes API from your application to the calling client in a safe, standardized, and stateless way. The calling client can use the Restful service to conduct preset actions. HTTP is the fundamental protocol underpinning REST. Well, REST is an acronym that stands for REpresentational State Transfer.
The Web Consortium also published the specification of a new standard known as RESTful in 2004. This standard has gained a lot of traction during the last few years. It is used by a lot of well-known websites all around the world, like Facebook and Twitter.
RESTful Key Elements
REST is a technique for getting at resources located in a specific context. You may, for instance, have a server holding crucial papers, images, or videos. These are all illustrations of resources. A client, like a web browser, must request the server to access these resources. Now, a method for accessing these resources is defined through REST services.
The following are the critical elements of a RESTful implementation:
-
Resources - The resource itself is the first essential component.
-
Request Verbs- Verbs used in requests express what you wish to accomplish with the resource. When requesting data from an endpoint, a browser uses a GET verb. However, there are other more verbs that may be used, such as POST, PUT, and DELETE.
-
Request headers- These are supplementary instructions included with the request. These may specify the desired answer type or the specifics of the authorization.
-
Request Body- Data is supplied with the request in the request body. When a POST request is performed to the REST web services, data is often supplied in the request. The client informs the REST web services that it wants to add a resource to the server with a POST call.
-
Response Body - This is the response's central body.
- Response Status Codes - These are the specific codes returned with the web server response.

RESTful Methods
The graphic below depicts most of the verbs (POST, GET, PUT, and DELETE) and a REST API sample of what they would entail.
Assume we have a RESTful web service defined here. When a client requests this web service, it can use any of the standard HTTP verbs such as GET, POST, DELETE, and PUT. The following is what would happen if the client submitted the appropriate verbs. NOTE, that we are discussing the operations in context to the link given above where we have taken an example of our own website.
-
POST - Used to establish a course (e.g data structure and algorithm, web development) using the RESTful web service.
-
GET - The RESTful web service would be used to retrieve a list of all courses.
-
PUT - The RESTful web service would be used to update all courses.
-
DELETE - This is used to delete all courses utilizing RESTful services.
Applications of the RESTful Web Service
Some of the most common and valuable applications of the RESTful web service are:
Heterogeneous languages and environments - This is also one of the fundamental causes, as we have seen with SOAP.
-
It allows online applications written in different programming languages to connect.
-
With the aid of Restful services, these web apps may live in diverse settings, some on Windows and others on Linux.
However, regardless of the context, the final result should always be the same: they should be able to communicate with one another. Restful web services enable apps developed on different programming languages and platforms to communicate with one another.
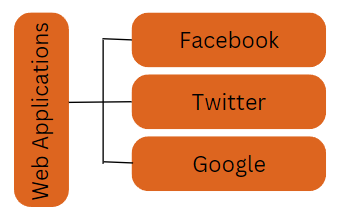
The image below is an actual example of a web application that must communicate with other programs such as Facebook, Twitter, and Google.
If a client application needed to interact with sites like Facebook, Twitter, and others, they would presumably need to know what language Facebook, Google, and Twitter are built on, as well as what platform they are based on.
We can develop the interface code for our web application based on this, but it may be a headache.
Restful web services are used by Facebook, Twitter, and Google to offer their capabilities. This enables any client application to use REST to access these web services.
The Devices event - Nowadays, everything must function on Mobile devices, whether mobile devices, laptop computers, or even automotive systems.
Can you imagine the amount of effort it would take to try to build applications on these devices to communicate with standard web applications? Again, Restful APIs can make this work easier since, as indicated in point 1, you don't need to know what the device's underlying layer is.
Finally, an event of the Cloud - everything is shifting to the Cloud. Applications are gradually migrating to cloud-based platforms like Azure or Amazon. Azure and Amazon both provide a large number of Restful APIs. As a result, programs must now be designed in such a way that they are compatible with the Cloud. Although all Cloud-based architectures are built on the REST principle, it is more efficient for web services to be designed using the REST services-based architecture to make the maximum use of Cloud-based services.
RESTful Architecture
The following traits define a RESTful or REST-style application or architecture:
State and functionality are separated into distributed resources.
Every resource should be reachable using the standard HTTP GET, POST, PUT, or DELETE commands. As a result, if someone wants to download a file from a server, they should be able to do so by sending a GET request. They should be able to send a POST or PUT request if they want to upload a file to the server. Finally, they can send a DELETE request if they wish to remove a file from the server.
Client/server, stateless, multilayer, and cache-supporting architecture
-
The conventional architecture is client-server, where the client can be as basic as a web browser, and the server might be the web server hosting the application.
-
Stateless applications do not use REST to retain their state. For instance, you cannot anticipate that the following request would get the delete information if you use the DELETE command to remove a resource from a server.
You would have to send the GET request to make sure the resource was destroyed. First, the server's resources would be retrieved via the GET request. Then, it would be necessary to check to verify if the resource had indeed been removed.
RESTFul Principles and Constraints
A few properties described below form the foundation of the REST architecture. Any RESTful web service must meet the requirements listed below to be referred to as such. When using RESTful-based services, these qualities—also referred to as design principles—must be observed.
RESTful Client-server

The most basic prerequisite for a REST-based design is this. It denotes that the server would have a RESTful web service that will offer the client the necessary capabilities. The web service on the server receives a request from the client. The server would either deny the request or grant it and provide the client with a suitable answer.
Stateless
Statelessness refers to the idea that the client is responsible for ensuring that the server receives all necessary data. This is most necessary so that the server can handle the answer properly. Between client requests, the server shouldn't store any data. It is a fairly straightforward independent question-answer format. When a client asks a question, the server promptly responds. The client will follow up with another query. The server will have to respond separately to the new query because it won't recall the prior question-answer scenario.
Cache

The stateless issue, which was discussed in the previous paragraph, is addressed by the cache notion. Since each client request to the server is unique, the client may occasionally make an identical request to the server more than once. Even though it had previously requested it, this is what happened. The server will receive this request and respond with its decision. As a result, network traffic has increased. A notion called the cache is used on the client to store requests that have previously been forwarded to the server. Therefore, if the client makes an identical request, the requested information would be obtained from the cache rather than the server.
Layered System
The idea behind a layered system is that any extra layer, like a middleware layer, may be added between the client and the server that is really hosting the RESTFul web service. Before making a call to the web service, the client might interact with this additional service that has been built. However, the deployment of this layer must be seamless to avoid interfering with client-server communication.
Interface/Uniform Contract
This is the fundamental method through which RESTful web services need to function. RESTful mostly utilizes the HTTP web layer and the following essential verbs to interact with server resources.
-
POST : Create a resource on the server using POST.
-
GET: To get a resource off of a server.
-
PUT : To update or alter the status of a resource
-
DELETE : To take a resource off the server or delete it
Create your first ever Restful web service in ASP.NET
We will now learn how to develop Restful web service in ASP.NET:

A number of languages may be used to develop web services. REST-based services may be developed using a variety of integrated development environments.
Let's develop our first RESTful web service that implements the aforementioned using the techniques listed below in this RESTful API tutorial.
Step 1) Create a new project.
Create a blank Asp.Net Web application as the initial stage. Select File -> New project from the menu in Visual Studio 2013.

Following your selection of the New Project option, Visual Studio will present you with a new dialogue box where you can select the project type and enter the appropriate project information.
Step 2) Enter project name and location.
- Make sure to first select the ASP.NET Web application's RESTful web services C# web template. To construct a web services project, the project must be of this kind. By selecting this option, Visual Studio will then take the necessary actions to add the files that any web-based application requires.
- Your project should have a name, which in our instance is "Webservice.REST."
- Make careful to provide the place where the project files will be kept after that.

Once finished, Visual Studio 2013's solution explorer will display the newly generated project file.
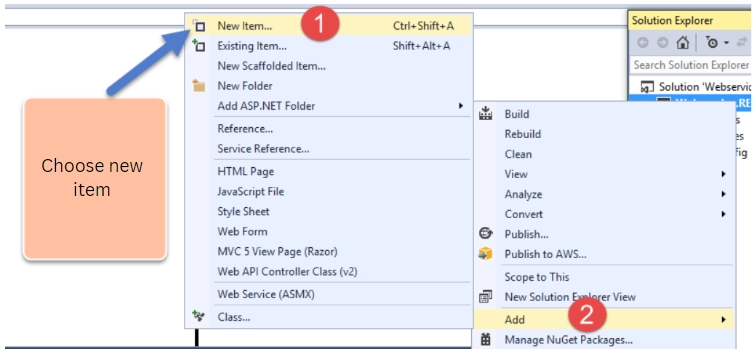
Step 3) Create the web service file.
Making the web service file that will include the RESTful web service is the next step.
- First, right-click on the project file.
- then Choose the option "Add -> new item."
Step 4) Make a Configuration
- Click on the Web.config file to open the code
- Find for the line <enableWebScript>
- Change the line to <webHttp>

Step 5) Add our main code for implementation.
The next step in this RESTful API tutorial is to add our main code for implementation.

Step 6) Define the main code for our GET method.
Next, we will define the main code for our GET method.

Step 7) Return the output.
The very next step is to write up the main code for our POST method.

Step 8) Write the code for the POST method.
Then the next step is to write up the main code for our POST method.
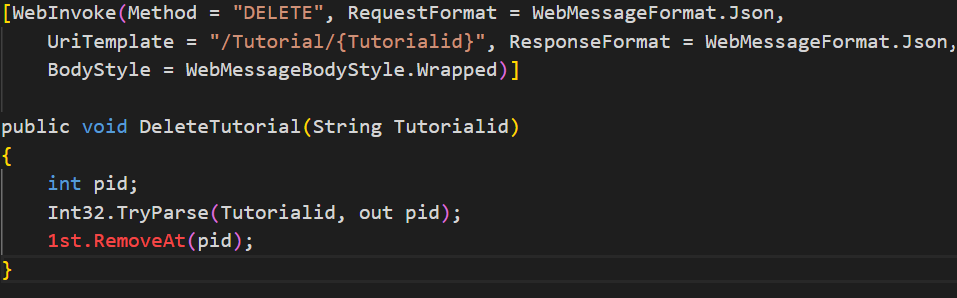
Step 9) Add a method to handle the DELETE operation.
Finally, we are going to add our method to handle the DELETE operation.