
Introduction
Linked List is always on the mind of interviewers when it comes to coding interviews. Having a good grasp of the interviewer’s favorite topic surely gives us an upper hand. Instead of traditional problem-solving today, we will see an iterator that is provided by Java for linked lists, i.e., LinkedList descendingIterator.
But what is an iterator?
In simple words, an Iterator is an object that is used to loop through different collections, like ArrayList, HashSet, and Linked List.
Let’s now talk about the LinkedList descendingIterator.
DescendingIterator()
Like any other iterator, the descendingIterator() method returns an iterator to loop through the elements of the LinkedList, but the difference here is it returns the elements in reverse order. In other words, we can say the elements will be returned from tail to head, and the iterator would be pointing towards the tail of the linked list.
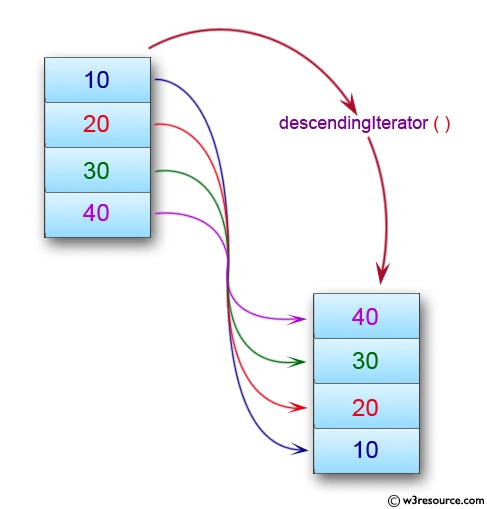
Here you can see the linked list originally was 10 -> 20 -> 30 -> 40, but descendingIterator is returning an iterator that is pointing towards 40, i.e., in reverse order.
We need to use ‘import java.util.Iterator’ in order to use the descendingIterator.
Now let’s look at some coding examples to understand its syntax and working.
Example 1
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class DescendingIterator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating a new Linked List.
LinkedList<String> TestList = new LinkedList<>();
// Adding elements to the list.
TestList.add("I");
TestList.add("Love");
TestList.add("Coding");
TestList.add("Ninjas");
// descendingIterator pointed to 'IT'.
Iterator<String> it = TestList.descendingIterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
System.out.print(it.next() + " ");
}
}
}Output
Ninjas Coding Love IExample 2
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class DescendingIterator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating a new Linked List.
LinkedList<Integer> TestList = new LinkedList<>();
// Adding elements to the list.
TestList.add(1);
TestList.add(2);
TestList.add(3);
TestList.add(4);
// descendingIterator pointed to 'IT'.
Iterator<String> it = TestList.descendingIterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
System.out.print(it.next() + " ");
}
}
}Output
4 3 2 1Time Complexity
O(N), where ‘N’ is the number of elements in the Linked List.
As it takes O(N) to reverse the list.
Space Complexity
O(1).
The iterator doesn’t take up any extra space.
Check out this problem - Reverse Nodes In K Group




