Difference with normal function
A regular function can perform multiple operations in its function body but lambda function is synthetically restricted to a single operation. But lambda function is easy to implement for simple logical operations and it can be used to implement such functions that are used just one time.
Both types of functions are implemented for the same objective.
##normal function
def fun(x,y):
return x*y
fun(2,3)

You can also try this code with Online Python Compiler
Output
6
Example
##lambda function
multiply=lambda x,y: x*y
multiply(2,3)

You can also try this code with Online Python Compiler
Output
6

You can also try this code with Online Python Compiler
Use cases
Lambda function for singular value
To use the function, just for a single time we don’t need to call the function separately we can pass the values of the arguments along with its definition.
Let’s see through an example
(lambda x,y: x*y)(2,3)

You can also try this code with Online Python Compiler
Output
6
In the above lambda function values (2,3) of the arguments (x,y) is passed along with its definition.
Lambda function with a list
Lambda function can be used for list comprehension. Let’s implement this scenario using for loop.
list=[lambda x=x: x*10 for x in range (1,6)]
for fun in list:
print(fun())

You can also try this code with Online Python Compiler
Output
10
20
30
40
50
Lambda function for higher-order functions
Lambda function can be used in higher-order functions like filter( ), map( ) that accept a function as its argument. Let’s understand such use cases through the following examples.
Filter
filter( ) is an inbuilt function in python that only returns the values from a set of values that satisfy a certain condition. Let’s see the syntax of this filter function.
filter(function, iterable)
#we can any anonymous function like lambda function for the 1st argument
#interable can be a list or any set

You can also try this code with Online Python Compiler
In the below example we will filter the odd numbers from a list by using lambda function as selection criteria.
lis=[3,4,7,9,2,13,6]
lis=filter(lambda x:x%2==1,lis)
for i in lis:
print(i)

You can also try this code with Online Python Compiler
Output
3
7
9
13
Map
The map is also an inbuilt function. Its syntax is the same as filter i.e. filter(function, iterable. It takes any list or tuple and each element is mapped to a different element based on the given function argument. It returns the list of mapped elements.
lis=[1,2,3,4]
mapped=map(lambda x:x*x,lis) #each element mapped to its square
for i in mapped:
print(i)

You can also try this code with Online Python Compiler
Output
1
4
9
16
Lambda function using if……else
We can use a conditional statement to implement the lambda function. Let’s see an example.
min=(lambda x,y:x if x<y else y)
min(2,3)

You can also try this code with Online Python Compiler
Output
2
You can practice by yourself with the help of online python compiler.
Also check out Python Square Root here.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How lambda function is used to manipulate values inside Pandas data frame?
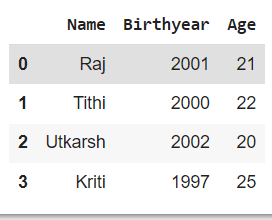
It can be used with apply( ) function to manipulate values of any column. See the below example.
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({
'Name': ['Raj','Tithi','Utkarsh','Kriti'],
'Birthyear': [2001, 2000, 2002, 1997],
})
df['Age']=df['Birthyear'].apply(lambda x:2022-x)
## age is calculated using birth year
df

You can also try this code with Online Python Compiler
Output
2. Apply lambda function to filter values greater than 10 from a list.
lis=[3,4,7,19,2,13,6]
filtered = list(filter(lambda x:(x>10),lis))

You can also try this code with Online Python Compiler
3. Is there any alternative to the lambda function?
Predefined functions in the operator module can be used as an alternative to the lambda function.
Conclusion
In this article, We discussed Python's lambda function in the previous article, including its syntax, its intention, and how to use it in practice. Programmers appreciate lambda functions because of the flexibility they provide in making small unnamed functions. When used in combination with functions such as map(), filter(), and sorted(), the code becomes neater. Knowing how and when to use lambda functions enhances one's ability to program functions in Python.
Recommended Readings:





