
Introduction
In this article, we will deal with the concept of Line configuration in computer networks. We will start with understanding what line configuration means and knowing the types of line configuration with appropriate examples for more clarity.
Before starting, let me give you some quick prerequisites that will help you better understand and make the most out of this blog.
Prerequisites
- Network - A network comprises two or more devices connected via a communication link.
- Link - A link is a medium that can be wired or wireless that connects the devices in a network for communication. Examples of a wired medium can be cables/wires, while microwaves or radiowaves are some examples of wireless medium.
-
Nodes/Devices - Any device capable of receiving and sending data in a network is referred to as nodes/devices in the network.
Examples - laptops, computers, smartphones, etc.
Also read, Basic Networking Commands
Line Configuration
Line configuration refers to the method by which two or more devices are attached to a link and is also known as a connection.
But why do we need a line configuration?
This is because the devices can communicate with each other only when they are connected to the link simultaneously.
You can visualize the devices in the network as points and the link between two points as a line.
In the OSI reference model, the physical layer responsible for the transmission of bits over a medium takes care of the line configuration.
Let’s see the types of line configuration in the next section.
Also read, Basic Networking Commands
Types of Line Configuration
There are two types of line configuration -
- Point-to-Point line configuration/connection
- Multipoint line configuration/connection
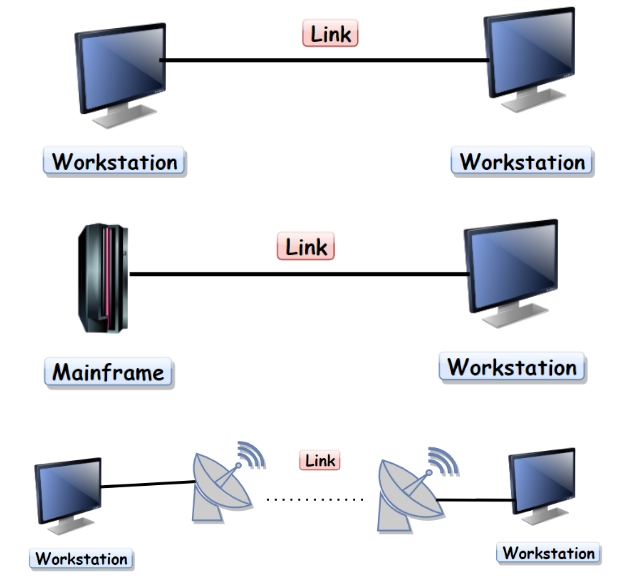
Point-to-Point connection
As the name suggests, a point-to-point connection provides a link between exactly two devices/nodes, which implies the link can only be used by the two devices connected to it, i.e. the sender and receiver and no other device can use it.
The important features of the point-to-point connection are as follows:
-
The entire capacity of the link is reserved for data transmission between the two nodes connected to it.
-
Like, if the capacity of a link is 10MBPS, which means 10 megabits of data can be transmitted through it per second, then only the two devices can utilize it, and no other device can claim this.
-
Mostly cables/wires are used to attach the two endpoints in point-to-point line configuration, but microwaves or radiowaves can also be used.
- It is one of the most basic and simplest configurations to implement.
Examples
-
One real-life example is controlling a T.V. through an infrared remote, which does nothing but establish a point-to-point connection between the T.V and remote.
- Another best example is a telephone call in which there is a point-to-point connection between 2 telephones.
A diagram showing the point-to-point line configuration will help us understand the concept more clearly.
Multipoint connection
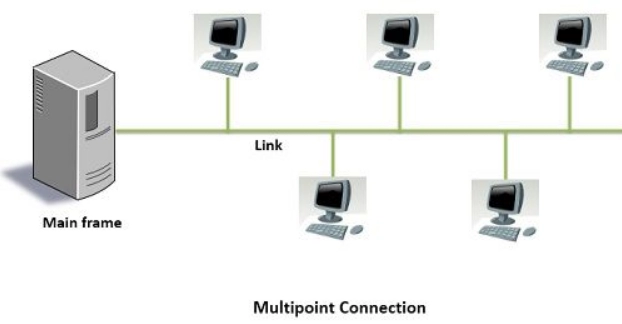
As you might have guessed, in a multipoint connection two or more devices can share a single link, i.e. there can be one sender and multiple receivers.
The important features are as follows:
-
It is also called a Multidrop connection.
-
More than two devices can share the entire capacity of the link.
There can be two ways of sharing capacity on the same link -
-
Spatial sharing - In spatial sharing, two or more devices can utilize the link capacity simultaneously.
-
Temporal sharing - In temporal sharing, the devices take turns using the link one by one; hence, they don't utilize the link simultaneously and the link is time-shared among them.
Advantages of Multipoint connection
Some of the advantages of the multipoint connection over the point-to-point connection are the ease of installation, reliability and low cost, as in multipoint connection, more than two devices can share the same link, unlike in point-to-point connection.





