Introduction
In this blog, we will solve a question of dynamic programming Array data structure problem in which we will see how to form non-overlapping sub-arrays. With every problem we see, a different approach is used which teaches us how a problem like that should be solved. The examples given below clearly explain what the problem says, what type the input should be, what type the output should be, and the complexity analysis of the solution provided.
In this problem particularly, we will see how sub-arrays are formed, which can be usednot only in this problem but also in numerous other problems.
Also Read About, Array Implementation of Queue and Rabin Karp Algorithm
What is an Array Data Structure?
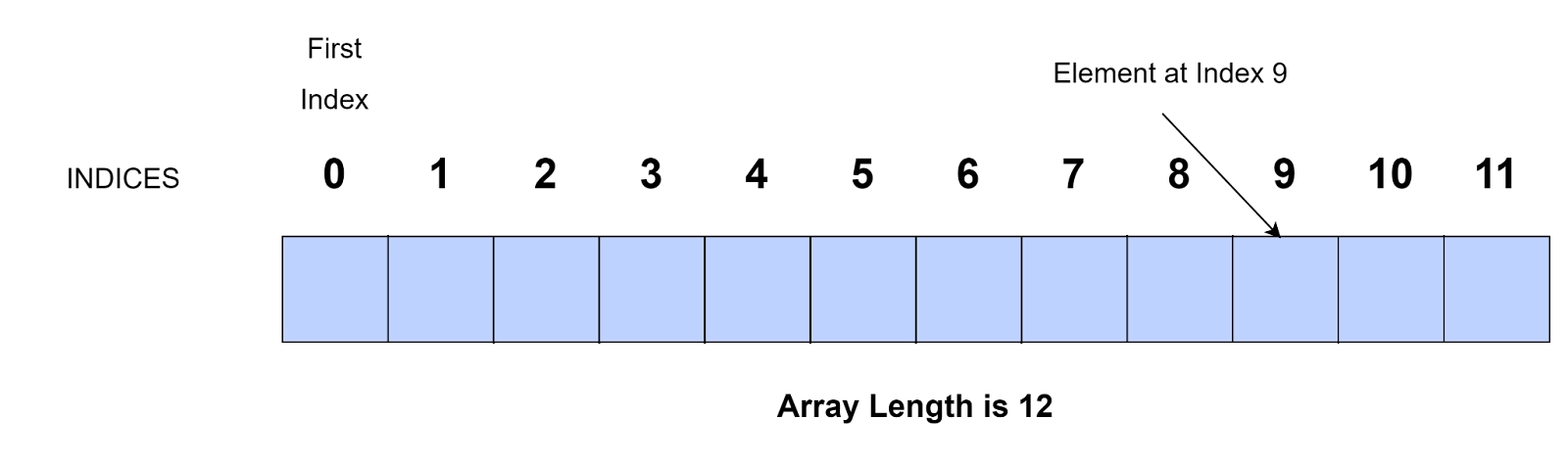
A collection of elements stored at contiguous memory locations is an Array. The elements stored in the array are of the same type. The contiguous memory locations of the array make it easier to calculate the position of each element in the array.
The first element is at index 0. As we transverse the array, the index increases by 1 till n-1 if there are n elements in the array.
Problem statement
Firstly, we will have a look at what exactly the problem says.
Given an array of n elements. From that array, we need to create all non-overlapping contiguous sub-arrays. We will also input one other value, k. The variable ‘k’ will specify the number of maximum sums that needs to be created. Once the sub-arrays have been created, we will find the sum of the elements of sub-arrays and display the ‘k’ maximum sums.
Here, we are assuming that all the elements in an array are positive.
Sample Examples
Example 1:

Explanation:
In the example above, we have taken an array of 6 elements as input and value of k as 1. The program will run to find sub-arrays and pick up that one whose elements add to give maximum sums. Since, value of k is 1 here, only one value will be returned in the output. The subarray which will give the above sum is {3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17}.
Example 2:

Explanation:
In this example, we have taken a different array, input[], and value of k as 3. Again for this input, the program will run, sub-arrays would be determined and those would be picked up whose elements add to give maximum sums. Since the value of k is 3 here, three values are returned. The subarrays which will give the above sums would be {1,4}, {2, 2}, {0}.
Approach
To solve this problem, we will use Kadane’s Algorithm.
Kadane’s Algorithm is a dynamic programming algorithm using which we search for sub-arrays. To read more about this algorithm, refer to this.
Now, that we know what is Kadane’s Algorithm, we will find sub-arrays using that algorithm and the sum of their elements respectively.
As per the value of k, which can be any positive integer, we will determine how many values are to be returned. The values returned should be the maximum sums of all sub-arrays that could be created from that input array.
PseudoCode
static void max(int input[], int k, int len)
{
int a = 0;
while(a < k)
{
// Kadane's algorithm.
int mmax = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int hmax = 0;
int first = 0, last = 0, sum = 0;
int b = 0;
while(b < len)
{
hmax += input[b];
if (mmax < hmax)
{
mmax = hmax;
first = sum;
last = b;
}
if (hmax < 0)
{
hmax = 0;
sum = b + 1;
}
b++;
}
System.out.println(mmax);
for (int c = first; c <= last; c++)
{
input[c] = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
}
a++;
}
System.out.println();
}Implementation in Java
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Test case
int input[] = {4, 2, 1, 0, -3, -5, 6, 2, 8, 2};
int k = 3;
int len = input.length;
// Function calling
max(input, k, len);
}
static void max(int input[], int k, int len)
{
int a = 0;
while(a < k)
{
// Kadane's algorithm.
int mmax = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int hmax = 0;
int first = 0, last = 0, sum = 0;
int b = 0;
while(b < len)
{
hmax += input[b];
if (mmax < hmax)
{
mmax = hmax;
first = sum;
last = b;
}
if (hmax < 0)
{
hmax = 0;
sum = b + 1;
}
b++;
}
System.out.println(mmax);
for (int c = first; c <= last; c++)
{
input[c] = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
}
a++;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
Input:
input[]= {12, 3, -9, -2, 10, 4, 0, 3}, k=2
Output:
sums[]= {18, 7, 0}
Complexity Analysis:
We are using nested loops in the above code, the outer loop is running k times while the inner loop will run n times, therefore when we combine them the time complexity would be O(n*k).
Since we have not used any extra space. So, the space complexity for the above code is O(1).




