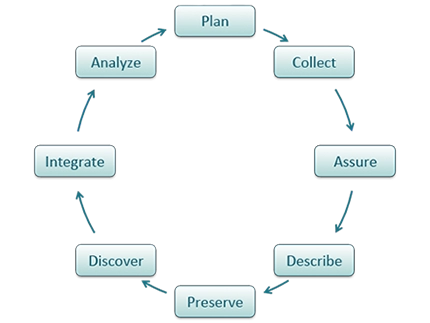
Introduction
In this article, we will learn about the fundamentals of Big Data and how to manage big data. The main aim of the fundamentals of big data is to find applicable information through transforming, inspecting, and modeling. Big data organization, management, and large-scale management of both formal and informal data helps to ensure a high level of Business Intelligence data.
Fundamental of big data
It will become difficult to manage all the customers' data with small data, but it will become very easy for them to manage the data when the big data is introduced. Handling the data at a large scale became easy for the organizations when the concept of big data occurred.
In today's scenario, the challenge is how companies can make sense of the intersection of all different types of data when dealing with so much information. For example, if a company is selling the goods and all the customers are buying the same goods, it is easy to manage. But when the demand for the goods increases and companies start selling more goods, there are many opportunities for the customers to select any good.
Let us look at some challenges faced in the management of Big data.
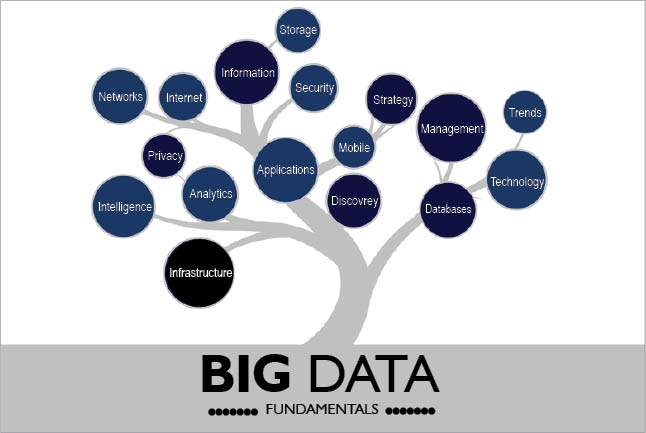
Challenges Faced in Management of Big Data
1. Lack of proper understanding of Big Data
Companies fail in their Big Data systems due to insufficient understanding. Employees may not know what data is, its storage, processing, value, and resources. Data experts may know what's going on, but some may not have a clear picture. For example, if employees do not understand the importance of data storage, they may not keep backup sensitive data. They may not use the database properly to store it. As a result, when this important data is needed, it cannot be easily retrieved.
2. Data growth problems
One of the biggest pressures of Big Data is keeping all of these big data sets in order. The amount of data stored on data centers and corporate websites is growing rapidly. As these data sets grow larger over time, it becomes more difficult to manage.
Most of the data is not created and appears in documents, videos, audio, text files, and other sources. This means you can't find them on the website.
3. Confusion when choosing a Big Data tool
Companies often get confused while choosing the best tool for big data analysis and storage. Is HBase or Cassandra the best data storage technology? Is Hadoop MapReduce good enough or will Spark be the best option for data analysis and storage?
These questions bother companies and sometimes they can't find the answers. They end up making the right decisions and choosing the wrong technology. As a result, money, time, effort, and hours of work are wasted.
4. Lack of data professionals
In order to use these modern technologies and Big Data tools, companies need competent data professionals. These experts will include data scientists, data analysts, and data engineers who are experienced in working with tools and making sense of large data sets. Companies are facing a shortage of Big Data professionals. This is because data management tools have changed rapidly, but in most cases, professionals have not changed. Steps need to be taken to close this gap.
Understanding the waves of Managing Data
When the new technology comes into effect in the market, it requires the discoveries of new approaches with a set of tools to allow the company/market to study the relationship between the data elements. In that case, you have access to the large scale of data that needs monitoring, so to prevent them from any damage, new inventions become a must to prevent the data from hacking. Every data management wave was born to tackle a specific type of data management problem.
The evolution of data management over the last five decades has led us to comprehend big data. To do so, you must first understand the foundations of earlier waves. You should also be aware of the fact that as we move from one wave to the next wave, we do not discard the tools, technology, or processes that we have been employing to address a different set of issues.
Wave 1: Creating manageable data structures
Wave 2: Web and content management
Wave 3: Managing Big Data
In this blog, we will be discussing Wave 3: Managing Big Data in detail.