ISDN Services
ISDN revolutionizes the way services are delivered over telecommunications networks, offering a broad spectrum of digital services that transcend traditional voice calls. This versatility is one of ISDN's standout features, catering to various needs such as data transfer, video conferencing, and fax services, all through the same network.
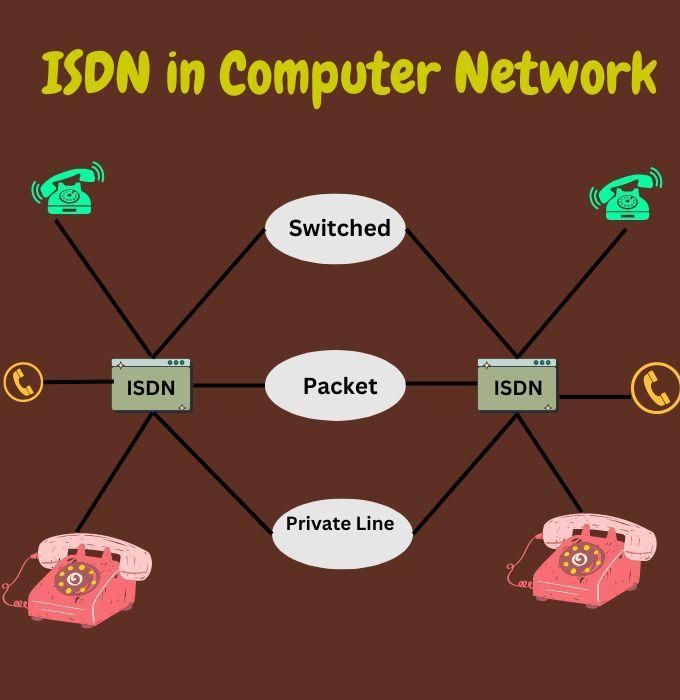
At the heart of ISDN's service offering are two types of channels: the bearer (B) channels and the delta (D) channels. B channels, carrying a bandwidth of 64 Kbps each, are the workhorses of ISDN, designed for transmitting voice, data, and other multimedia content. D channels, while primarily used for signaling and control, can also carry data, albeit at lower rates, making them suitable for tasks such as sending SMS messages or dial-up connections.
One of the key services enabled by ISDN is high-speed internet access. Before the widespread adoption of broadband technologies like DSL and cable, ISDN was a significant upgrade from traditional dial-up connections, offering faster and more reliable internet access. For example, a typical ISDN setup could combine multiple B channels to increase the available bandwidth, a process known as bonding. This capability made ISDN a preferred choice for businesses requiring stable and relatively high-speed internet connections.
Another notable ISDN service is video conferencing. By leveraging the digital transmission capabilities of B channels, ISDN supports high-quality video and audio streams, enabling effective and efficient remote communication. This service has been particularly valuable for organizations with distributed teams or those needing to conduct remote meetings with clients or partners.
To illustrate, let's consider a simple setup for ISDN-based internet access:
# Configuration for ISDN-based internet access
interface Dialer1
mtu 1500
ip address negotiated
encapsulation ppp
dialer pool 1
dialer-group 1
ppp chap hostname user
ppp chap password 0 password
This configuration snippet sets up a dialer interface for ISDN, specifying PPP encapsulation and CHAP authentication with a username and password. The dialer pool and dialer-group commands associate the dialer interface with the ISDN hardware, facilitating the internet connection setup.
Principle of ISDN
ISDN operates on a unique principle that differentiates it from traditional analog phone systems, laying the groundwork for its diverse range of digital services. This principle is centered around the simultaneous transmission of voice, video, and data over a single network, utilizing a digital signaling system. This integration is made possible through the use of multiple channels, specifically the bearer (B) and delta (D) channels, each serving distinct purposes but working in tandem to provide comprehensive communication solutions.
The core idea behind ISDN is to digitize the telephone network, allowing it to carry not just voice calls but also data and multimedia, all through the same infrastructure. This is achieved by converting analog signals into digital form right at the user's premises, eliminating the need for conversion along the network. This direct digital connection ensures higher quality, more reliable communications, and more efficient use of the network's bandwidth.
Moreover, ISDN embraces the concept of channel multiplexing, where multiple B channels can be combined—or bonded—to provide greater bandwidth for data-intensive applications, such as video conferencing or large file transfers. This flexibility allows users to tailor their ISDN connections to their specific needs, scaling the service up or down as required.
For a practical understanding, consider how an ISDN connection is established for a voice call:
-
The user's equipment sends a digital signal to the ISDN network, initiating the call.
-
The network responds by allocating a B channel for the call, utilizing the D channel for signaling and setup.
-
Once the connection is established, voice data is transmitted digitally over the B channel, ensuring clear and uninterrupted communication.
- This process highlights the efficiency and clarity of ISDN calls, attributed to the direct digital transmission and dedicated channels for different types of data.
Advantages of ISDN
ISDN, with its digital architecture, brings several advantages to the table, making it a compelling choice for many applications. Here are some key benefits:
Enhanced Quality & Reliability
ISDN transforms voice and data signals into digital form right from the user's end, leading to clearer voice calls and more reliable data transmission. This digital clarity is particularly noticeable in environments where traditional analog lines may suffer from noise and interference.
Multiple Services Over a Single Line
ISDN allows for the simultaneous transmission of voice, data, and video over the same line. This multiplexing capability means businesses and individuals can access a variety of services without needing multiple separate connections, streamlining communication and reducing costs.
Faster Connection Times
The digital nature of ISDN results in significantly faster call setup times compared to analog lines. This rapid connection is crucial for businesses where time is of the essence and for services requiring frequent call setups, such as internet access.
Flexible Bandwidth Allocation
With ISDN's B channels, users can combine (or bond) channels to increase bandwidth for data-intensive applications. This flexibility allows for efficient bandwidth management, adapting to the varying needs of different services like high-definition video conferencing or large file transfers.
Integrated Services
ISDN supports a wide range of integrated services, from traditional voice calls to advanced digital communications like video conferencing and data transfer. This integration facilitates seamless communication, enhancing productivity and collaboration.
An example of ISDN's flexibility in bandwidth allocation can be seen in how businesses might configure their ISDN lines for varying needs:
# Example of bandwidth allocation with ISDN
interface Multilink1
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
ppp multilink
ppp multilink group 1
!
interface BRI0
no ip address
encapsulation ppp
dialer pool-member 1
ppp multilink
!
interface BRI1
no ip address
encapsulation ppp
dialer pool-member 1
ppp multilink
This configuration creates a multilink bundle using two BRI interfaces, effectively doubling the available bandwidth for data transmission. Such setups demonstrate ISDN's adaptability to different communication demands.
Disadvantages of ISDN
While ISDN offers several advantages, it's important to consider its limitations, especially in the context of newer technologies that have emerged. Here are some of the notable disadvantages:
Cost
One of the significant drawbacks of ISDN is its cost. The installation and monthly charges can be higher compared to traditional analog lines, making it less attractive for small businesses or residential users. Additionally, the cost of ISDN equipment and maintenance can add to the overall expenses.
Availability
ISDN requires special infrastructure from the service provider, which might not be available in all areas, especially in rural or underdeveloped regions. This limited availability can restrict access to ISDN's benefits for some users.
Complexity
Setting up and managing an ISDN system can be complex, requiring specialized knowledge and equipment. This complexity might pose challenges for smaller organizations without dedicated IT staff.
Transition to Newer Technologies
With the advent of newer, more efficient technologies like DSL, fiber optics, and VoIP, ISDN is becoming less relevant. These technologies often offer higher bandwidth, lower costs, and greater flexibility, making them more appealing to many users.
Limited Bandwidth
Although ISDN provides more bandwidth than traditional analog lines, it still falls short of the capabilities offered by high-speed broadband connections. This limitation can be a significant drawback for data-intensive applications, such as streaming high-definition video or large-scale data transfers.
Despite these disadvantages, ISDN remains in use for specific applications where its features, such as clear digital voice transmission and integrated services, are particularly valued. For instance, in certain industrial or security applications where reliability and the integration of voice and data services are paramount, ISDN's advantages may outweigh its drawbacks.
Frequently Asked Questions
What makes ISDN different from traditional telephone services?
ISDN digitizes voice and data signals at the source, offering clearer, more reliable communication over a single line. Unlike analog services, ISDN supports multiple digital channels, enabling simultaneous voice, data, and video transmission.
Can ISDN be used for internet access?
Yes, ISDN provides high-speed internet access compared to traditional dial-up services. It allows for the bonding of multiple B channels to increase bandwidth, accommodating faster data transmission rates.
Is ISDN still relevant with the advent of newer technologies?
While newer technologies like DSL and fiber optics offer higher bandwidth and lower costs, ISDN remains relevant for specific applications requiring integrated digital services, especially in areas where newer infrastructure may not be available.
Conclusion
ISDN, with its ability to carry voice, data, and video over a single network, revolutionized telecommunications. It introduced a level of clarity and reliability previously unseen in analog services, catering to a broad spectrum of communication needs. Despite facing challenges from newer technologies, ISDN's legacy of integrated services and digital transmission continues to influence modern telecommunications. As we move forward, the principles behind ISDN remain a testament to the ever-evolving landscape of digital communication, underscoring the importance of adaptability and innovation in meeting the demands of connectivity in an increasingly digital world.
You can refer to our guided paths on the Coding Ninjas. You can check our course to learn more about DSA, DBMS, Competitive Programming, Python, Java, JavaScript, etc.
Also, check out some of the Guided Paths on topics such as Data Structure and Algorithms, Competitive Programming, Operating Systems, Computer Networks, DBMS, System Design, etc., as well as some Contests, Test Series, and Interview Experiences curated by top Industry Experts.