Introduction
Before directly diving into the topic of Iterative Inorder Traversal of Binary tree, let’s cover the basics and have a quick recap, and see what a tree and its type and about preorder traversal. Because then only we will understand the algorithm and intuition behind Inorder Traversal without recursion.
A tree can be defined as a type of data structure that is formed by a collection of nodes. These nodes represent the value and are interconnected via edges.
Following are the defining properties of a tree:
1. The one node from which the entire tree originates is called the root node.
2. Every node can have only 1 parent and multiple children.
3. Root node does not have a parent node.
4. Each node is connected to its child node and vice versa via edge.
Trees can be of the following types:
-
General Tree: General tree is a type of tree in which there are no restrictions as so to the number of children a node can have
Example: Family tree, Folder Structure, etc. -
Binary Tree: A tree in which every node is allowed to have at most two children. Namely a left node and a right node. Binary trees are further divided into many types based on their application.
Full Binary Tree: A tree that has either zero or two children.
Perfect Binary tree: A tree in which all the interior nodes have two children and all the leaves have the same depth. - Balanced Tree: When the height of the left subtree and the right subtree at any node differ by at most one, then that tree can be called a balanced tree.
- Binary Search Tree: A simple binary tree that also contains binary search properties is turned into a binary search tree. Binary search property means that the value of all the nodes in the left subtree should be less than the root node and the values of all nodes in the right subtree is greater than the root node. Further, the left and right subtree must also be a binary search tree. Binary search tree variants are AVL tree, B-Tree, Red-black tree, etc.
What is Inorder Traversal of a Binary Tree?
The left sub-tree comes first, followed by the root node, and then the right subtree. Symmetric traversal is another name for in-order traversal. The in-order algorithm is also known as the LNR traversal algorithm (Left-Node-Right). An in-order traversal algorithm is usually used to display the elements of a binary search tree.
Let us look at an example to understand this:
- Traverse to the left subtree
- Traverse to the root
- Traverse to the right subtree.
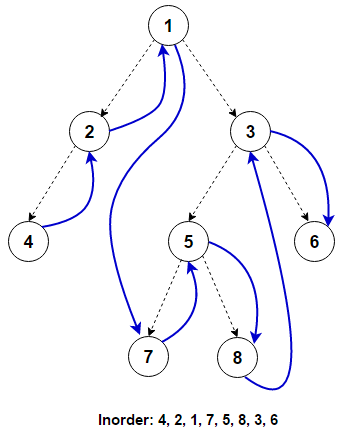
Source:- Inorder
Recommended: Try the Problem yourself before moving on to the solution
Algorithm for Inorder traversal without Recursion
STEP 1. Let's create an empty stack and call it "S".
STEP 2. Now we shall initialize the current node as the root node.
Step 3. Keep pushing the current node to “S” and set current = current->left until the current becomes NULL
STEP 4. If the current node is null and the stack is not empty then:
a) Pop the top item from the stack.
b) Print the popped item, set current = poppedItem->right
c) Go to step 3.
STEP 5. If there is a NULL value in the current and the stack is empty(no more nodes to explore) then we stop.Code for Iterative Inorder Traversal in JAVA
// inorder traversal without recursion of binary tree
import java.util.Stack;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
// construct binary tree
TreeToProcess bt = TreeToProcess.create();
// traversing the binary tree
System.out.println("The nodes for binary tree in their Inorder:");
bt.ProcessinOrderWithoutRecursion();
}
}
class TreeToProcess
{
static class TreeNode
{
String data; TreeNode left, right;
TreeNode(String value)
{
this.data = value;
left = right = null;
}
boolean isLeaf()
{
return left == null ? right == null : false;
}
}
TreeNode root;
// root of the binary tree
public void ProcessinOrderWithoutRecursion()
{
Stack<TreeNode> nodes = new Stack<>();
TreeNode current = root;
while (!nodes.isEmpty() || current != null)
{
if (current != null)
{
nodes.push(current); current = current.left;
}
else
{
TreeNode node = nodes.pop();
System.out.printf("%s ", node.data); current = node.right;
}
}
}
// Defining the tree "t" to test the same
public static TreeToProcess create()
{
TreeToProcess t = new TreeToProcess();
// 4
// / \
// 2 0
// / \ \
// 1 3 6
// / / \
// 5 7 8
TreeNode root = new TreeNode("4");
t.root = root;
t.root.left = new TreeNode("2");
t.root.left.left = new TreeNode("1");
t.root.left.left.left = new TreeNode("5");
t.root.left.right = new TreeNode("3");
t.root.right = new TreeNode("0");
t.root.right.right = new TreeNode("6");
t.root.right.right.left = new TreeNode("7");
t.root.right.right.right = new TreeNode("8");
return t;
}
}
Output:
The nodes for binary tree in their Inorder:
5 1 2 3 4 0 7 6 8 .Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(n), where n is the total number of nodes in a tree as we are traversing the whole binary tree.
Space Complexity: O(h), where h is the height of the tree due to the space consumed in maintaining the stack. The height of the tree can be n for skewed binary trees, where n is the number of nodes in the binary tree.
You can watch this video for proper conceptual knowledge along with preorder traversal and postorder traversal of a BST.




