Introduction
As you know paging is a very important concept of an Operating system, but have you ever wondered about the need for paging? Why is it being employed?
Well, in this article, we will discuss the need for paging with an example:
Before we directly jump onto the need let’s take a look at the different types of memory management techniques:
There are two types of memory management techniques:
-
Contiguous memory allocation, which is further divided into two types:
- Fixed Size Partitioning
- Dynamic partitioning
- Non-contiguous memory allocation, which is further divided into two types:
As you can see above, paging is under the category of non-contiguous memory allocation. By this, we can easily get a rough idea of the need for paging. It also indicates that there must be some issues or dilemmas that the Contiguous memory allocation is unable to handle. But in order to make this rough idea clearer, we’ll dive deeper into the concept of Contiguous memory allocation and will understand the core need for paging.
Let’s get started now!
“Must Recommended Topic, Internal and External Fragmentation“
Contiguous Memory Allocation
Contiguous memory allocation is a way of allocating a contiguous section/part of memory to a process or file that requires it. The allotment will be contiguous, meaning scattering is prohibited.
Fixed Sized Partitioning
In fixed-sized partitioning, the main memory is partitioned into divisions of equal or different sizes. The RAM is allocated to the processes in a logical order.
In fixed-sized partitioning,
- The partitions cannot overlap.
- A process must be continuously present in a partition for execution.
Problems With fixed Sized Partitioning
The process should either be the same or small size as the partition but not more than that. Processes with lesser size than the partition cause memory wastage which is often known as internal fragmentation.
So to solve this problem we have dynamic partitioning.
Dynamic Partitioning
In dynamic partitioning, the partition size is not mentioned at the start of this approach. It is stated when the process is loaded. The operating system takes up the first partition. The remaining area has been divided into sections. Each partition will be the same size as the entire process. The partition size varies according to the process's requirements in order to minimize internal fragmentation.
Problems With Dynamic Partitioning
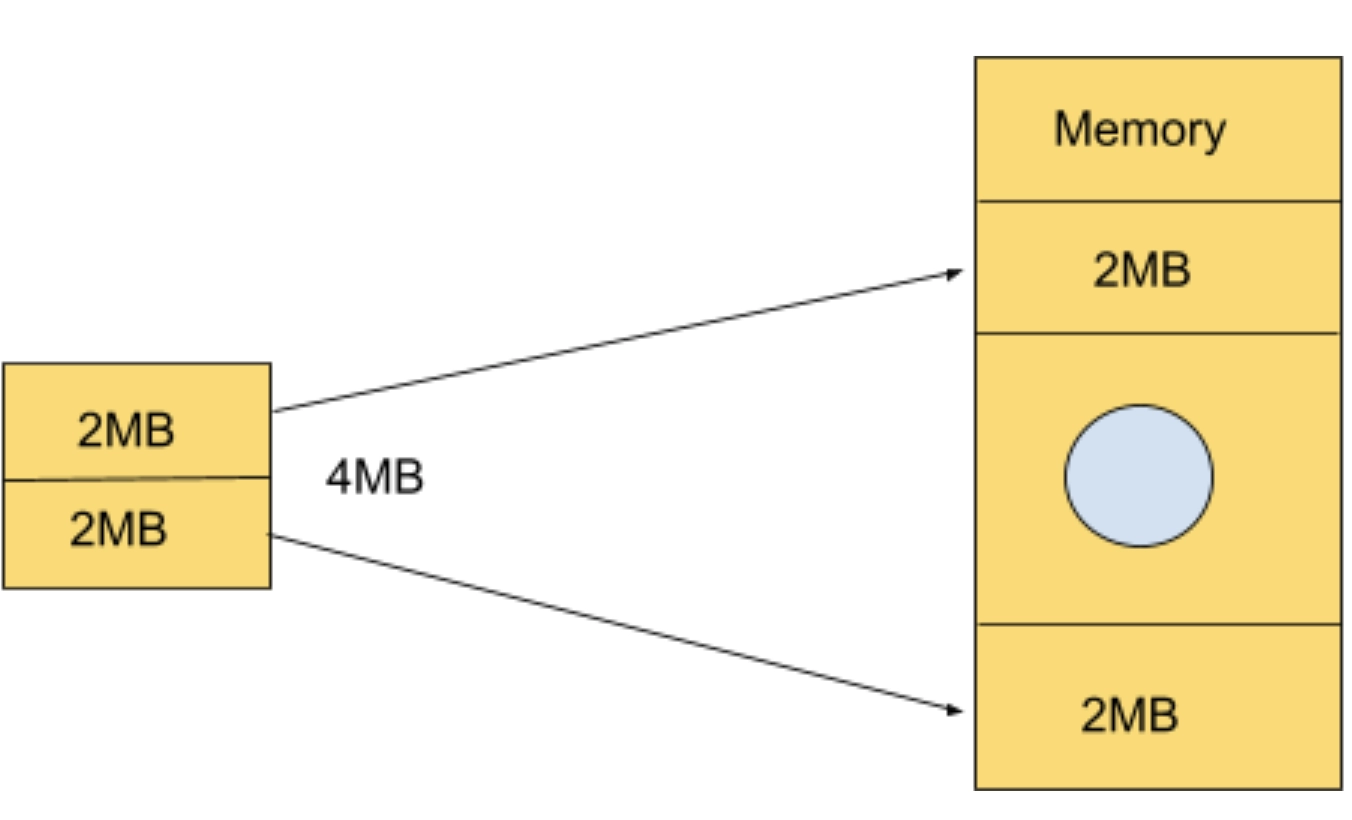
The absence of Internal fragmentation does not mean that external fragmentation will not occur.
External fragmentation occurs when we are unable to allocate space to a process despite having total memory space available, but that space is not contiguous.
The holes or vacant spaces left by leaving a process mark empty spaces in the memory, and the non-contiguous spaces are not a good fit for a new upcoming process.
You can refer to this article to understand the difference between Internal and External Fragmentation.
However, the problem of External fragmentation can be solved by the Compaction method.
Compaction
Compaction is a method of gathering free space in a huge memory chunk in order to free up space for processes. Due to the processes going in and out of memory, swapping creates many fragments in the memory. Compaction is the process of integrating all of the vacant areas and processes.
When the system is compacted, the efficiency of the system is reduced since all of the available spaces are relocated from multiple locations to a single one.
This method will take a long time to complete, and the CPU will be idle the entire time. Despite the fact that the compaction avoids external fragmentation, it makes the system inefficient.
As you can see, the compaction makes the system inefficient. So to solve the problem of inefficiency we are shifting towards non-contiguous memory allocation.
Here, the paging comes into play: