Commands to manage Group
Multiple commands like usermod, groupadd, and groupmod can be used to manage groups of Linux. Let’s discuss each of these commands with examples.
groupadd
We can use this command to create a new Group in Linux. The syntax is as follows: groupadd <group name>.
Example:
groupadd coding_ninjas
🔸The above command will create a new group in Linux with the name coding_ninjas.
usermod
The useradd or usermod command can be used to change a group's membership. If the group is not provided in the command, the usermod command will by default remove the user from all groups that he is a part of. This behavior is avoided when the -a (append) flag is used.
Example:
usermod -a -G coding_ninjas ninja
🔸The above command will add user ‘ninja’ to the group ‘coding_ninjas’.
groupmod
An existing group's name can be changed with the help of the groupmod command. The syntax is as follows: groupmod -n <newGroup> <oldGroup>.
Example:
groupmod -n Coding Ninjas Studio coding_ninjas
🔸The above command will change the name of group coding_ninjas to Coding Ninjas Studio.
groupdel
This command can be used to delete the group from the system. The syntax is as follows: groupdel <group name>.
Example:
groupdel Coding Ninjas Studio
🔸The above command will permanently delete the group Coding Ninjas Studio from the system.
groups
Using the groups command, we may find out which groups the current user is a member of.
Example:
groups
Output:
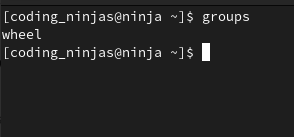
The current user is only part of the ‘wheel’ group, which is why only wheel is printed as the output of the above command.
Frequently asked questions
What is the exit code in Linux?
In Linux, an exit code indicates how a command or script performed. It ranges from 0 to 255. We can tell whether a process ran successfully or not by looking at the exit codes.
Name the two types of Linux User Mode?
Command Line and GUI are the two types of Linux user modes.
What is the maximum length for a filename under Linux?
Under Linux, a filename can only be 255 bytes long.
Conclusion
In this blog, we have discussed what groups are in Linux and how we can create, manage, or add users to groups using commands.
If you think this blog has helped you enhance your knowledge about the above question, and if you want to learn more, check out our articles.
🔥 Linux - Decision Making
🔥 Linux File System
🔥 Linux- Shell Loops
🔥 Linux Security
And many more on our Coding Ninjas Studio.
Visit our website to read more such blogs. Make sure that you enroll in the courses we provide, take mock tests, solve problems available, and interview puzzles. Also, you can pay attention to interview stuff- interview experiences and an interview bundle for placement preparations.
Please upvote our blog to help other ninjas grow.
Happy Learning!