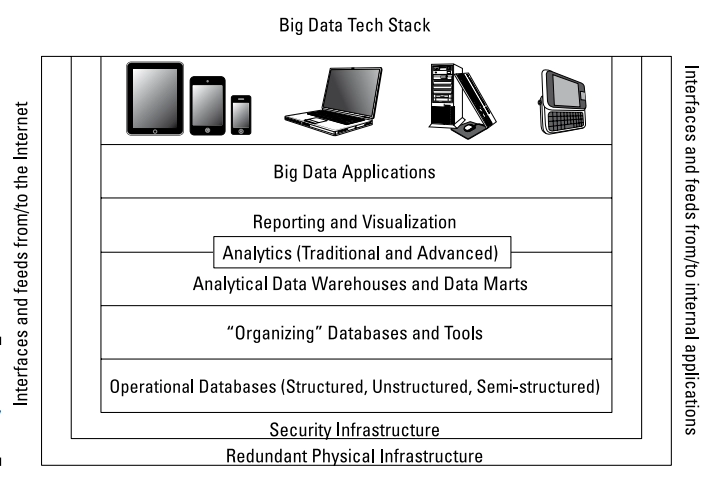
Layer 0: Redundant Physical Infrastructure
Physical Infrastructure, which comprises hardware, network, and so on is at the lowest level of the stack. Already present data centers and investments made earlier on physical infrastructure just cannot be ignored. There has to be a way to use those existing assets. Big Data implementations have very confined requirements which have to be studied on a layer-to-layer basis. This will ensure that the implementation will take as per the demands of the business.
Some prioritized requirements which judge the efficiency of Physical Infrastructure are-
- Responsiveness
- Availability of staff and service
- Availability of networks, servers, and storage
- Scalability in terms of disk space and computing power
- Flexibility to add resources and recover from failures
- Cost on the basis of necessities
Importance of Physical Infrastructure
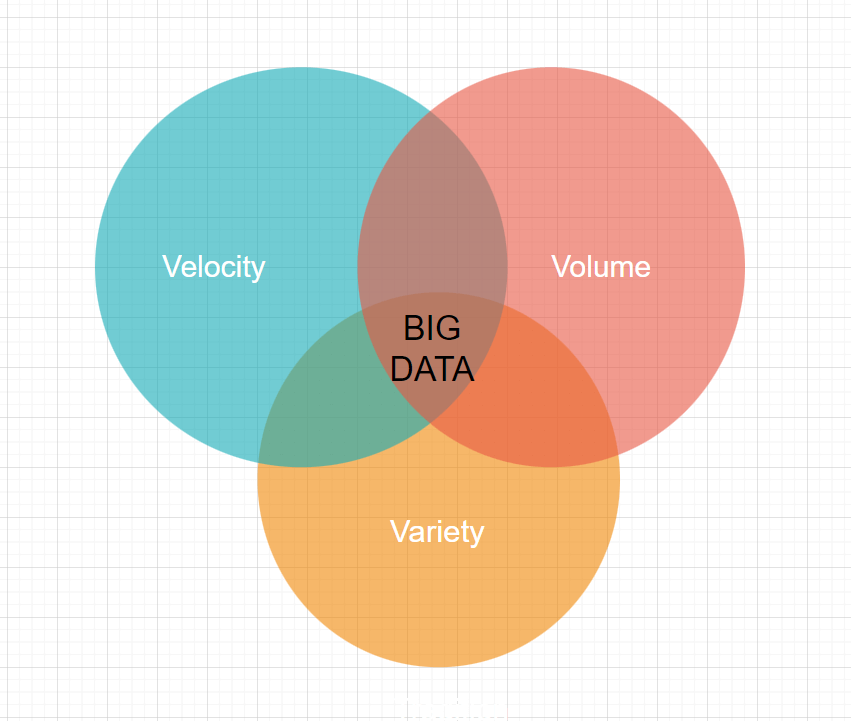
Big Data goes around 3V’s, that is, Velocity, Volume, and Variety. When these are the essential conditions, Physical Infrastructure can literally ‘make’ or ‘break’ the implementation. The more resilient infrastructure is, the more its resources are in place, ready to jump into action, which leads to less failure of hardware. Redundancy ensures that malfunction won’t cause an outage.
Resiliency and Redundancy are interrelated. Resiliency ensures single points of failure in the infrastructure are eliminated and this further reduces the risks. For example, large data centers that have business continuity requirements, have multiple network connections existing between their business and the Internet.
Design Considerations
Some important design considerations which are to be taken care of while designing physical infrastructure are mentioned below:
Physical Redundant Networks
Redundancy and capacity accommodation for expected volume and velocity are the most basic qualities a redundant network should possess. In addition to the normal network traffic, the capability to handle a Big Data environment is also necessary. This is because Velocity and Volume will surely increase as you make data an integral part of the computing business.
The responsibility to create flexible physical implementations that are prepared for expected increases is with the designer. The infrastructure should come with monitoring capabilities so that the changes in workload can be made when in need of more resources.
Hardware Management
Hardware devices are assets in any computer architectural environment which play a vital role in making a system. Storage devices and servers must have enough speed and capacity to handle all the problems which come in the way while dealing with Big Data. If any of these, storage devices or servers lack the capability, it is most likely to become a bottleneck. An efficient set of storage devices and servers, however, can help enhance the performance of the whole system.
Infrastructure Operations
Infrastructure Operations Management ensures the highest levels of performance. In a well-managed environment, strategies are flexible, and prediction of failures can be done and therefore, prevented. Maintaining the integrity and security of data is of the utmost importance. For Infrastructure to be decided, firstly, the type of data is analyzed and coordination of devices is maintained among all the devices.
FAQs
Where does Big Data come from?
Businesses collect data they want in several ways. These are Email tracking, Smart devices, Online purchases, Web interactions, Internet cookies, Search and Transaction histories, Social Media activities, etc.
How is Big Data being used for competitive advantage?
Big Data collected and analyzed boosts confidence while making decisions; ensures optimization of staff, assets, and energy; reduces cost; may generate new revenue sources, and results in better customer engagement.
What are the steps involved in the deployment of a Big Data solution?
The three steps involved in the solution of any Big Data problem are Data Ingestion, Data Storage, and Data processing.
What can be the disadvantages of Big Data?
There may be many disadvantages of Big Data. Some of them are storage can cost a lot; most of the data is unstructured; sometimes violate principles of privacy; may result in social stratification; is not useful in the short run etc.
Conclusion
Through this article, we gained insights on Big Data Stack and specifically about its first layer, that is, redundant physical infrastructure, in detail. If such a massive amount of data is analyzed for a longer duration, it will leverage wonder benefits.
We hope that this blog helped you enhance your knowledge regarding Redundant Physical Infrastructure and if you would like to learn more, check out our articles here. To know more about Big Data, Hadoop and Databases, check these out. Do upvote our blog to help other ninjas grow.
For peeps out there who want to learn more about Data Structures, Algorithms, Power programming, JavaScript, or any other upskilling, please refer to guided paths on Coding Ninjas Studio. Enroll in our courses, go for mock tests and solve problems available and interview puzzles. Also, you can put your attention towards interview stuff- interview experiences and an interview bundle for placement preparations. Do upvote our blog to help other ninjas grow.
Happy Coding!