
Introduction
You are given a two-dimensional matrix, and your task is to print the matrix in a waveform manner.
Sample Test Case
Input: matrix[][] = {{ 1, 6, 11, 16}
{ 2, 7, 12, 17}
{ 3, 8, 13, 18}
{ 4, 9, 14, 19}
{ 5, 10, 15, 20}}
Output : 1 2 3 4 5 10 9 8 7 6 11 12 13 14 15 20 19 18 17 16Approach
Our task is to print the matrix in a waveform manner. In order to get the desired output, we need to print the elements of a column of the matrix in the downward direction or in the upward direction, depending on the column index. In order to get the desired output, we can use a flag that is initially the flag is set to true:
- If the flag is true, we start traversing the current column from top to bottom, and once we have traversed the column, we invert the flag.
- If the flag is false, we start traversing the current column from bottom to top, and once we have traversed the column, we invert the flag.
If we look closely, it can be observed that all the columns having the even index are printed in the downward direction that is from top to bottom, whereas all the columns having the odd index are printed in the upward direction that is from bottom to top.
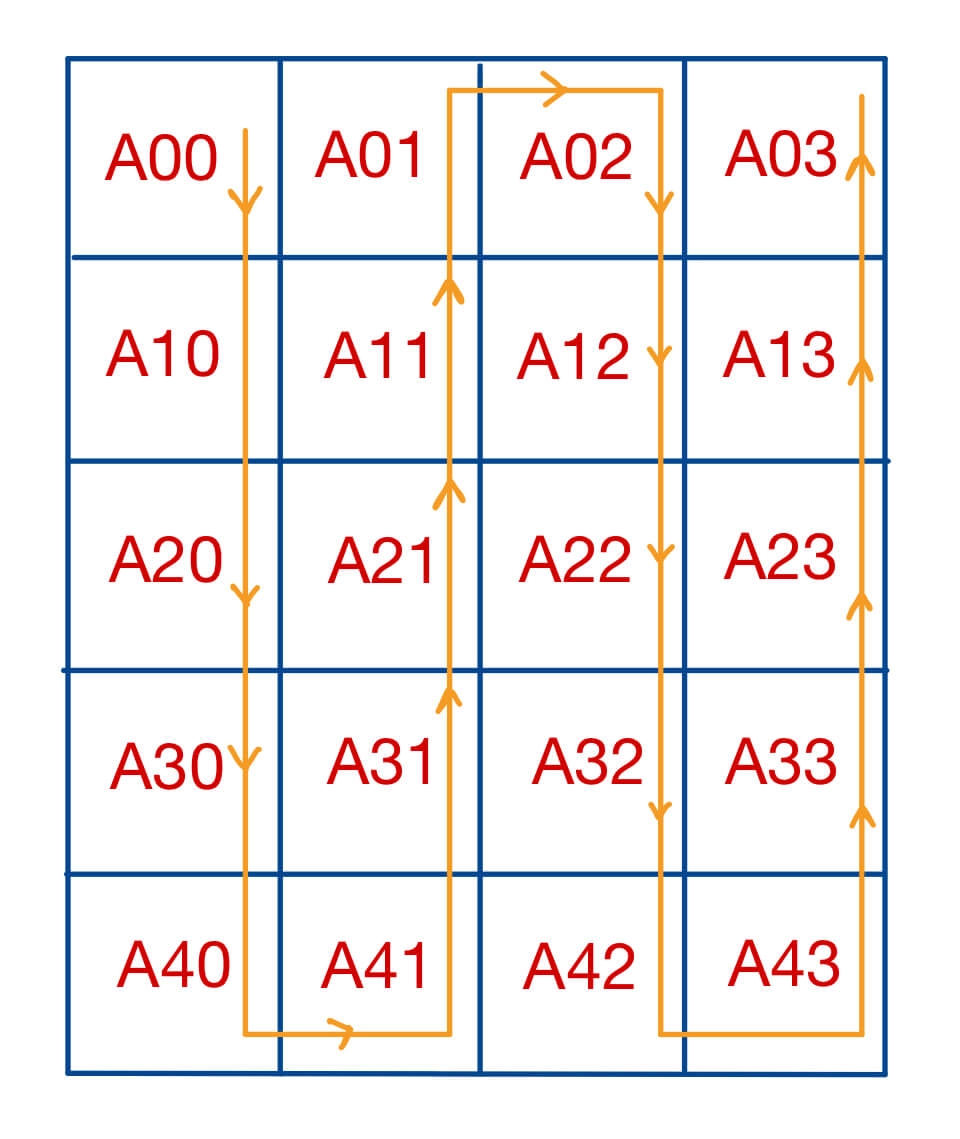
Below is the C implementation of the above approach
Code in C
#include <stdio.h>
#define R 5
#define C 4
void printWaveForm(int m, int n, int matrix[R][C])
{
// select the column
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
// PRINT
// even index column, top-bottom
if (j % 2 == 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
printf("%d ", matrix[i][j]);
}
}
// odd index column, bottom-top
else {
for (int i = m - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
printf("%d ", matrix[i][j]);
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int matrix[R][C] ={{ 1, 6, 11, 16},
{ 2, 7, 12, 17},
{ 3, 8, 13, 18},
{ 4, 9, 14, 19},
{ 5, 10, 15, 20}};
printf("Wave form of array : ");
printWaveForm(R, C, matrix);
}
Output
Wave form of array : 1 2 3 4 5 10 9 8 7 6 11 12 13 14 15 20 19 18 17 16
Below is the C++ implementation of the above approach
Code in C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define R 5
#define C 4
void printWaveForm(int m, int n, int matrix[R][C])
{
// select the column
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
// PRINT
// even index column, top-bottom
if (j % 2 == 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
cout<<matrix[i][j]<<" ";
}
}
// odd index column, bottom-top
else {
for (int i = m - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
cout<<matrix[i][j]<<" ";
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int matrix[R][C] ={{ 1, 6, 11, 16},
{ 2, 7, 12, 17},
{ 3, 8, 13, 18},
{ 4, 9, 14, 19},
{ 5, 10, 15, 20}};
cout<<"Wave form of array : ";
printWaveForm(R, C, matrix);
}
Output
Wave form of array : 1 2 3 4 5 10 9 8 7 6 11 12 13 14 15 20 19 18 17 16
Below is the Java implementation of the above approach
Code in Java
import java.io.*;
class Main {
public static int R = 5;
public static int C = 4;
public static void printWaveForm(int m, int n, int[][] matrix)
{
// select the column
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
// PRINT
// even index column, top-bottom
if (j % 2 == 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
System.out.print(matrix[i][j] + " ");
}
}
// odd index column, bottom-top
else {
for (int i = m - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
System.out.print(matrix[i][j] + " ");
}
}
}
}
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int[][] matrix ={{ 1, 6, 11, 16},
{ 2, 7, 12, 17},
{ 3, 8, 13, 18},
{ 4, 9, 14, 19},
{ 5, 10, 15, 20}};
System.out.print("Wave form of array : ");
printWaveForm(R, C, matrix);
}
}
Output
Wave form of array : 1 2 3 4 5 10 9 8 7 6 11 12 13 14 15 20 19 18 17 16
Below is the python implementation of the above approach
Code in Python
# define rows and columns
R = 5
C = 4
def printWaveForm(m, n, matrix):
# select the column
for j in range(n):
#even index column, top-bottom
if (j % 2 == 0):
for i in range(m):
print(matrix[i][j], end= " ")
# odd index column, bottom-top
else:
for i in range(m - 1, -1, -1):
print(matrix[i][j], end= " ")
# Driver Code
matrix = [[1, 6, 11, 16], [2, 7, 12, 17], [3, 8, 13, 18], [4, 9, 14, 19], [5, 10, 15, 20]]
print("Wave form of array :",end=" ")
printWaveForm(R, C, matrix)
Output
Wave form of array : 1 2 3 4 5 10 9 8 7 6 11 12 13 14 15 20 19 18 17 16
Time Complexity: O(N2), where N=max(r,c)
We run two nested loops, one for selecting a column(outer loop) and one for selecting a row (inner loop). For every iteration of outer loop the inner loop runs N times.
Space Complexity: O(1)
No extra space is used.
Check out this problem - Check If A String Is Palindrome






