TWO: LEARN ABOUT OBJECT-ORIENTED PROGRAMMING SYSTEM
Java and OOPS are two converging lines of the IT industry, as each piece of code in Java are written in complete coupling with an object-oriented programming system. For beginners who haven’t worked on C++ before and are switching over to Java from any procedural programming language, creating objects and classes and synchronising them might be challenging initially. But gradually as they get familiar with the class-object hierarchy they understand the benefits of OOPs and their properties.
If you claim to have learnt OOPs you should be able to explain and implement the following features of object-oriented programming :
- Class implementation
- Interfaces
- Abstract classes
- Constructors
- Destructors
- Class inheritance
- Data abstraction (data hiding)
- Encapsulation (data binding)
- Run-time polymorphism
- Compile-time polymorphism
- This pointer
- Friend function
- Virtual function
- Pure-virtual function
With reference to a recent CodeGym Portal survey, 78.8% of Junior Java Developers and trainees avail of Object-oriented programming concepts in their job very frequently, 12.1% occasionally, and 7.6% of them avail of these concepts quite rarely. The last ones belong to testing or a domain other than Development. These numbers clearly indicate the importance of OOPs in Java development; therefore the candidates should brush up on their Object-oriented programming skills even if they apply for the post a Junior Java Developer.
Also see, Eclipse ide for Java Developers
THREE: LEARN THE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE COLLECTIONS FRAMEWORK
A set of individual objects clubbed together as a single unit are referred to as collections in Java. There are numerous frameworks for the various collections in Java. Collections are bagged by the various pre-existing data structures such as lists, sets, hash maps, hash sets, linked lists, regular and connected graphs, and so on. For efficiently implementing collections, first, you need to work on Data Structures and Algorithms.
Data structures reduce the space and time complexity of any code exponentially and reduce the probability of system crashes during software execution significantly. Data Structures such as Linked Lists are widely used in-memory mapping via shadow page tables whereas data structures like queues are used for resource allocation and stack for storing function calls and back-tracking operations.
The popular Java data structures that you must know :
- Array Lists
- Linked Lists
- Doubly Linked List
- Circular Linked List
- Stack
- Queue
- Dequeue
- Circular Queue
- Set
- Map
- ArrayList
- LinkedList
- Queue
- Deque
- Graph
- Trie
- HashSet, HashMap, HashTable
- TreeSet, TreeMap
The main challenge while using Collections or data structures is to figure out which collection should be used at which place, this accuracy comes with regular practise only. The more problem you solve, the more accurate decisions you take. However, there are always multiple solutions for a single problem statement. Before, starting the implementation of any Data Structures; figure out its time and space complexity with the help of the Recursion-tree method or Mater’s theorem. A few of them like lists, stacks, and queue are widely used in Java codes, there’s a big no in skipping them.
FOUR: GET HANDS-ON KNOWLEDGE ABOUT EXCEPTION HANDLING
Exceptions are the unusual situations that are detected when your programme is triggered. The usual exceptions are “divide by zero error”, each exception encountered is a subtype of the Java class java.lang.Exception. The most common advantage of the exception handling mechanism is that it implies the error-detection process in our programmes. Some common codes such as the division of two numbers, even include the “the can’t divide by zero” exception.
Frequently encountered exceptions topics are:
- Logcat the exceptions
- Exceptions handling mechanism
- Try-catch-finally
- Throw, throws
- Hierarchy of exceptions in Java
- Checked/unchecked exceptions
- Backtracking exceptions
- Difference between error and exception
- Unreachable catch block error
- Manual exceptions throwing
FIVE: JAVA INPUT/OUTPUT STREAMS
Taking input and output from the standard console, Standard streams (System. in, System. out), comes under core Java and that is the first thing that even beginners learn. But as we move forward, towards the professional domain input and output operations using streams becomes a necessity. A stream is referred to as a continuous flow of data. We can have a stream of bytes, a file as a stream, and so on.
In addition to the standard I/O stream you must have knowledge about:
- Byte streams (FileInputStream, FileOutputStream)
- Character streams (FileReader, FileWriter)
- Java multithreading/concurrency
Earlier, multithreading was an optional domain, but nowadays features such as split-screen and multi-window are gaining popularity, with this it becomes necessary to learn how to implement multiple threads in a programme and club their results for parallel computing. You must be familiar with the lifecycle of a thread (new, runnable, waiting, time waiting, terminated). Thread operations including Wait, notify, notifyAll, and Interrupting threads functions such as Sleep, yield, join.
SIX: LEARN TO USE LAMBDA EXPRESSIONS
With the ingress of Java 8, lambda functions were introduced. Although it is a contemporary feature, yet its demand is quite high, as lambda functions make functional programming very convenient. Lambda functions are functions that can be created without enclosing them into a class, they are passed on as objects or are triggered when invoked.
You need to work on the following topics while learning about lambda expressions :
-
Lambdas, single method interface
- Anonymous interface implementations
- Writing lambda function body
- Returning a value from a lambda expression
- Handling lambdas as objects
- Lambda type inference
- Lambda parameters
- Capturing variables
- Referring to methods as lambdas
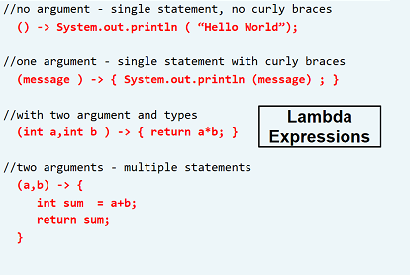 Image Source: shrishti_labs
Image Source: shrishti_labs
SEVEN: FOR BACK-END DEVELOPERS SPRING/HIBERNATE IS NECESSARY
Earlier, freshers were not expected to know about these back-end management frameworks, rather they were taught to a trainee. However, nowadays some vacancies require thorough knowledge about Spring, while some of them require only adequate knowledge about them. Spring provides us a variety of non-functional components that are usually redundant in the development process. This helps to eliminate the need for code generation and XML configuration.
Spring helps us in building an application, running it, and including some custom services and functionalities. It enables us to build REST APIs and server configuration. With the increasing congestion, there is a dire need for optimisation of APIs. The minimisation of API calls reduces the congestion at the server and overall run time of the developed application.
After learning about all these concepts it is necessary to implement them into a project and make that repository available on GitHub or any other online server, this enables you to exhibit your Java knowledge when you send your applications to recruiters while seeking a job.
 Image Source: Medium
Image Source: Medium

 Image Source: shrishti_labs
Image Source: shrishti_labs

