Introduction
This article focuses on the MySQL database storage engines that ensure proper performance and manage SQL operations for multiple table types. The article discusses the different most popular MySQL storage engines.
MySQL is the world's most popular Relational Database Management System (RDBMS). MySQL databases are used by a wide range of services and applications. As a result, they must perform admirably to meet functional and business requirements.
MySQL Storage Engines
MySQL table types/storage engines are critical features that optimize database performance. It handles database creation, read, and update operations for storing and managing data in a database. In this blog, we will see various storage engines and table types available in MySQL.
MySQL supports the following storage engines, which developers can use to suit their needs:
- InnoDB
- MyISAM
- Federated
- MEMORY
- MERGE
- Archive
- CSV
- Blackhole
- Example
We can use the below query to determine which table types/storage engines our MySQL server supports.
| mysql> SHOW ENGINES; |
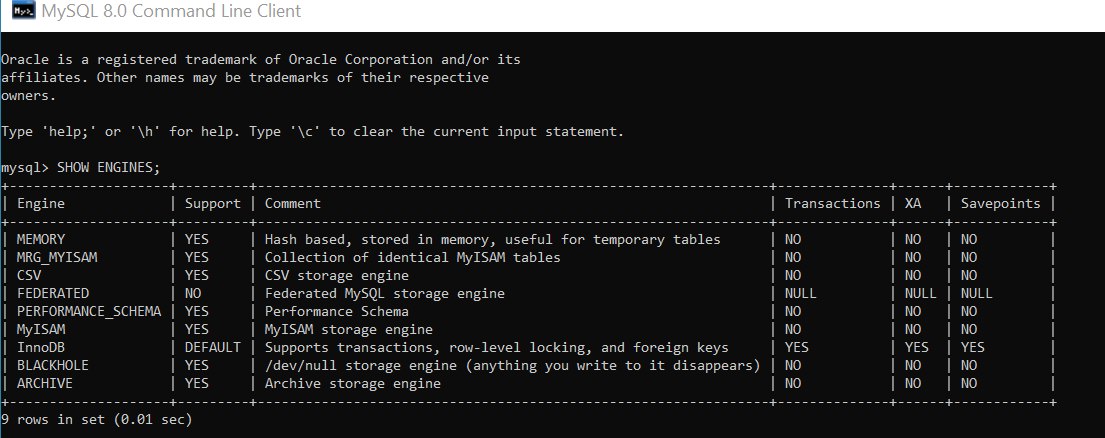
The value of the Support column indicates whether or not an engine can be used in the current server. A YES, NO, or DEFAULT value indicates that the table type is available, unavailable, or available but not currently set as the default table type/storage engine.
It is critical to understand the features of each table type in MySQL to choose the best one for our table and maximize the performance of our databases. Each table type in MySQL has its own set of benefits and drawbacks. Before deciding which one to use, let's go over each table type/storage engine.
ISAM
The ISAM engine was MySQL's first storage engine. Indexed Sequential Access Method is an abbreviation for Indexed Sequential Access Method. This table type/storage engine has been deprecated and is no longer supported by MySQL 5. x. MyISAM has taken over the functionality of this table. The size of an ISAM table is 4 GB, which necessitates expensive hardware. It is not transportable.
Example
This engine allows you to construct tables, but it does not store or retrieve data. This is intended to teach developers how to create a new storage engine.
MyISAM
Before version 5.5.1, MyISAM was the default storage engine in MySQL, and It is a famous choice due to its ease of use and speed.
Furthermore, because this engine requires less disc space, it is appropriate in cases where disc space is limited. It is extremely fast with SELECT and INSERT statements, a significant advantage. Still, it can be slow with DELETE and UPDATE statements because it does not support transactions with rollbacks and table-level locking.
MERGE
A MERGE table is a group of identical MyISAM tables used as a single entity. The term "identical" refers to all tables having the same column and index information. You can't merge tables with columns listed in a different order, columns that aren't the same, or indexes in the same order. MyISAMpack, on the other hand, can compress any or all of the tables.
InnoDB
MySQL's InnoDB is a transaction-safe storage engine that is ACID-compliant. It is the first table type to include foreign keys. InnoDB tables also provide excellent performance. Its size can be up to 64TB. InnoDB tables are also portable between systems, similar to MyISAM tables. MySQL can also check and repair InnoDB tables as needed.
MEMORY (HEAP)
This memory table type/storage engine generates tables saved in our memory. Before MySQL version 4.1, it was also known as HEAP. This storage engine is faster than MyISAM because it employs hash indexes, which allow for faster retrieval of results. We now know that data stored in memory can be corrupted due to power outages or hardware failure. That's why we can only use this table for temporary work areas or read-only data caches from other tables. As a result, the memory/heap tables are lost whenever the MySQL server halts or restarts. The database server's uptime determines the data life of a memory/heap table.
ARCHIVE
As the name implies, this engine excels at searching for rarely-referenced historical data. The tables are not indexed, and compression occurs only during insert. Use this storage engine to archive and retrieve previous data.
Black Hole
This engine accepts data but does not save it. Like UNIX /dev/null, Queries always return an empty set. This is useful in a distributed database environment where you don't want to store data locally and in performance or other testing situations.
CSV
This storage engine comes in handy when data needs to be shared with other applications that use CSV formatted data. The tables are saved in the form of comma-separated value text files. Although this facilitates data sharing with scripts and applications, one disadvantage is that the CSV files are not indexed. As a result, until the Import/Export stage of the process, the data should be stored in an InnoDB table.
FEDERATED
While not the default storage engine for MySQL, Federated is a well-known storage engine. Its unique feature is that it allows access to data from a remote MySQL database. Simultaneously, it does not require replication or cluster technologies. The local Federated table serves as the key. When a query is directed at that table, it is automatically extended to the small federated table. The information is not saved locally.
Federated, on the other hand, has a potentially fatal flaw. It is not the best solution for dealing with joined tables because of their slow work speed.




