Introduction
A LinkedList is a dynamic-sized linear type of data structure that, unlike arrays, can expand and contract in size when new elements are added or deleted from it. Each element in a Linked List is known as a node which in most use cases (generally speaking) is composed of the following elements:
- A data element part (that contains the actual value of the element that you will likely want the list to be made up of)
- A Pointer of the same node type points to the next element in the list.
Implementation of LinkedList in Javascript
Linked List in Javascript: The following structure denotes a LinkedList in javascript after it is implemented:
Implementation
const list = {
head: {
data: 6
next: {
data: 10
next: {
data: 12
next: {
data: 3
next: null
}
}
}
}
}
};Implementing a node of linkedlist in Javascript
As the elements of linkedlist are all comprised of nodes with a data and link part therefore in javascript, It can depict this behaviour in the following manner:
class ListNode {
constructor(data) {
this.data = data
this.next = null
}
}Implementing a linkedlist in Javascript
As the elements of linkedlist are all comprised of nodes with a data and link part therefore in javascript, It can depict this behaviour in the following manner:
class LinkedList {
constructor(head = null) {
this.head = head
this.size = 0
}
}Abstract Functionality and Methods Implementation
A basic level of linkedlist implementation can be done by defining and implementing the functionalities of the following internal methods of a linkedlist:
// Functions that would be implemented
// addNode(data)
// insertNodeAt(data, index)
// removeNodeFrom(index)
// removeNode(data)
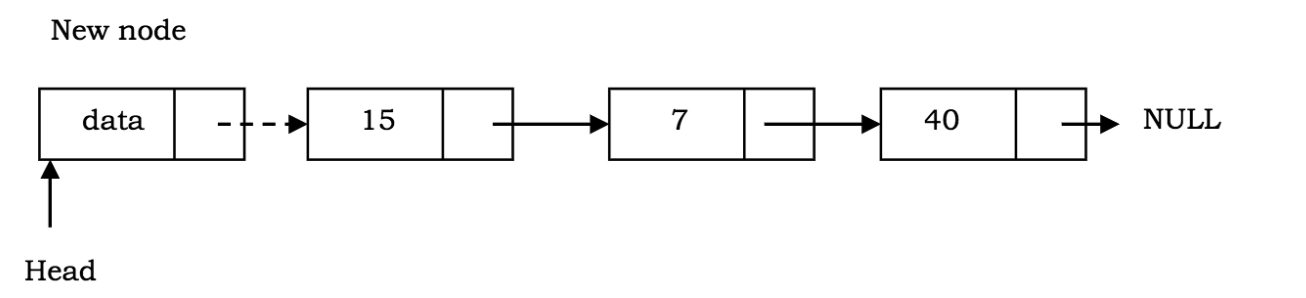
1. addNode: This method adds a new node at the end of a linkedlist in javascript.
// This method adds an element at the end of a linkedlist.
addNode(data)
{
// creates a new node
var node = new Node(data);
// to store current new node that will be added
var current;
// if list is Empty then we add the element and make it head
if (this.head == null)
this.head = node;
else {
current = this.head;
// iterate to the end of the list
while (current.next) {
current = current.next;
}
// add node
current.next = node;
}
this.size++;
}
2. insertNodeAt: This method inserts a new node at a specific index given for a linkedlist in javascript.
// This method inserts a new node at a specific index
insertNodeAt(data, index)
{
if (index < 0 || index > this.size)
return console.log("Please enter valid index.");
else {
// Adds a new node
var node = new Node(data);
var curr, prev;
curr = this.head;
// This adds a new element to the first index
if (index == 0) {
node.next = this.head;
this.head = node;
} else {
curr = this.head;
var it = 0;
// iterate over the list in order to find the position to insert data at
while (it < index) {
it++;
prev = curr;
curr = curr.next;
}
// adding an element
node.next = curr;
prev.next = node;
}
this.size++;
}
}
3. removeNodeFrom: This method removes a node a specified index in a linkedlist in javascript.
// This method removes a node a specified index in a linkedlist
removeNodeFrom(index)
{
if (index < 0 || index >= this.size)
return console.log("Please Enter a valid index");
else {
var curr, prev, it = 0;
curr = this.head;
prev = curr;
// deleting first element
if (index == = 0) {
this.head = curr.next;
} else {
// iterate over the list to the position to remove an element
while (it < index) {
it++;
prev = curr;
curr = curr.next;
}
// remove the element
prev.next = curr.next;
}
this.size--;
// return the remove element
return curr.data;
}
}
4. removeNode: This method removes a node from the linkedlist if it is present in the list; otherwise, it returns -1.
// This method removes a node from the linkedlist if it is present in the list; otherwise, it returns -1
removeNode(data)
{
var current = this.head;
var prev = null;
// iterate over the list
while (current != null) {
// comparing element with current
// element if found then remove the
// and return true
if (current.data == = data) {
if (prev == null) {
this.head = current.next;
} else {
prev.next = current.next;
}
this.size--;
return current.data;
}
prev = current;
current = current.next;
}
return -1;
}
Now, let’s use the LinkedList class and its different methods described above.
// creating an object of the Linkedlist class
var list = new LinkedList();
// adding element to the list
list.addNode(9);
// prints 9
list.printList();
// adding more elements to the list
list.addNode(6);
list.addNode(40);
list.addNode(20);
list.addNode(10);
// returns 9 6 40 20 10
list.printList();
// prints 50 from the list
console.log("is element removed ?" + list.removeNode(10));
// prints 9 6 40 20
list.printList();
// insert 60 at second position and contains 9 6 60 40 20
list.insertNodeAt(60, 2);
list.printList();
// remove 3rd element from the list
console.log(list.removeNodeFrom(3));
// prints 9 6 60 20
list.printList();
You can compile with the help of Online Javascript Compiler for better understanding.




