Introduction
In this blog, we will solve a question of dynamic programming Array data structure problem. With every problem we see, a different approach is used which teaches us how a problem like that should be solved. The examples given below will explain what the problem says, what the input the output should be, and we will also discuss the complexity analysis of the solution to the problem.
What is an Array Data Structure?
A collection of elements stored at contiguous memory locations is an Array. The elements stored in the array are of the same type. The contiguous memory locations of the array make it easier to calculate the position of each element in the array.
The first element is at index 0. As we transverse the array, the index increases by 1 till n-1 if there are n elements in the array.
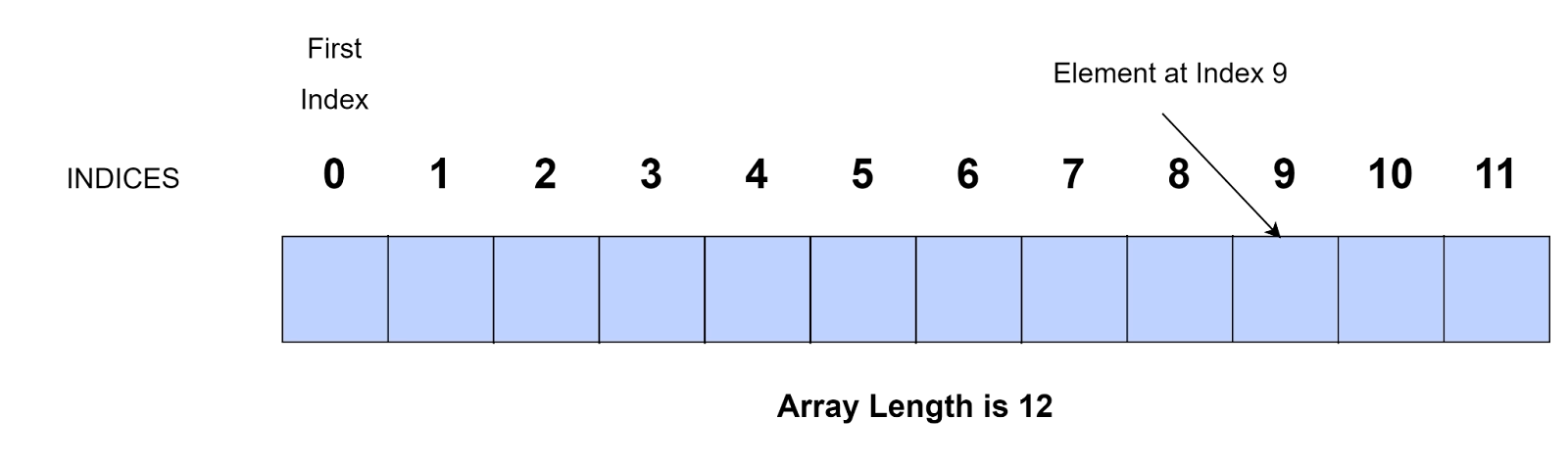
Example Array
Problem Statement
Firstly, we will have a look at what exactly the problem says.
Given an array of ‘n’ elements. The variable ‘k’ signifies the number of smallest elements present in the array. The only condition here is that the sequence or order of the elements should not change, that is, the order of those elements in the output array should be the same as they were in the input array. Also, the space complexity of the solution code should not exceed O(1).
Example 1:

Explanation: In the example given above, we are provided with an array and value of the variable, k. According to the problem statement, we have to return the 4 smallest elements in the given array, and their order should not change. Hence, the output will be sorted, if the given array is sorted.
Example 2:

Explanation: In the example given above, we are provided with an array and value of the variable, k. This time we have taken an example of a sorted array. According to the problem statement, we have to return the 3 smallest elements in the given array, and their order should not change. As you can see in the output all the k smallest elements are present in the same order as they are present in the array.
Also see, Euclid GCD Algorithm
Approach
We know there are several approaches to solve a coding problem. If we had the option of using extra space or it wouldn’t have been the compulsion to return the output in the same order, we would have certain other approaches.
But here, it is specifically mentioned to not use extra space, and also, the output to be in the same order, so we will use the Insertion sort approach.
This idea of Insertion sort will move ‘k’ smallest elements in the beginning and also, in the same order. Every element of the array is checked against its next element and swapped if we find the larger element in the previous element. That is, of the two elements being checked, the smaller one should be in the right always.
PseudoCode
public static void smallk(int input[], int len, int k)
{
int x=k;
while(x<len)
{
int m= input[k-1];
int loc= k-1;
for(int y= k-2; y>=0; y--)
{
if(input[y] > m)
{
m= input[y];
loc=y;
}
}
if(m> input[x])
{
for(int y= loc; y < k-1; y++)
{
input[y]= input[y+1];
}
input[k-1] = input[x];
}
++x;
}
int z=0;
while(z<k)
{
System.out.print(input[z]+ " ");
z++;
}
}Implementation in Java
import java.lang.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int[] input = {19, 11, 5, 7, 9, 14, 10, 6, 4, 13};
int len = input.length;
int k = 3;
smallk(input, len, k);
}
//function to get the smallest k values
public static void smallk(int input[], int len, int k)
{
int x=k;
while(x<len)
{
int m= input[k-1];
int loc= k-1;
for(int y= k-2; y>=0; y--)
{
if(input[y] > m)
{
m= input[y];
loc=y;
}
}
if(m> input[x])
{
for(int y= loc; y < k-1; y++){
input[y]= input[y+1];
}
input[k-1] = input[x];
}
++x;
}
int z=0;
while(z<k)
{
System.out.print(input[z]+ " ");
z++;
}
}
}
Input
input[]= {19, 11, 5, 7, 9, 14, 10, 6, 4, 13}, k= 3
Output
5, 6, 4
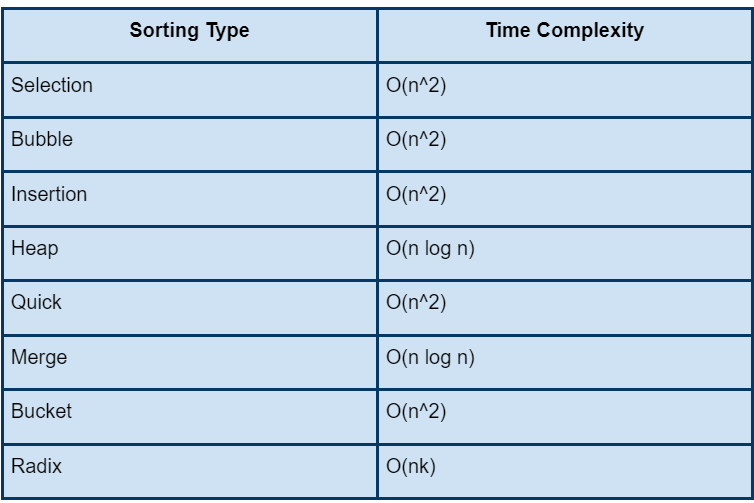
Complexity Analysis:
Time Complexity
Here, we have used nested loops, that is, one loop inside another, and in the worst case both the loops will traverse from 1 to n therefore the time complexity would O(n*n) i.e, O(n^2).
Space Complexity
We can see that no extra space has been used in the solution above, So, the space complexity for the given code will be: O(1)