Introduction
Linked List is a linear data structure that is used to store the data. It is a dynamic data structure and can also be considered a custom data type. Linked Lists are one of the easiest Data Structures to start with and have a wide range of applications across various fields.
There is a very famous and useful method for LinkedList add() method. This method is used to add the data to our LinkedList.
There are two ways to apply this method. Let us discuss each of them:-
Recommended Topic, Floyds Algorithm And Rabin Karp Algorithm
1) linkedList add(Object X)
Using the above method we can add the data at the end of the Linked List.
Syntax: boolean add(Object X)
We need to pass the data to this method which we need to add to our LinkedList. This method appends the data at the end of the LinkedList. The above method returns true if the element is appended to the LinkedList.
Refer to the below code for more understanding.
import java.util.*;
public class LinkedListDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
LinkedList<String> list = new LinkedList<>();
list.add("10");
list.add("20");
list.add("30");
list.add("40");
list.add("50");
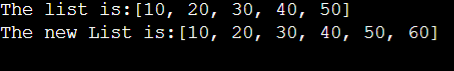
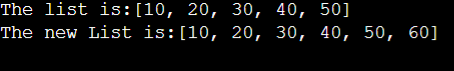
System.out.println("The list is:" + list);
list.add("60");
System.out.println("The new List is:" + list);
}
}
Output:
Time Complexity: The time complexity for the above functions is O(1).
Space Complexity: The space complexity for the above method is O(N) to maintain all the ‘N’ elements of the LinkedList.