Altering Loops
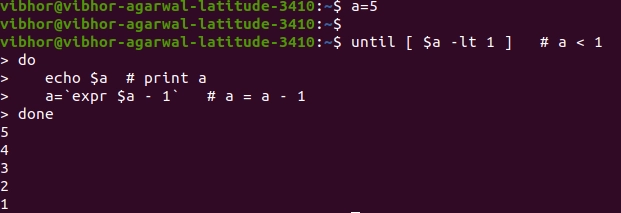
Infinite loops
Each shell loop has a set amount of time before it exits, depending on whether the condition is true or not.
A shell loop might go on indefinitely if the necessary condition is not satisfied. A loop that never stops running repeats itself an unlimited number of times. These loops are known as infinite loops for this reason.
temp=10
until [ $temp -lt 10 ]
do
echo $temp
temp=`expr $temp + 1`
done
Now, if we have to alter the infinite loops or if we want to break the loop after some particular condition, we will use keywords, i.e., break and continue.
Break
To end the loop, we use the break statement. All lines below the break are ignored while the line above break is executed. Next to the conclusion of the loop, execution begins on the following line.
Syntax
To exit a loop, use the break Statement shown below.
break
Code
for temp in 19 9 0 8 7 6 5 0 1 6 7
do
if [ $temp -eq 0 ] # a == 0
then
break
fi
echo $temp
Done
Output
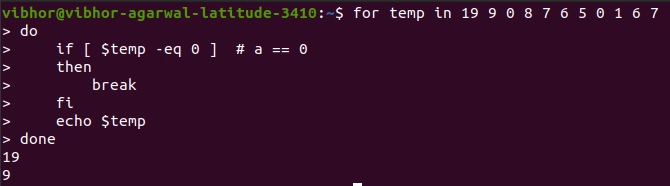
Explanation: As soon as we reach 0 in the given set, the break Statement will get executed, and the loop will come to an end, and before 0, we have 19 and 9, so it will get printed before breaking the loop.
Continue
While the break command causes the entire loop to quit, the continue statement only forces the current iteration of the loop.
The loop's iterations are ended using the continue statement. All lines below continue are ignored while the line above continues is executed. Execution then begins at the beginning of the loop's subsequent iteration.
Syntax
continue
Code
for temp in 19 9 0 8 7 6 5 0 1 6 7
do
if [ $temp -eq 0 ] # a == 0
then
continue
fi
echo $temp
Done
Output
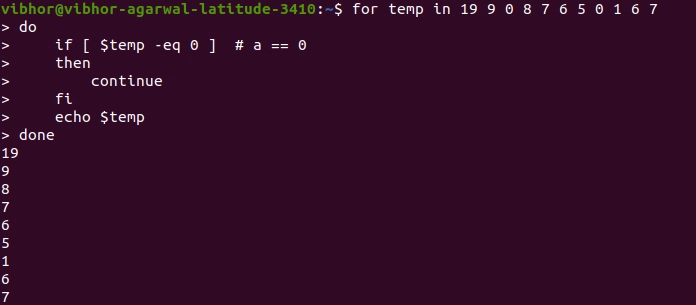
Explanation: Whenever we reach the 0, due to continuing, keyword 0 will not be printed; hence output does not contain any 0.
Frequently asked questions
What is shell scripting?
A set or sequence of UNIX commands written in a plain text file constitutes shell scripting. In shell scripting, we provide a list of UNIX commands, like a to-do list in a file to execute it rather than defining one job or command at a time.
What are loops?
Loops are when a section of the program or script is repeated either a predetermined number of times or until a specific condition is met.
What is the continue statement and how is it used for?
Continue is a keyword that is used to pass statements inside of the loop that hasn't yet been performed to return control to the beginning of the loop. Any loop in the program's code that encounters the keyword Continue sees control instantly transfer to the beginning of the loop. Continue is frequently connected to an if.
What is a break statement and how is it used for?
We use the keyword break when we want to exit a loop immediately without waiting to return to the control command. The first Statement after a loop will automatically take control of the program when the keyword break is used inside any loop. An if is typically connected to a break.
What do you mean by shell script?
As the name implies, a shell script is one created just for the shell. The script in this context refers to a computer language used to run programs. Simply put, it enables the execution of various commands entered into the shell. It generally aids in the development of intricate programs with conditional statements, loops, and functions. In comparison to building large programs, it is significantly faster and much easier to debug, and it can streamline routine automation procedures.
Conclusion
This blog discusses the blog about Linux-shell control, then we discuss how to declare loops in Linux, and then study the Linux loop control.
For Related Blogs, please refer to:
- Types of Unix Operating Systems
- Introduction to Linux Shell and Shell Scripting
-
Ubuntu Operating System
Refer to our guided paths on Coding Ninjas Studio to learn more about DSA, Competitive Programming, JavaScript, System Design, etc. Enrol in our courses and refer to the mock test and problems available; look at the Top 150 Interview Puzzles, interview experiences, and interview bundle for placement preparations. Read our blogs on aptitude, competitive programming, interview questions, IT certifications, and data structures and algorithms for the best preparation.