Introduction
A Linked List is a collection of nodes-objects containing two fields-the data stored and the pointer having the address of the next node in memory. The first node is usually called the ‘Head’, where the linked list is traversed from.
Also see, Data Structures and Rabin Karp Algorithm.

Can we reverse a linked list in less than O(n) time?
Linked list operations usually require reversing them, and working with single and double-linked lists in programs usually needs the least time possible for operations. Hence the question here is: Can we reverse a linked list in less than O(n) time?
Also read - Merge sort in linked list
The solution
Singly-linked list
The structure of a linked list is like this:
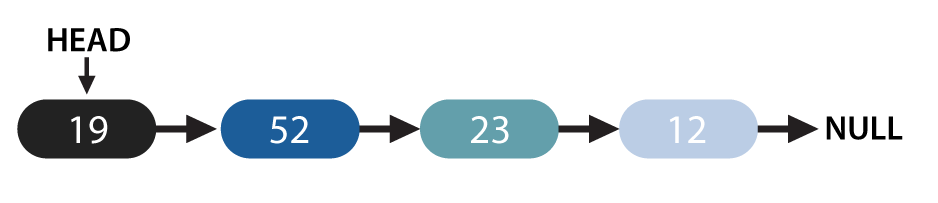
A singly linked list can be reversed using iteration and recursion, but the least possible time doing that is O(n). Every node in the linked list will be visited once to reverse it, even if we transverse the list only once. For example, for the above shown linked list to be reversed, all nodes—starting from 19 to 52, 23 and 12, respectively—will be visited when we navigate through the list. Recursion and iteration will take linear time, meaning the order will not go any lower than O(n) in either of the methods used to reverse-using extra space or simply modify and reverse the pointers.
Let’s consider the memory-efficient doubly linked list now.
Doubly linked list
A Doubly Linked List has nodes with both head and tail pointers, and it looks like this:
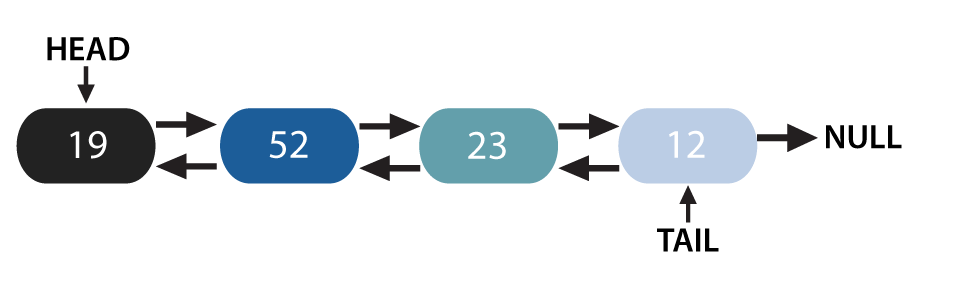
If we traverse such a linked list from the pointer to the node, that will be the reverse order of the linked list. Hence for doubly-linked lists, we can swap the head and tail pointers, which takes constant time. Now, this process will take O(1) time, but to traverse in the forward direction, we will need to use the prev pointer, and to move in the reverse direction, we will need the next pointer. This is bound to cause a lot of confusion and may not be valid.
Therefore, we cannot reverse a linked list in less than O(n) time.
Must Read C Program to Reverse a Number




