
Introduction
This blog will mainly discuss the various possible types of multiplexing and what are the advantages of multiplexing. Let’s start this by discussing what multiplexing is,
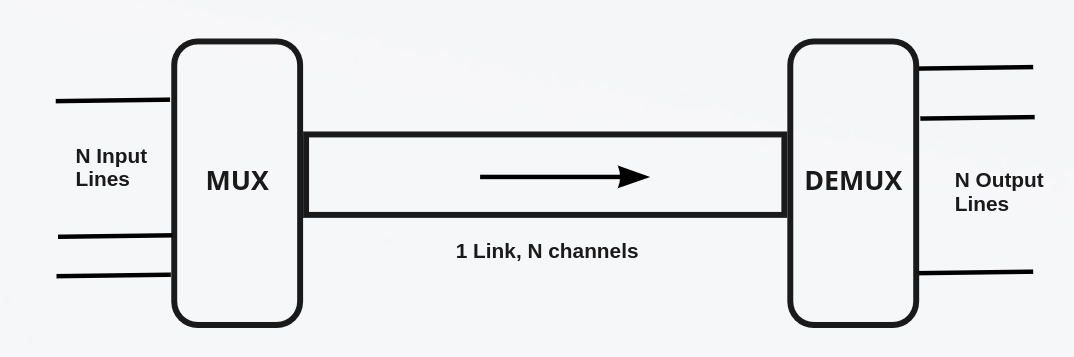
- Multiplexing is the group of different methods that permits multiple signals to transmit simultaneously across a single data link.
- Multiplexing is practiced with the help of a device known as a Multiplexer, commonly known as MUX.
- The multiplexer is used to combine the ‘N’ number of input lines to produce one output line.
- In multiplexing, one device is also used along with the multiplexer, which is used to separate the signal into its respective signals. This device is known as Demultiplexer, commonly known as DEMUX.
Also see, Message Switching in Computer Networks.
Types of Multiplexing
Three major types of Multiplexing are as follows:-
Frequency Division Multiplexing
- Frequency division multiplexing is basically a kind of analog method.
- In this type of multiplexing, the transmission of signals of different frequencies is made by combining all the frequencies into a composite signal and then transmitting it through a single link.
- The most important condition is that the bandwidth of the single link which is being used must be greater than the bandwidth of the combination of various frequencies.
- In this type of multiplexing, Guard bands, and strips of unused bandwidths are used to separate the channels.
- Frequency Division Multiplexing is used for AM and FM broadcasting of radio and also the broadcasting of television.
- It is also used in the cellular telephone of the first generation.

Wave Division Multiplexing
- Wave Division Multiplexing is also a type of analog method.
- Wave division multiplexing also works the same as that of Frequency division multiplexing.
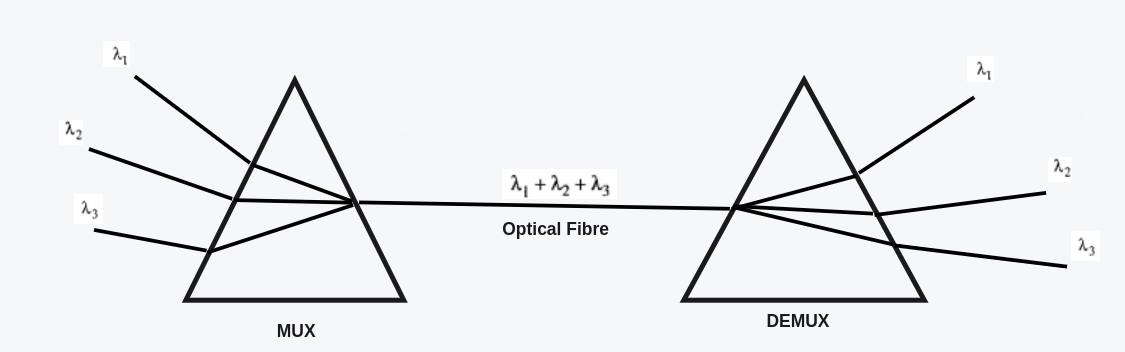
- The different types of signals in wave division multiplexing are either optical signals or light signals which are transmitted with the help of optical fibers.
- In this Wave Division Multiplexing, the combination of different types of light waves from different sources transmits across the channel to the receiver end.
- The Demultiplexer is used at the receiver end, which is being used to separate the composite light signal into different light waves.
- Prism is used to combine and split the light waves. We can explore the working of prism on this link.
- The configuration of WDM is straightforward.
- High security is being provided by this method.
- Complete Duplex transmission is possible with the help of wave division multiplexing.
- Signals can be transmitted simultaneously.
- Scalability is the central issue in this method.
- The use of optical instruments increases the cost of the method.
Time Division Multiplexing
- Time Division Multiplexing is a type of digital multiplexing method.
- In this type of multiplexing, the channels are divided according to the time.
- The total amount of time is carved up between the various users.
- In this type of multiplexing, the capacity of transmission of data rate should be greater than the data rate required by sending of receiving devices.
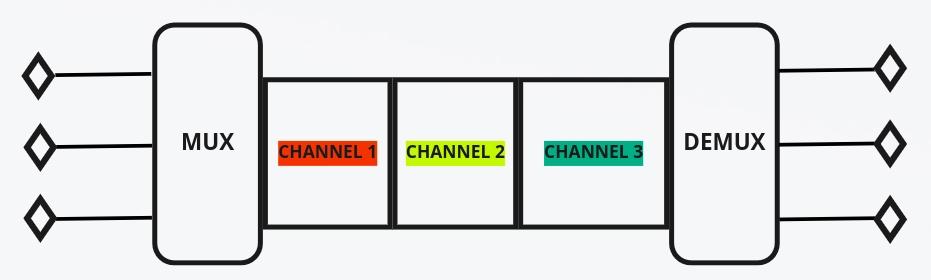
There are two types of Time Division Multiplexing:
1) Synchronous Time Division Multiplexing:
- In synchronous TDM, the time slots are divided equally to transmit the data over the link regardless of the data is associated with the device or not.
- Data is placed by each device one by one when their timeslot arrives.
- The time slot of the respective device stays empty if the data is not available with the device.
- Frames are used to organize all the time slots, and we can accumulate any number of time slots in one frame.
- The total number of frames equals the total number of sending devices.
- Implementation of Synchronous TDM is easy.
- Time slots get wasted if the user has no data to transmit.
2) Asynchronous Time Division Multiplexing:
- It is also called Statistical Time Division Multiplexing.
- In this type of multiplexing, the time slots are flexible in nature, which means that they are not fixed.
- The total speed of input lines can be greater than the capacity of the path.
- In this type of multiplexing, the total number of slots is less than the total number of input lines.
- Slots are assigned based on the availability of data.
- Efficient use of the capacity of transmission is there in this method.
- This method does not provide guarantee a fixed waiting time.
You can read related articles such as Congestion Control in Computer Networks here.





