Introduction
Binary Trees are popular Data Structures and have a wide range of applications throughout various fields. Binary Trees are also important when it comes to interviews with top tech companies. A mastery of Binary Trees could help us solve a lot of problems. In this article, we are going to take a look at one such problem.
Binary search tree (BST)
Before jumping to the question, let’s understand what a Binary search tree is:
A Binary search tree (BST) is a type of binary tree in which the nodes are arranged in a specific order. It is also known as an ordered binary tree.
Properties of a Binary search tree (BST):
- The value of all the nodes in the left subtree of a node is smaller than the node’s value.
- The value of all the nodes in the right subtree of a node is greater than the node’s value.
- All the left subtrees and right subtrees of the root node must follow the above properties.
Example:
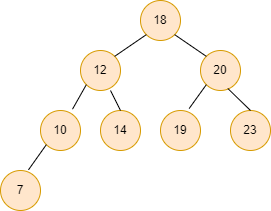
Problem statement
We are given a Binary search tree. Our task is to find the node with the maximum value in the Binary search tree.
Example:
Input1:
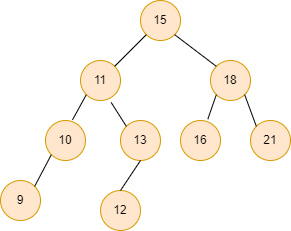
Output1: 21 // maximum value in the Binary search tree
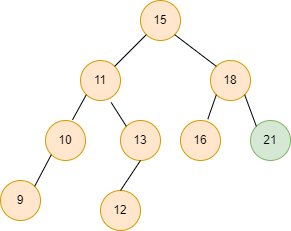
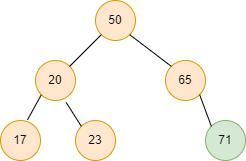
Input2:
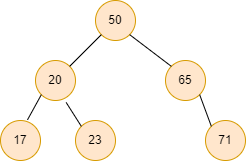
Output2: 71 // maximum value in the Binary search tree
Approach
Finding the maximum value in the Binary search tree is a simple operation because of its ordered structure.
In a Binary search tree (BST), the left child of each node must be less than its parent node, and the right child must be greater than its parent.
So, if we consider the root node of the Binary search tree (BST), the left subtree of the binary search tree must have nodes with values less than or equal to the root node, and the right subtree must have nodes with values greater than the root node.
So, the node with the maximum value in the Binary search tree is the rightmost node of the tree.
Algorithm:
- Declare a curr pointer pointing to the root of the Binary search tree.
- Run a while loop till curr -> right != NULL and do curr = curr -> right inside the while loop.
-
After the completion of the loop, print curr -> data, which is the maximum value in the Binary search tree.
Let’s understand the above algorithm with an example:
Input:

Steps:
Initially, the curr pointer points to the root of the Binary search tree.
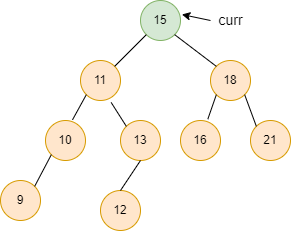
Now, curr->right!=NULL, so we move the curr pointer to the right node, curr = curr -> right.
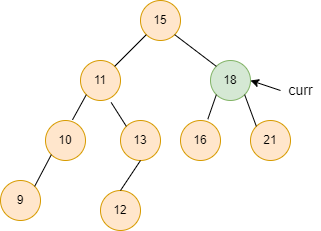
Similarly, curr = curr -> right.
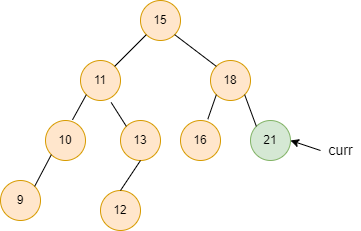
Here curr -> right = NULL, print the curr -> data, which is the maximum value in the Binary search tree.





