The largest element in an array
An array is a collection of elements of the same kind stored in contiguous memory locations. It may be accessed separately using a unique identifier's index.
A number array, such as an integer array, float array, double array, or long array, can hold numbers of various sizes. In an array, we can discover the largest number of these.
To follow these examples, you need to be familiar with the following Java programming concepts:
- Loops in Java
- Methods in Java
- Concept of Recursion
Problem Statement
Write a programme to discover the largest element in an array arr[] of size n.
Let's consider a small example of an array of 5 elements.
Input: arr[ ] = {32, 57, 63, 55, 48}
Output: 63
Explanation: The largest element of the given array is 63.
Solutions
There are several methods for determining the greatest element. There is support for finding the maximum in the library in every programming language. Internally, though, they are identical. The following are some of the methods that have been discussed.
- Sorting: Arrange the elements in ascending order, with the last element at the last index.
- Traverse: Update the maximum value when traversing the array.
Approach 1(Sorting)
Arranging the elements in descending order is a straightforward technique to identify the array's greatest element. After sorting, the largest element will be represented by the first element, the second-largest by the next, and until the last part represents the array's smallest element.
Steps to a Solution
- Sort the data in the array.
- Return the element to the array's first index.
Algorithm
- Start.
- Array Declaration.
- Initialization of the array.
- To find the largest element in a given array, use two for loops
- To hold each element of the array, use the first for loop.
- To compare the element to the rest of the elements, use the second for loop.
- To sort the elements, swap them around.
- Show the element that is the largest.
- Exit.
Here is the Java programme for the Sorting Method:
Program
/*Java Program to find the largest element in an array using Sorting of elements*/
import java.util.Scanner;
class Coding_Ninjas_01
{
public static void main(String []args)
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int r; //Declaring the size of the array
System.out.println("Enter the size of your array");
r=sc.nextInt(); //Initialise array size
int arr[]=new int[r]; //Declaring the array
System.out.println("Enter your array");
for(int i=0;i<r;i++) //Initialising the array
{
arr[i]=sc.nextInt();
}
for(int i=0;i<r;i++) //Use to hold an element of the given array.
{
for(int j=i+1;j<r;j++) //Use to check for rest of the elements of the array
{
if(arr[i]<arr[j]) //Comparing and swapping
{
int temp=arr[i];
arr[i]=arr[j];
arr[j]=temp;
}
}
}
System.out.println("The Largest element of the given array is "+arr[0]); //Display the Largest after sorting
}

You can also try this code with Online Java Compiler
Output
Enter the size of the array 5
Enter the array 32 57 63 55 48
The Largest element of the given array is 63

You can also try this code with Online Java Compiler
Time complexity: O(N2) where there are N elements in the array
Space complexity: O(1)
Approach 2(Iterative Method)
This program aims to discover the largest element in the array. This can be done by keeping a variable called large, which will initially retain the value of the first element. By comparing the value of ‘large’ with the array's items, you may loop across the array. If any element's values are more than large, the element's value is stored in large.
Algorithm
- Declare a variable called large and set its value to the first entry of the array.
- Check each index from 1 to n(size of the array) in a loop.
- Set large = arr[i] if arr[i]>large.
- Print the largest number after completing all iterations.
Here is the Java Program for the Iterative method:
Program
public class Coding_Ninjas_02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Initialise array
int [] arr = new int [] {32, 57, 63, 55, 48};
//Initialise large with first element of array.
int large = arr[0];
//Loop through the array
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
//Compare elements of array with large
if(arr[i] >large)
large = arr[i];
}
System.out.println("The largest element in the given array: " + large);
}
}

You can also try this code with Online Java Compiler
Output
The largest element in the given array: 63

You can also try this code with Online Java Compiler
Time complexity: O(N) where there are N elements in the array
Space complexity: O(1)
Learn more: Array in Java
Approach 3(Recursive Method)
The Top-down Recursive approach mainly consists of three steps:
- Creation of a Recursive Function: Construct a recursive function with the name getmin (int arr[], int num)
- Deciding a base condition: If (num==1) is true, return arr[0]
- Otherwise condition: Return max(arr[num-1], getmax(arr, num-1)) if base condition is not true.
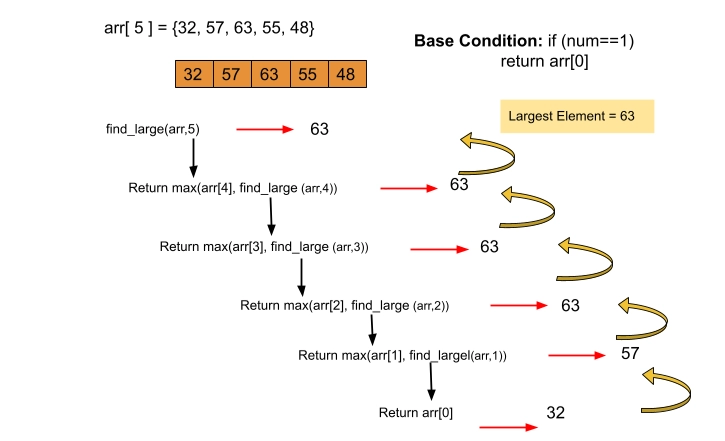
Here is the Recursive program to find the largest element of the given array.
Program
// Recursive Java program to find maximum
import java.util.*;
class Coding_Ninjas_03 {
// Recursive function to return maximum element using recursion
public static int findlarge(int arr[], int num)
{
// if num== 1 means we have only one element
if(num == 1)
return arr[0];
return Math.max(arr[num-1], findlarge(arr, num-1));
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
int arr[] = {52, 47, 63, 55, 48};
int num = arr.length;
// Calling Recursive Function
System.out.println(findlarge(arr, num));
}
}

You can also try this code with Online Java Compiler
Output
63

You can also try this code with Online Java Compiler
Try it by yourself on java online compiler.
Also check out Addition of Two Numbers in Java here.
Real-Life Use Cases
1. Processing Exam Scores
In educational software, you may need to determine the highest score among all students to award top performers. This can be done using a simple Java loop that compares each score in the array.
int[] scores = {85, 92, 78, 96, 88};
int max = scores[0];
for (int score : scores) {
if (score > max) max = score;
}
System.out.println("Top Score: " + max);
This logic helps educators or systems quickly highlight the top scorer in a batch of results.
2. Finding Max Temperature in Weather Data
Weather monitoring systems often store daily temperatures. Finding the maximum temperature helps identify heatwaves or peak conditions for alerts.
int[] temps = {32, 35, 37, 40, 38};
int maxTemp = temps[0];
for (int temp : temps) {
if (temp > maxTemp) maxTemp = temp;
}
System.out.println("Hottest Day: " + maxTemp + "°C");
This logic ensures safety alerts or summaries in weather apps are data-driven and accurate.
Frequently Asked Questions
How to declare an array in Java?
In Java, you may declare an array in the following way:
dataType[] arrayVariableName = new dataType[arraySize];
You may declare an int array as follows for the int data type:
int[] temp = new int[20];
Can we resize the array in Java after creation?
We can't adjust the size of an array after it's been created. On the other hand, other data structures can alter in size after being created.
Can we pass a negative number as the size of the array?
No, a negative value cannot be used as an Array size. We won't get a compile-time error if we use a negative number for Array size. Instead, the NegativeArraySizeException will be thrown at runtime.
What's the distinction between an ArrayStoreException and an ArrayOutOfBoundsException?
If you try to add an incompatible data type, an ArrayStoreException is produced. For example, if you try to add an integer object to a String Array, you'll get an ArrayStoreException.
When an attempt is made to access an Array with an illegal index, an ArrayOutOfBoundsException is issued. For instance, an illegal index is either negative or bigger than or equal to the Array's size.
In Java, what is an Anonymous Array?
Anonymous Arrays are arrays that have no name (or reference). They're helpful in situations where we just need to use Array once. As an example,
Anonymous int array: new int[] {3, 4, 2, 8, 9};
Conclusion
This article has discussed the Java Program to find the largest element of a given array using the Sorting method, iterative and Recursive Methods.
We hope this article has helped you. You can also learn Object-Oriented Properties of Java, such as Abstraction in java, Inheritance in Java. You can also learn about the properties like association, aggregation, composition, and many more.
Recommended problems -








