Introduction
Trees are popular Data Structures having a Wide Range of Applications. These are also among the popular topics that are asked about in interviews with top technology companies. There are numerous problems that involve the usage of Tree Data Structure and the operations that can be performed on trees.
This blog will discuss the "Maximum Level Sum in N-ary Tree" problem. In this problem, we will have an N-ary tree with 'N' vertices numbered from 0 to N, each vertex will have a value associated with it, and we have to find the maximum level order sum for this given tree. The level order sum refers to the sum of the values associated with all the vertices in that level of the tree.
Let's take an example to understand the problem:
Assume we have been given a tree with eight vertices numbered from 0 to 7 and an array 'val[8]', which denotes that vertex 'i' has a value 'val[i]' associated with it.
Here val[8] = {1, 8, 9, 7, 2, 3, 4, 6}
The tree is shown below:
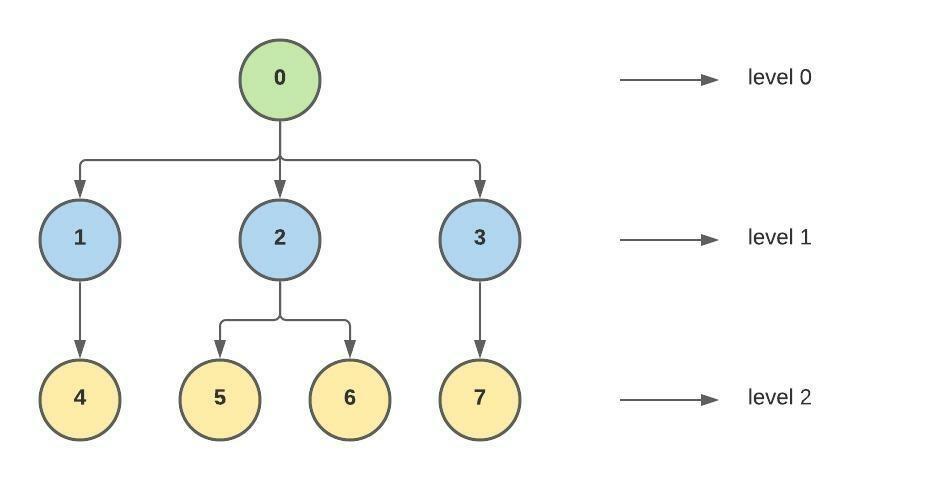
In this tree:
Sum for level 0 = val[0] = 1
Sum for level 1 = val[1] + val[2] + val[3] = 8 + 9 + 7 = 24
Sum for level 2 = val[4] + val[5] + val[6] + val[7] = 2 + 3 + 4 + 6 = 15
So, the maximum level order sum will be 24, which is the level order sum for level 1.
Now that we understand the problem of finding the maximum level order sum in N-ary tree let's discuss the approach.
Solution Approach
The approach to find the maximum level order traversal in N-ary tree is based on the level order traversal of a tree. We will do the level order traversal of the given N-ary tree, calculate the level sum for each level and keep track of the maximum level sum. And, finally, after traversing all the levels, we will return the maximum level sum.
Algorithm
Step 1. Create a function "maximumLevelSum()' to find the maximum level sum in N-ary tree, which takes the following three inputs:
- N - Total number of nodes
- tree - A 2-D array representing the edges of the tree
- Val - A vector containing the values associated with each node in the tree
Step 2. Create the adjacency list representation of the tree using the array 'tree', which has stored all the edges of the tree
Step 3. Initialize a variable "maxLevelSum" with the level sum of level 0. Now create a queue to store nodes while traversing the tree in level order.
Step 4. Perform level order traversal of the tree, store the sum for each level, and keep updating the variable "maxLevelSum" after traversing each level.
Step 5. Finally, after traversing the complete tree, return "maxLevelSum".
C++ code
// C++ program to find maximum level sum in N-ary tree
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to find the maximum level sum in N-ary tree
int maximumLevelSum(int N, int tree[][2], vector<int> val)
{
// Creating the adjacency list representation for the tree
vector<int> adj[N];
for (int i = 0; i < (N - 1); i++)
{
adj[tree[i][0]].push_back(tree[i][1]);
}
// Initialize the maximum level sum as the val[0] which is the level sum for level 0
int maxLevelSum = val[0];
// Creating a queue to store the nodes of each level for performing the level order traversal
queue<int> q;
// Inserting the root node into the queue
q.push(0);
// level order traversal
while (!q.empty())
{
// Variable to store the number of nodes in the current level
int curr_count = q.size();
// Variable to store the sum of current level
int curr_sum = 0;
// Traverse the current level
while (curr_count--)
{
// Get the current node from the queue
int curr_node = q.front();
q.pop();
// Update sum of current level
curr_sum = curr_sum + val[curr_node];
// Inserting the children of current node into the queue
for (int i = 0; i < adj[curr_node].size(); i++)
{
q.push(adj[curr_node][i]);
}
}
// Update maximum level sum
maxLevelSum = max(maxLevelSum, curr_sum);
}
// Return the maximum level order sum
return maxLevelSum;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Variable to store the number of nodes in the given tree
int N = 8;
// 2-D array to store the edges of the N-ary tree
int tree[][2] = { { 0, 1 }, { 0, 2 }, { 0, 3 }, { 1, 4 }, { 1, 5 }, { 3, 6 }, { 6, 7 }, { 6, 8 }, { 6, 9 } };
// Vector to store the values associated with each of the vertices
vector<int> val = {1, 8, 9, 7, 2, 3, 4, 6};
// Call the function to find the maximum level sum in N-ary tree
cout << "The maximum level sum in N-ary tree given here is: " << maximumLevelSum(N, tree, val);
return 0;
}
Output:
The maximum level sum in N-ary tree given here is: 24Algorithm Complexity
Time Complexity: O(N)
In the function "maximumLevelSum()' to find the maximum level sum in the N-ary tree, we have traversed each node of the tree. So, the time complexity is O(N), where 'N' is the number of nodes in the tree.
Space Complexity: O(1)
In the function "maximumLevelSum()' to find the maximum level sum in the N-ary tree, we have created a queue to store the tree's nodes. So the space complexity is O(N), where 'N' is the number of nodes in the tree.
Check out this problem - Diameter Of Binary Tree




