Introduction to Java Server Pages(JSP)
Java Server Pages (JSP) is a server-side programming language that allows developers to create dynamic, platform-independent Web applications. JSPs have access to the entire Java API (Application Programming Interface) family, including the JDBC API( Java Database Connectivity API), enabling them to connect to enterprise databases.

It is an extension of Java Servlet that access Java API, implicit objects, and custom tags into HTML pages to create dynamic web content.
Let’s discuss the following set of JSP Interview Questions and Answers which have been categorised below:
- JSP Interview Questions for Freshers
- JSP Interview Questions for Experienced
- JSP MCQ
JSP Interview Questions for Freshers
1. What are Java Server Pages (JSP)?
JavaServer Pages (JSP) is a dynamic content-supporting Web page development technology that allows programmers to insert Java code into HTML(Hyper Text Markup Langauge) pages using specific JSP tags.
JSP is a technology that controls the content and appearance of Web pages through the use of servlets, which are small programs specified in a Web page and run on the Web server to modify the Web page before it is sent to the user who requested it. The JSP technology is also known as the Servlet application program interface by Sun Microsystems, the creator of Java (API). A Java Server Page calls a Java program executed by the Web server.
An HTML page that links to a Java servlet has sometimes named the file as a suffix.JSP, most of which start with <% and end with %>.
Also Read: Java OOPs Interview Questions
2. Explain the meaning of the dynamic web page?
A dynamic web page modifies its content every time it is viewed. For example, the page may change depending on the time of day, the user who accesses the webpage, or the type of user interaction.
There are two types of dynamic web pages:
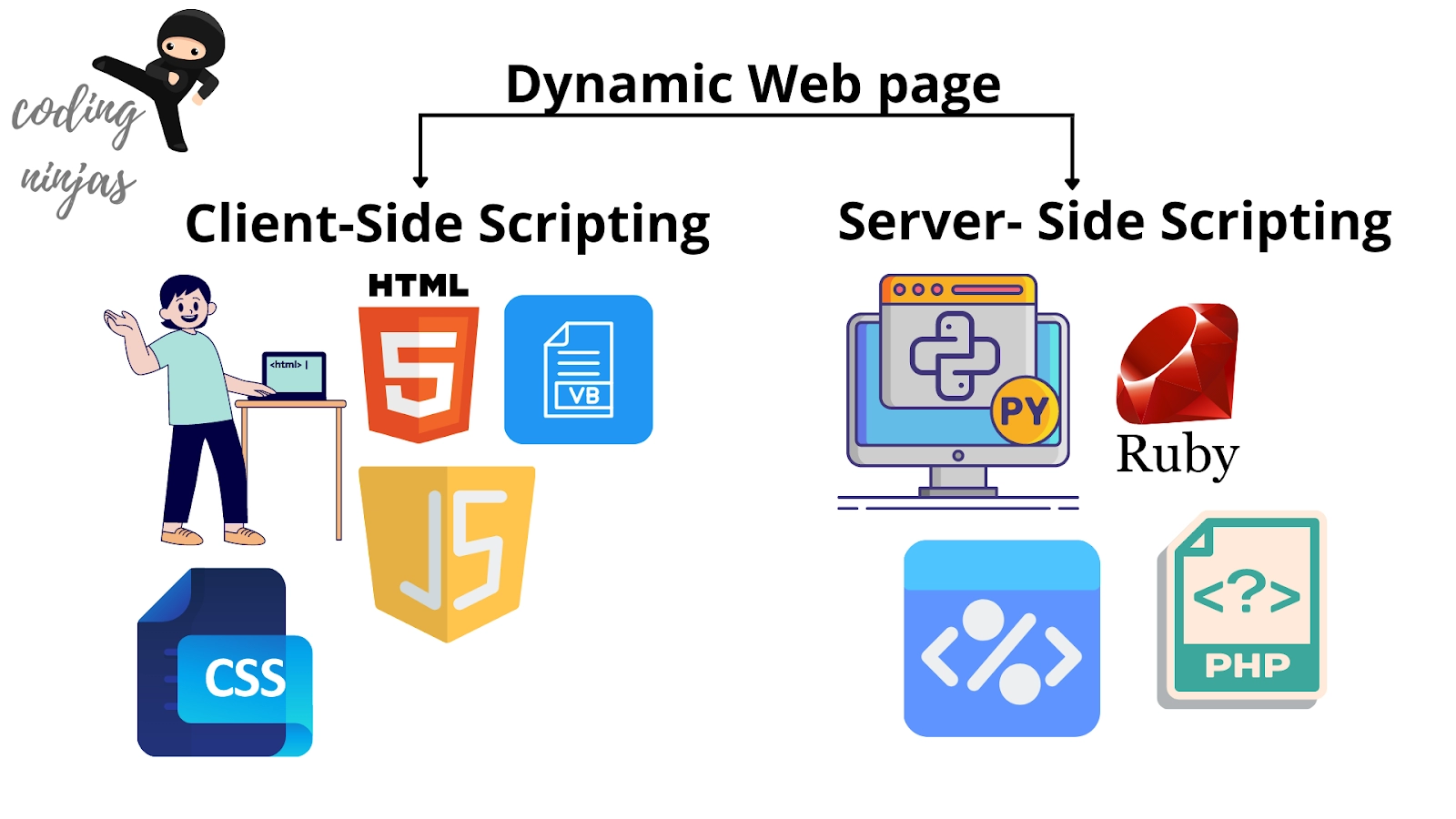
- CLIENT-SIDE SCRIPTING
It is used on web pages that change response to an action on the page, such as a mouse or keyboard action.
Client-side scripts create content for the client. The client-side content is on the user's computer rather than the server. The user's web browser would download the web page content from the server, process the code embedded in the web page, and then display the updated content to the user in these cases.
A web page can respond to client-side events using scripting languages like JavaScript and Flash.
- SERVER-SIDE SCRIPTING
It is used to change web pages when they are loaded or visited. The content generated when a web page is loaded known as server-side content. Server-side scripting is used on login pages, forums, submission forms, and shopping carts, for example, because those web pages change based on what is submitted to them.
A web page can respond to submission events using scripting languages like PHP, ASP, ASP.NET, etc.
3. What are the advantages of using JSP?
- Developers can easily update presentation code because JSP pages are dynamically compiled into servlets.
- Pre-compilation of JSP pages is possible.
- JSP pages can easily be combined with code that generates dynamic content and static templates, such as HTML or XML( Extensible Markup Language) fragments.
- Page authors can access customized JSP tag libraries using an XML-like syntax, which developers can provide.
- Without editing the individual pages that use the application's logic, developers can make logic changes at the component level.
4. What are the life-cycle methods for a JSP?
| S.No. | Life cycle methods | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Translation of JSP page to Servlet |
The JSP life cycle begins with this phase. |
| 2. | Compilation of JSP page | Now, a class file is created from the resulting Java servlet file (test.java) (test.class). |
| 3. | Classloading | The container is now loaded with the Servlet class that was loaded from the JSP source. |
| 4. | Instantiation | In this case, a class instance is created. |
| 5. | Initialization | After generating a Servlet instance from JSP, the jspInit() method is only ever called once during the life cycle. |
| 6. | Request processing | _jspService() is used to handle JSP requests. |
| 7. | JSP Cleanup | The jspDestroy()function is used to either remove the JSP from the container's use or to destroy the servlet method. |
5. Explain the JSP while loop.
The JSP While loop is used to iterate the elements where it has one parameter of the condition.
Syntax of While loop:
While(Condition)
{
// Statements
}6. How to include static files on a JSP page?
The JSP include directive is always used to have static pages. This way, the inclusion is done only once during the translation phase. It's worth noting that the file attribute requires a relative URL. While static resources can be included, it is not recommended because it is essential to have each request.
7. What are Servlets?
In the same application, JSP pages and servlets are frequently in use together. The Java servlet specification is the foundation for the JSP specification. Simply put, a servlet is a piece of code that adds new functionality to a web server, like CGI(Common Gateway Interface) and proprietary server extensions like NSAPI and ISAPI. Servlets have several advantages over other technologies:
- Platform and vendor independence
- Integration
- Efficiency
- Scalability
-
Security and robustness
Know What is Servlet in detail.
8. What is JSTL?
The JSTL(Java Server Pages Standard Tag Library )is a collection of custom JSP tag libraries that provide standard web development functionality.
Some of JSTL's properties are as follows:
- The code is neat.
- It provides a rich layer of portable functionality to JSP pages as a Standard Tag.
- It supports automatic Javabeans introspection. The JSTL expression language is very good at handling JavaBean code. The objects that retrieved as scoped attributes do not need to be downcast.
- Humans can read it more efficiently, and computers can understand it more easily.
9. What are Implicit JSP Objects?
| Variable Name | Java Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| request | javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest | The request object requests information like a parameter, header information, server name, etc. |
| session | javax.servlet.http.HttpSession | This is used to get, set, and remove attributes to session scope and get session information. |
| response | javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse | The response is an instance of a class that represents the response that can be given to the client |
| pageContext | javax.servlet.jsp.PageContext | This is used to get, set, and remove the attributes from a particular scope. |
| application | javax.servlet.ServletContext | This is used to get the context information and attributes in JSP. |
| out | javax.servlet.jsp.JspWriter | This implicit object is used to write the data to the buffer and send output to the client in response. |
| Config | javax.servlet.ServletConfig | Config is used to get the initialization parameter in web.xml |
| page | java.lang.Object | This implicit variable holds the currently executed servlet object for the corresponding JSP. |
| Exception | java. lang.Throwable | Exception, the implicit object of the throwable class, is used for exception handling in JSP. |
10. Explain how to use JSP in a loop.
The JSP ‘For’ loop is used to iterate the elements for a specific condition, and it has three parameters:
- The counter variable is set to zero.
- If the condition is true, the loop must be executed.
- It is necessary to increment the counter.
Syntax:
for(inti=0;i<n;i++)
{
// Block of statements
}11. What are the JSTL Core tags?
The JSTL Core tags are used for the following purposes:
- Iteration
- Conditional logic
- Catch exception
- URL forward
-
Redirect, etc.
Following is the syntax to include a tag library:
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri=http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core%>12. How are Custom Tags in JSP created?
The following steps are used to create custom tags in JSP.
- How to Make a Tag Handler Class.
- How to Make a TLD File
-
How to Make a JSP File
Let us discuss these in detail:
- How to Make a Tag Handler Class:
We must inherit the TagSupport Class and then override the doStartTag() method to create a Tag Handler Class.
The JspWriter class is used to write data for JSP pages.
The getOut() method of the PageContext class returns an instance of the JspWriter class.
The TagSupport class later provides a default instance of pageContext.
- How to Make a TLD File:
Tag Library Descriptor file (TLD) is an abbreviation for Tag Library Descriptor file. It's where you'll find information about tags and Tag Hander classes. It has to be kept in the WEB-INF folder.
- How to Make a JSP File:
The path to the TLD file will be directly specified. Using the URI(Uniform Resource Identifier) name rather than the full path to the TLD file is preferable.
Must Read Sdet Interview Questions
13. Which methods are used for reading from data using JSP?
Ans. The form data parsing is handled automatically using JSP. It terminates in one of the following ways, depending on the circumstances:
To get the value of a form parameter, use the
- getParameter(): It is a method that returns a parameter.
- getParameterValues(): It is called if a parameter appears multiple times and returns multiple values.
- getParameterNames(): It is used if you want a complete list of all parameters in the current request.
- getInputStream(): It reads binary data streams from the client.
14. Differentiate between <jsp:forward page =...> and response.sendRedirect(url).
Ans. The <jsp: forward> element passes the request object from one JSP file to the next. The target file can be HTML, servlet, or another JSP, but it must be in the same application context as the forwarding JSP.
SendRedirect sends the browser an HTTP temporary redirect response. After that, the browser sends a new request to the redirected page. The session variables are destroyed.
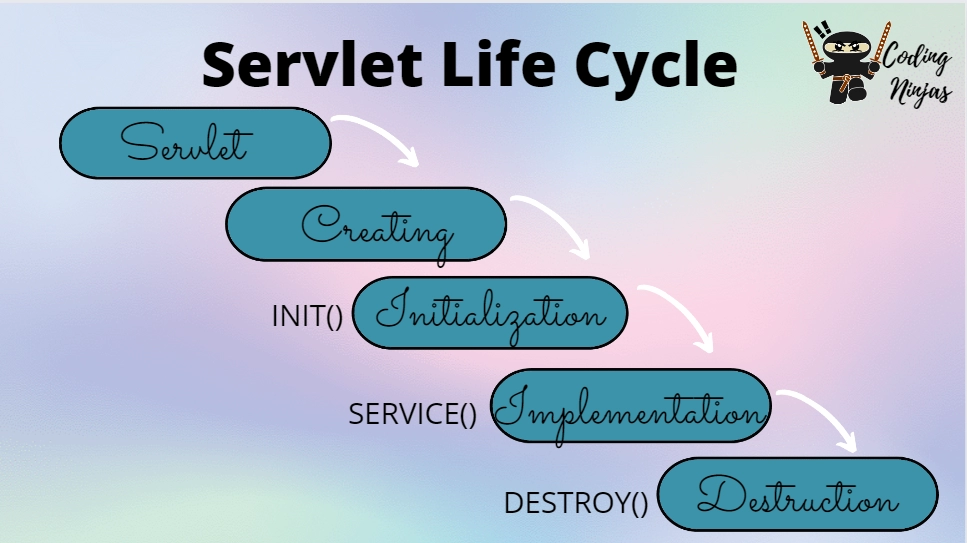
15. Explain the life cycle of a servlet.
Ans. These are the steps in the life cycle of a servlet:
-
Load Servlet Class: When the first request is received, the web container loads the servlet. This step is only performed once at the time of the initial request.
-
Create Servlet Instance: After loading the servlet class, the web container creates the servlet instance. For each servlet, only one instance is made, and the same servlet instance handles all concurrent requests.
-
Call init() method: After the servlet instance is created, the web container calls the servlet's init method. Before processing the first request, this method is used to initialize the servlet. The web container only makes one call to it.
-
Call service() method: Following the initialization process, the web container invokes the service() method. Every request invokes the service method. Servlet creates a new thread for each request.
- Call destroy() method: The web container calls this method before removing the servlet instance. The destroy method requests that the servlet release all resources associated with it. When all servlet threads have exited or if a timeout occurs, the web container only calls it once.