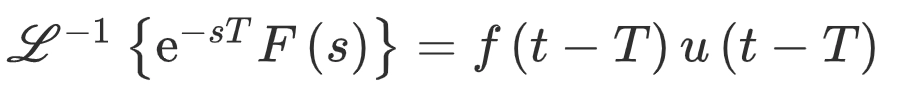Introduction
The Laplace Transform and Inverse Laplace Transform are powerful tools for solving non-homogeneous linear differential equations. In this article, we will learn what inverse Laplace transform does. We will also discuss the transformation formulas, some of their properties, and some questions to help you solve questions on inverse Laplace transform.
Inverse Laplace Transform
In Laplace Transform, we transformed a given derivative function with variable ‘t’ into a complex function with variable ‘s.’ Now, in Inverse Laplace Transform, we transform the complex function with variable ‘s’ back into a function with variable ‘t.’
The above statement can be expressed mathematically as
L{f(t)} → F(s) Laplace Transform
L-1{F(s)} → f(t) Inverse Laplace Transform
Now, you would be wondering that if we are taking the Laplace transform of a function and then we again take the inverse Laplace transform of the resultant function, then what is the point of transforming it in the first place? You will realize it when you are stuck in solving very tedious differential equations. The Laplace transform converts a somewhat differential calculation into a simple algebraic calculation. And in the end, we extract the equation in terms of its original variable using inverse Laplace transform.
We need to be well-versed with the Laplace transform to perform the inverse Laplace transform. We make use of the Laplace transform table only to get the inverse. We check that the given F(s) is of which form in the right-hand side of the Laplace transform table, and the result will be the left-hand side of the identity with which it matches. If we remember the Laplace transform table, then we will also be able to perform the inverse Laplace transform.
Transformation Table



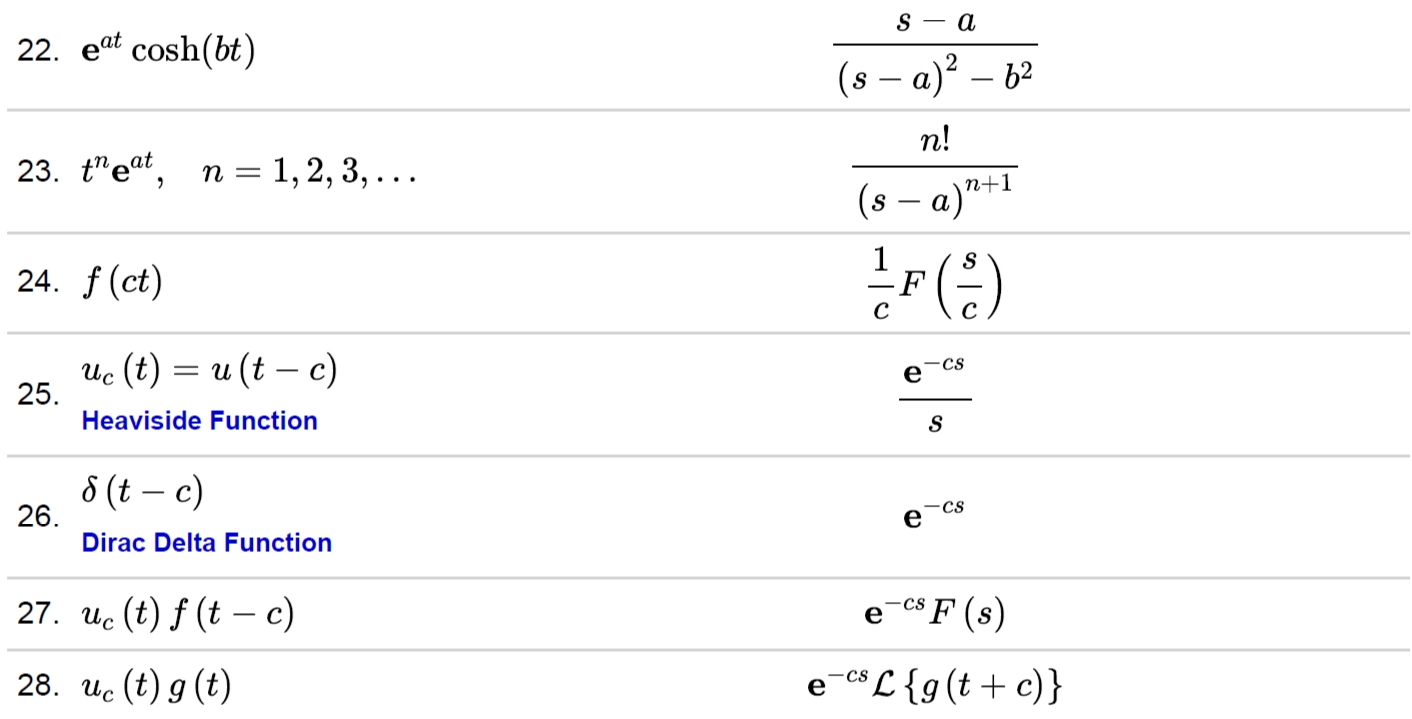

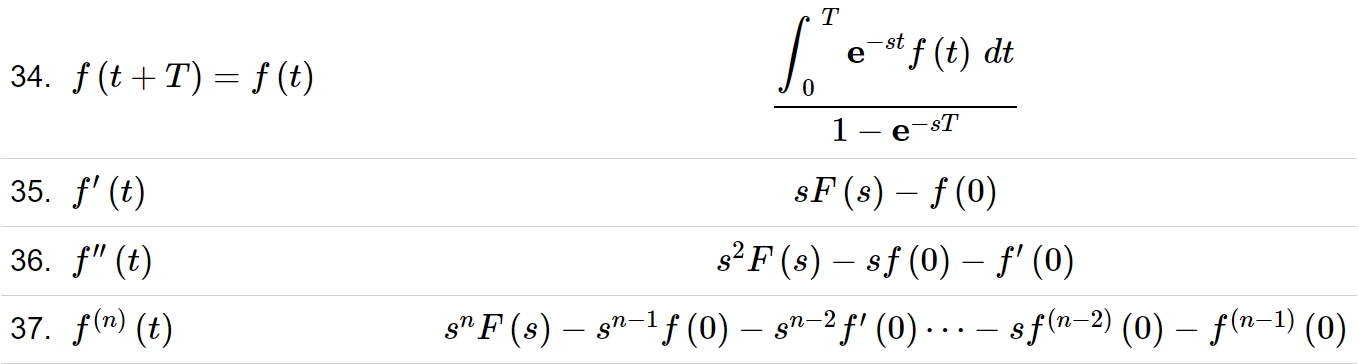
In the above table, the Inverse Laplace Transform is given on the left side, and Laplace Transform is shown on the right side. This table contains the most commonly used transformations but there are many other transformations as well.
Properties
Some essential properties which come in handy while solving problems on Inverse Laplace Transform are given below.
-
Additive Property
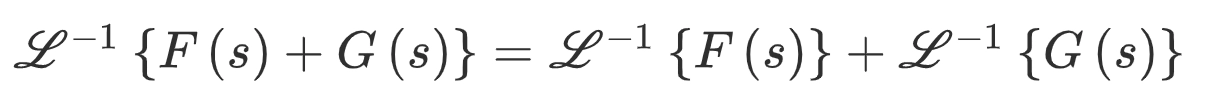
-
Linearity Property
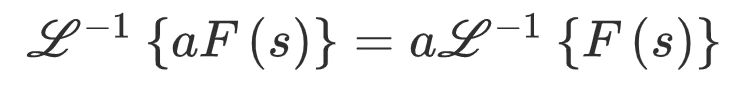
Where ‘a’ is some constant. -
First Shift Theorem
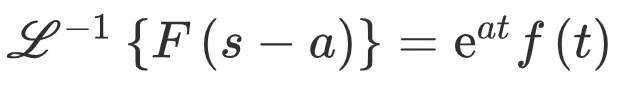
Where ‘a’ is some constant. -
Second Shift Theorem