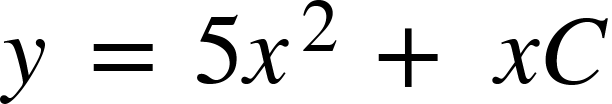Introduction
A linear differential equation is an equation with a variable, its derivative, and a few other functions.
Linear differential equations with constant coefficients are widely used in the study of electrical circuits, mechanical systems, transmission lines, beam loading, strut and column displacement, shaft whirling, and other topics.
Let’s learn about linear differential equations in-depth.
Linear Differential Equations Definition
The linear polynomial equation, which consists of derivatives of several variables, defines a linear differential equation. When the function is dependent on variables and the derivatives are partial, it is also known as Linear Partial Differential Equation.
The expression for a general first-order differential equation is:
 where y can be constant or function, and dy/dx is a derivative.
where y can be constant or function, and dy/dx is a derivative.
The value of variable y is determined by the solution of the linear differential equation.
A linear differential equation in y.

A linear differential equation in x.

A few examples of linear differential equations are:-
1.) dy/dx + 5y = cos(x)
2.) dx/dy + tan(x) = 10y
Non-Linear Differential Equations: A nonlinear differential equation is defined as the equation in which the unknown function and its derivatives are not linear.
We can use a formula to solve a linear differential equation, a common type of differential problem. Let's learn how to obtain the general solution of a linear differential equation using the formula and derivation.