Introduction
This blog will discuss the necessary filters commands in Linux. There are several filtering commands available in Linux Kernel, but the one we will discuss in the blog is the one you will mostly use during the filtering process. Before we talk about the Linux fIlters commands, let's have a brief about Linux to have a better understanding.

Linux is an open-source kernel that Linus Torvalds developed. A kernel is a software whose role is to communicate between the application and hardware of a system. By open source, I mean its source code is publicly available, which you can contribute to if you have enough knowledge about Linux.
Linux is a highly customizable kernel with various distributions, like Debian, Ubuntu, Kali, and many more. In today's world, Linux is used in various devices around you; for example, Android devices are based on Linux.
Filter Commands

Filters commands in Linux are implemented to filter out some text or text in a file by providing the input as stdin ( standard input) and having the output as stdout ( standard output). Filtering can be of different types, which we will see with the help of Linux filter commands.
Before we see the examples of Linux filter commands, let's give you a quick suggestion about the man command in Linux. The man command in Linux is used when you want to know the working of a particular command in Linux that you are not familiar with.
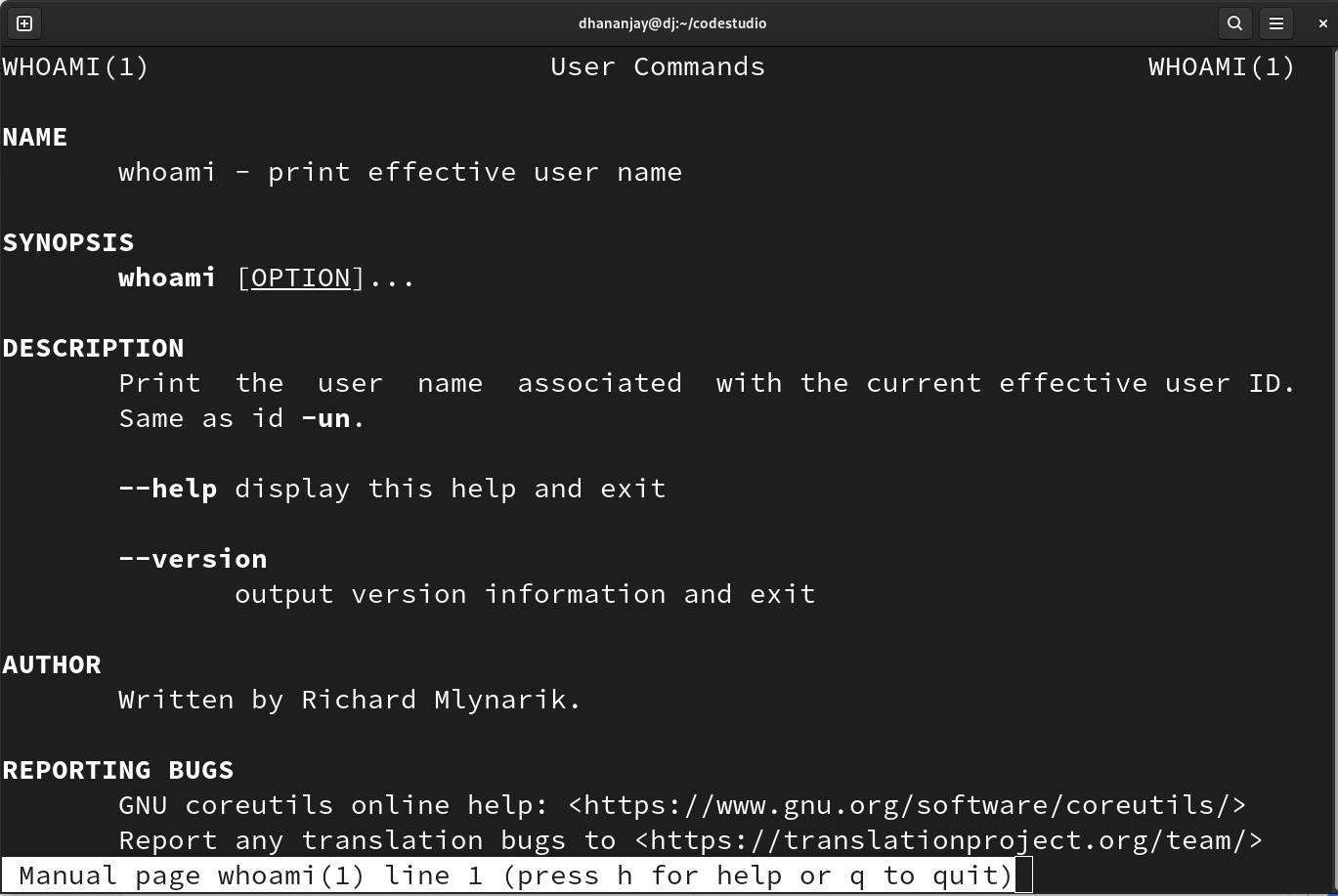
In the above images, we can see the description of the whoami command in Linux. The whoami command tells you about the name of the user profile on the system.
Now let's get back to the Linux filter commands.
cat
The cat command displays the content available in a file as the stdout on screen, shown below, and the tac command does the same but reverses the order of sentences in a file.
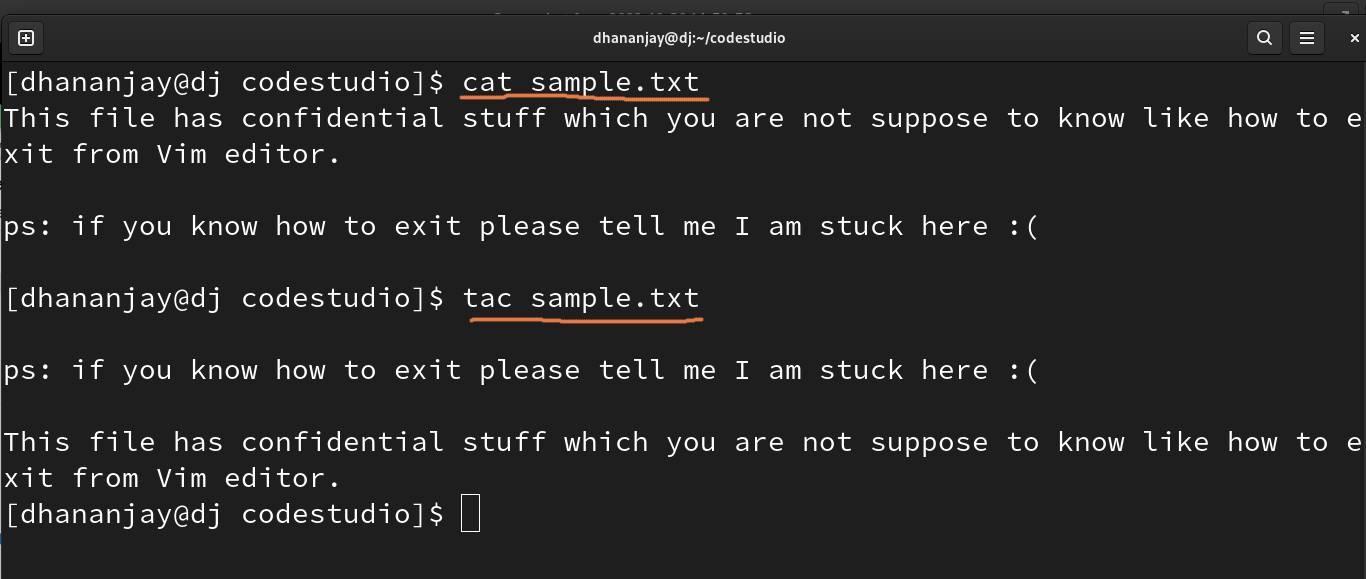
We can see the difference between both commands in the above image.
grep
The grep command in Linux tells you about a particular text in the sentence in a file. You need to type grep text_you_are_searching filename.txt in the terminal and enter to execute the command.
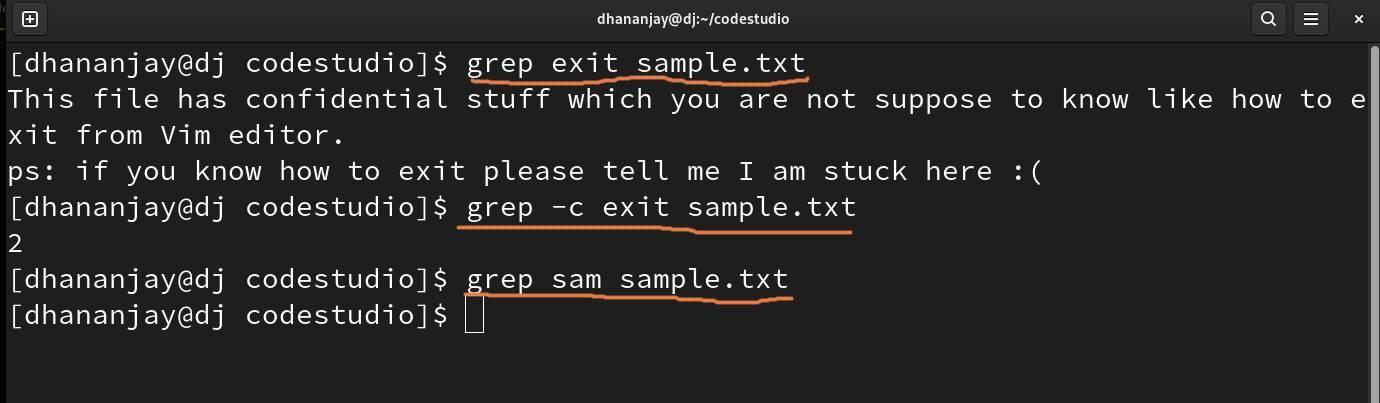
As you can see the result in the above image, we are searching for word exit in the file sample.txt, and we also have a -c flag in the second highlight to display the word count on the screen.
If you search for something not in the file, like sam, for example, you will get nothing as output.
head
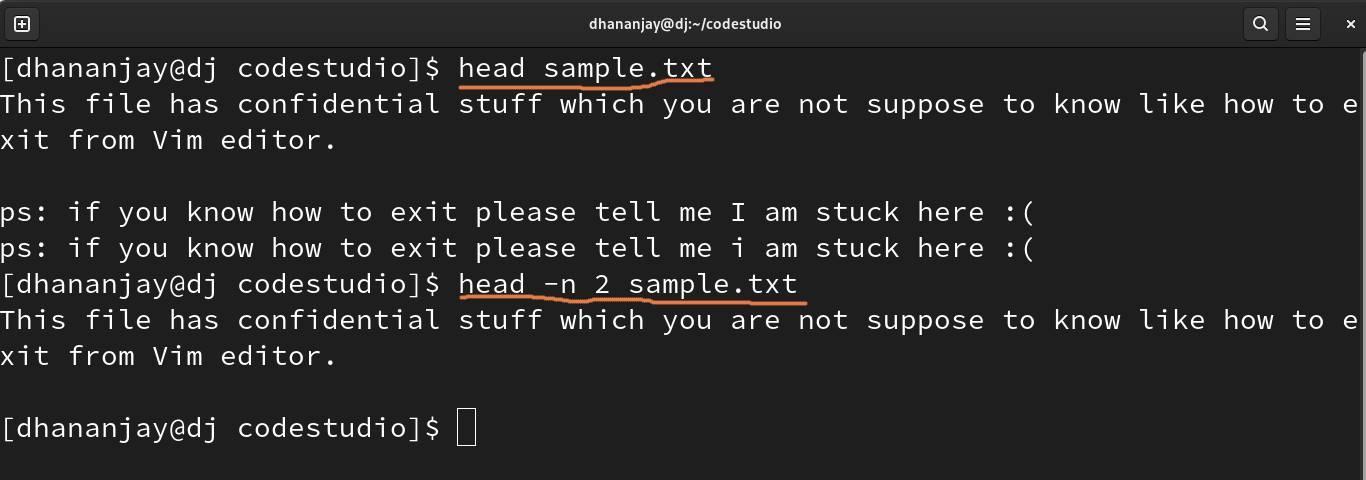
The head command in the Linux filter will display n number of lines as output. By default head command displays the first 10 lines from the file. To display some specific line, you need to add the -n flag and the total number of lines you want to display, like in the second highlight,
tail
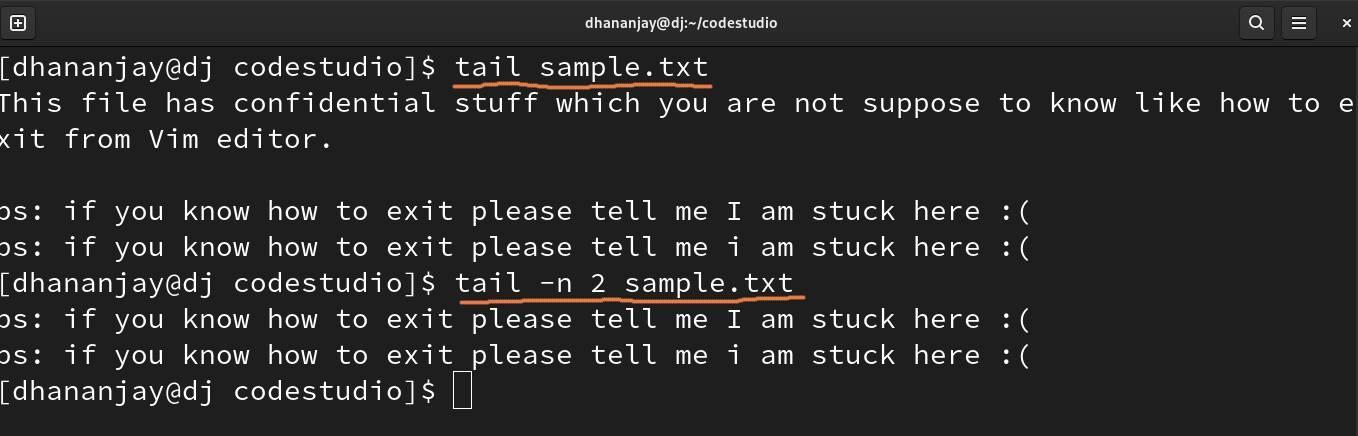
The tail command in the Linux filter does the same thing as the head command but displays the line in reverse order, meaning it starts from the end of the file to show the lines.
sort
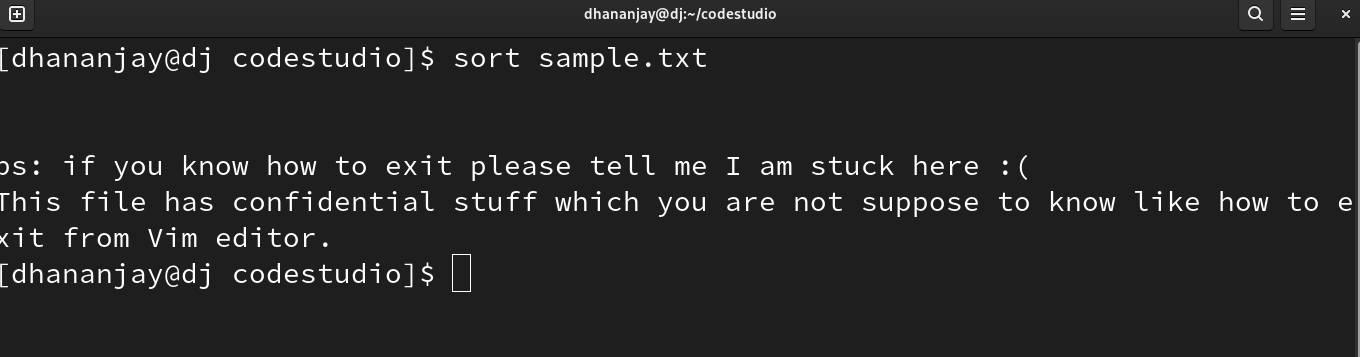
The sort command in Linux filter commands sorts the content in the file in alphabetical order and displays it on the screen.
wc
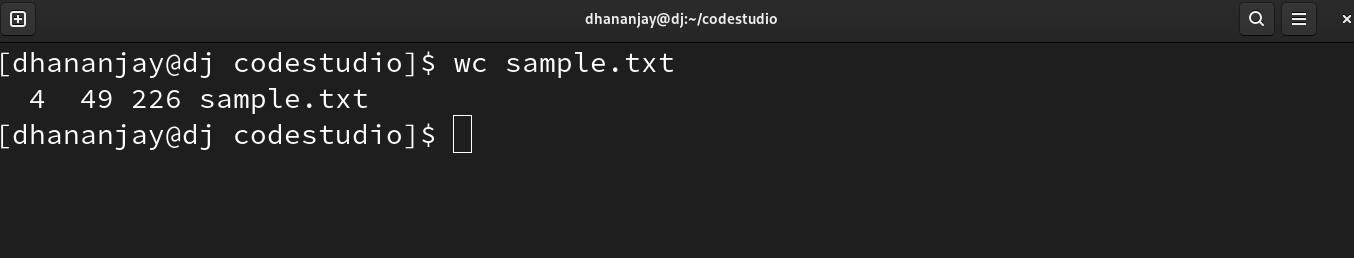
The wc command finds the total number of lines, words, and character count and displays it on the screen.
find
The find command helps you find a particular file or directory you are searching for in a particular folder or directory.

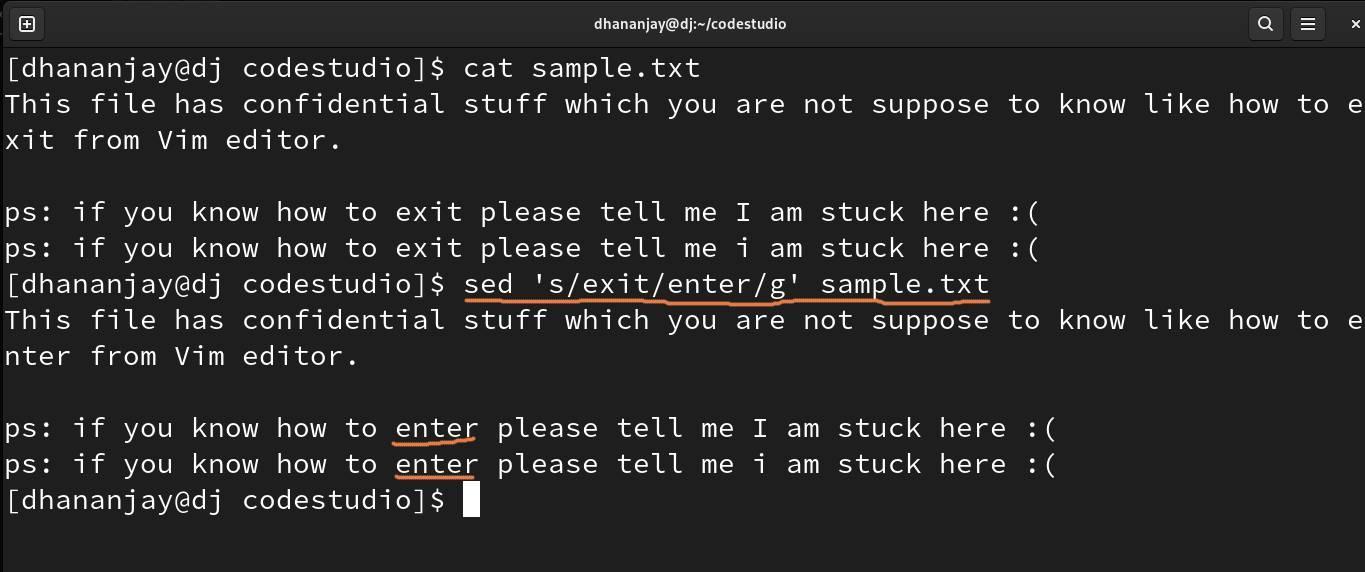
sed
With the help of the sed command, you can find and replace a particular text in the file. It is one of the advanced filters with various flags you can try.
uniq
With the uniq command, you can filter out the duplicate sentence in a file. Remember you can only filter out those duplicate sentences or words which are repeated one after the other like in the image below.
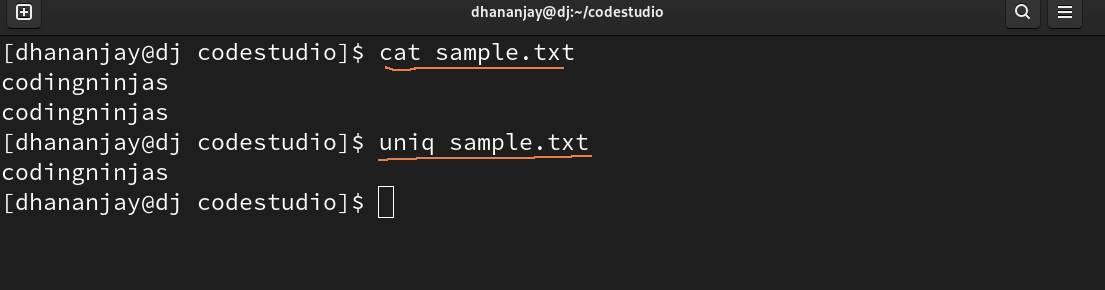
To use uniq command efficiently you can pipe it with the sort command like this : sort sample.txt | uniq.





