Processing/Parsing XML data in JSP
Before processing XML data in JSP, we need XPath and XML-related files into our two libraries <Tomcat Installation Directory> \ lib directory:
XercesImpl.jar: In this download http://www.apache.org/dist/xerces/j/
xalan.jar: In this download http://xml.apache.org/xalan-j/index.html
We will first create novel.xml file:-
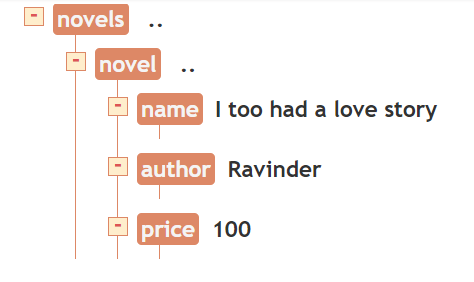
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<novels>
<novel>
<name>I too had a love story</name>
<author>Ravinder</author>
<price>100</price>
</novel>
<novel>
<name>Harry potter</name>
<author>J. K. rowling</author>
<price>2000</price>
</novel>
</novels>
Now create main.jsp file in same directory and write the following code -
<%@ taglib prefix = "c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
<%@ taglib prefix = "x" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/xml" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>JSTL x:parse Tags</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>Novels Info:</h3>
<c:import var = "novelInfo" url="http://localhost:8080/novel.xml"/>
<x:parse xml = "${novelInfo}" var = "output"/>
<b>The title of the first novel is</b>:
<x:out select = "$output/novels/novel[1]/name" />
<br>
<b>The price of the second novel</b>:
<x:out select = "$output/novels/novel[2]/price" />
</body>
</html>
We will visit http://localhost:8080/main.jsp to see the output.
Output:

Formating XML data in JSP
For formatting, we will create an XSLT stylesheet style.xsl file and write the following code in it -
<?xml version = "1.0"?>
<xsl:stylesheet xmlns:xsl = "http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform"
version = "1.0">
<xsl:output method = "html" indent = "yes"/>
<xsl:template match = "/">
<html>
<body>
<xsl:apply-templates/>
</body>
</html>
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match = "novels">
<table border = "1" width = "100%">
<xsl:for-each select = "novel">
<tr>
<td>
<i><xsl:value-of select = "name"/></i>
</td>
<td>
<xsl:value-of select = "author"/>
</td>
<td>
<xsl:value-of select = "price"/>
</td>
</tr>
</xsl:for-each>
</table>
</xsl:template>
</xsl:stylesheet>
And corresponding to this XSLT stylesheet style.xsl file create main.jsp file within which the above stylesheet will be applied -
<%@ taglib prefix = "c" uri = "http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
<%@ taglib prefix = "x" uri = "http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/xml" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>JSTL x:transform Tags</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>Novels Info:</h3>
<c:set var = "xmltext">
<novels>
<novel>
<name>I too had a love story</name>
<author>Ravinder</author>
<price>100</price>
</novel>
<novel>
<name>Harry Potter</name>
<author>J. K. Rowling</author>
<price>2000</price>
</novel>
</novels>
</c:set>
<c:import url = "http://localhost:8080/style.xsl" var = "xslt"/>
<x:transform xml = "${xmltext}" xslt = "${xslt}"/>
</body>
</html>
And now if you go to http://localhost:8080/style.xsl you will see the following output.
Output:

You can also read about the JSP Architecture and Lifecycle.
Must Read Apache Server
Frequently Asked Questions
1.Give some advantages of XML.
- Any simple editor can edit and view an XML document that contains plain text.
- XML documents are platform-independent.
- The XML document can be transmitted easily and take less space as they are Unicode-based.
- We can represent the XML data in a tree structure, making it easy to understand.
2.Why do we use Tomcat?
- Up-to-date versions of the servlet specs and JSP is supported by Tomcat.
- Tomcat is open-source.
- Without configuring a separate Web server, we can run it standalone.
Key Takeaways
In this blog, we learned about XML data in JSP. Don't come to a halt here. Check out our Top 8 Java Projects on GitHub | Coding Ninjas Blog. Can you also check out the JSP blogs? Check out more blogs here. More Blogs.
Happy Learning!