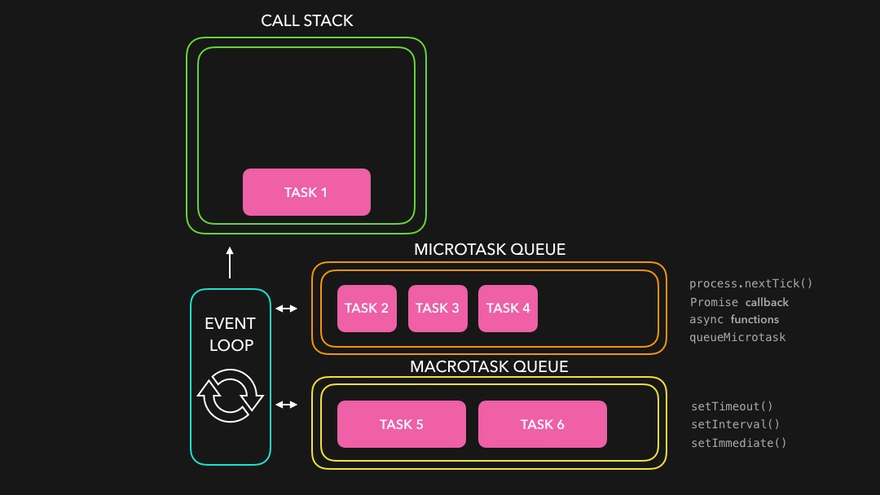
Microtasks
In the above section, we have learned about the event loop in JavaScript. Now, let’s learn about Microtask.
A microtask is a tiny function that is run after the function or programme that produced it has exited and only if the JavaScript execution stack is empty, but before the user agent returns control to the event loop that controls the script's execution environment.
This event loop could be the browser's main event loop or the event loop that controls a web worker. This allows the specified function to run without the risk of interfering with the execution of another script, while also ensuring that the microtask runs before the user agent has a chance to react to the microtask's actions.
Examples: process.nextTick, Promises, queueMicrotask, MutationObserver
Implementation
Before any other event handling, rendering, or “macrotask” occurs, all microtasks are performed. This is significant because it ensures that the application environment remains essentially the same (no changes in mouse coordinates, no new network data, etc.) between microtasks.
We can use "queueMicrotask" to plan a function to run asynchronously (after the current code) but before updates are rendered or new events are handled.
Here's an example with a "counting progress bar" that's similar to the previous one, but instead of "setTimeout," queueMicrotask is used. It renders at the very end, as you can see. Similarly to the synchronous code:
<!-- JavaScript queueMicrotask() function -->
<div id="progress"></div>
<script>
//Queue a microtask to update the progress bar
function function1() {
var progress = document.getElementById("progress");
//Update the progress bar
var i = 0;
var interval = setInterval(function() {
progress.innerHTML = i;
i++;
if (i > 100) {
clearInterval(interval);
}
}, 100);
}
window.queueMicrotask(function1());
//queueMicrotask() is a function that runs after the current task
</script>
Output

The output is taken after the count reaches 100.
You can practice by yourself with the help of Online Javascript Compiler for better understanding.
Macrotasks
A macrotask is a tiny function that runs after the JavaScript execution stack and microtask have both been cleared.
A macro-task represents a separate and independent piece of task. The JavaScript code is always executed here in macrotask queue, and the microtask queue is always empty. The macrotask queue is frequently confused with the task queue or the event queue. The macrotask queue, on the other hand, works in the same way as the task queue. The task queue is used for synchronous statements, whereas the macrotask queue is utilised for asynchronous statements.
In a single macrotask execution cycle, all logged microtasks are processed in one fell swoop. The macrotask queue, on the other hand, has a lower priority. Parsing HTML, producing DOM, executing main thread JavaScript code, and other events like page loading, input, network events, timer events, and so on are all macrotasks.
Example: setTimeout, setImmediate, requestAnimationFrame, setInterval, requestAnimationFrame, etc
Implementation
We will implement the setTimeout() macrotask function to see, how the macrotask works.
<!-- JavaScript setTimeout function macrotask -->
<script>
(function() {
// Start of Async Call
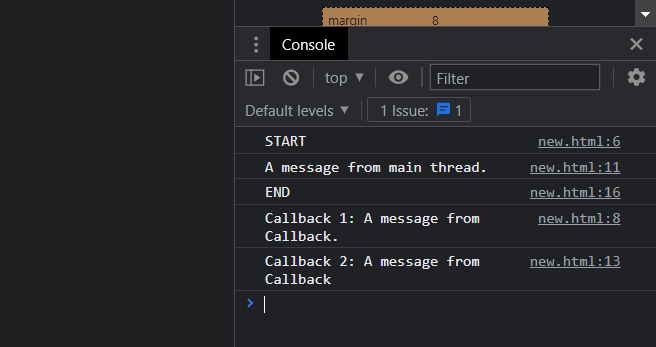
console.log('START');
setTimeout(function cb() {
console.log('Callback 1: A message from Callback.');
});
// setTimeout()
console.log('A message from main thread.');
setTimeout(function cb1() {
console.log('Callback 2: A message from Callback');
}, 0);
// print end to the console
console.log('END');
})();
</script>
The callback will not start after zero milliseconds if the delay is zero. When setTimeout is called with a delay of 0 (zero) milliseconds, the callback function is not executed after the specified interval. In the above example we have demonstrated the setTimeout() function.
Output
In the above example, the alert “Hello” is displayed after a 3000 milliseconds delay.
Recommended Topic: Fibonacci Series in Java and Fibonacci Series in JavaScript
FAQs
In JavaScript, what is the difference between microtasks and tasks?
A macro task is a collection of distinct and independent tasks. Microtasks are minor tasks that update the state of an application and should be completed before the browser moves on to other activities, such as re-rendering the user interface. Promise callbacks and DOM modification changes are examples of microtasks.
What is the difference between a task queue and a call stack?
It's up to it to check whether the callstack is empty and whether the task queue has any pending tasks to complete. If the callstack is empty, it will push the job from the queue to the callstack, where it will be processed.
Is a call stack similar to a queue?
This type of stack is often referred to as an execution stack, control stack, run-time stack, or machine stack, and is frequently abbreviated as "the stack." In summary, a job queue is a list of tasks to be completed (typically maintained persistently), while a call stack is a collection of functions.
What happens when the maximum call stack size is reached?
When there are too many function calls or a function lacks a base case, the JavaScript exception "too much recursion" or "Maximum call stack size exceeded" occurs.
Conclusion
In this article, we have covered “microtasks” and “macrotasks” in the event loop. To sum up the whole process of the event loop, we check the following:
Recommended Reading:
Difference Between Analog and Digital Computer
- ONLY when the stack is empty, check what's going on in the queues above and execute everything from the bottom to the top of the stack.
- Check the micro stack and, if necessary, execute everything there with the help of the stack, one micro-task at a time, until the microtask queue is empty or no longer requires execution, and ONLY THEN check the macro stack.
- Check the macro stack and, if necessary, execute everything there using the stack.
We hope that this blog has helped you enhance your knowledge regarding microtasks and “macrotasks” in the JavaScript event loop and if you would like to learn more, check out our articles on Javascript BOM, Eventloop in JavaScript, JavaScript DOM, Function Execution in JavaScript, Modules in JavaScript, Screen Object in JavaScript. Do upvote our blog to help other ninjas grow.
Head over to our practice platform Coding Ninjas Studio to practice top problems, attempt mock tests, read interview experiences, interview bundle, follow guided paths for placement preparations and much more.!
Happy Reading!