Introduction
In this article, we will be learning about the operators in the swift language. An operator is a special symbol that performs specific mathematical and logical operations on the variables (operands). Operators in swift are of three types based on the number of operands:
- Unary: It uses one operand. Unary operators work with only one target (such as -a). Unary prefix operators (such as !b) and unary postfix operators (such as c!) appear immediately before and after their targets, respectively.
- Binary: It consists of two operands. Binary operators (such as 2 + 3) operate on two targets and are infix because they appear between the two targets.
- Ternary: Ternary operators are focused on three distinct targets. Swift contains only one ternary operator, the ternary conditional operator (a? b: c), similar to C.
Now let's discuss the type of operators based on their operations.
Know more about Unary operator overloading in c++ in detail here.
Types of Operators
In this section, we will discuss different types of operators:
Arithmetic Operators
In swift, we use arithmetic operations to perform several mathematical operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, etc.
Arithmetic operators are:
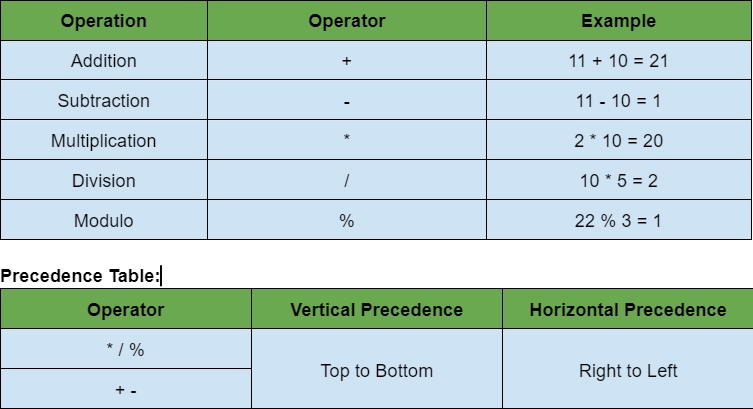
Example: In this example, we will use different operators.
Code:
var a = 7
var b = 3
// Addition
print (a + b)
// Subtraction
print (a - b)
// Multiplication
print (a * b)
// Division
print(a / b)
// Modulo
print(a % b)
Output:
10
4
21
2
1Assignment Operators
In swift, we use the assignment operator to assign the value to the variables. Types of assignment operators are:
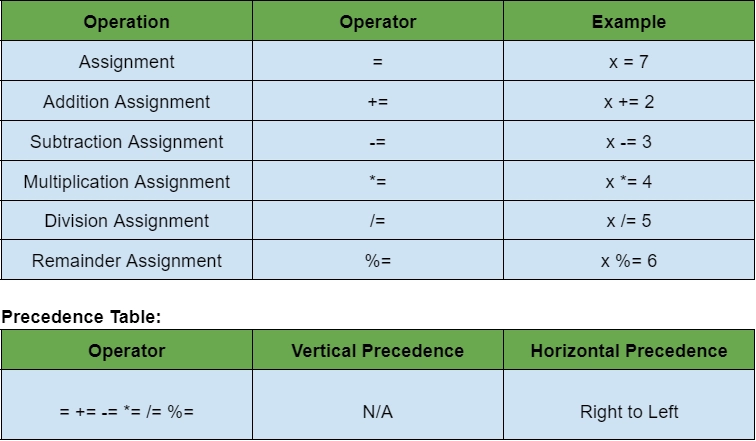
Example: In this example, we will discuss all the assignment operators.
Code:
// Assign 2 to x
var x = 2
// Assign 8 to y
var y = 8
// Using addition assignment.
x += y
print(x) //x = 10
// Using subraction assignment.
x -= 2
print(x) //x = 8
// Using multiplication assignment.
y *= 2
print(y) //y = 16
// Using division assignment.
x /= 2
print(x) //x = 4
// Using modulo assignment.
x %= 3
print(x) //x = 1
Output:
10
8
16
4
1Comparison Operators
In swift, we use a comparison operator to compare the two variables. Types of comparison operators are:
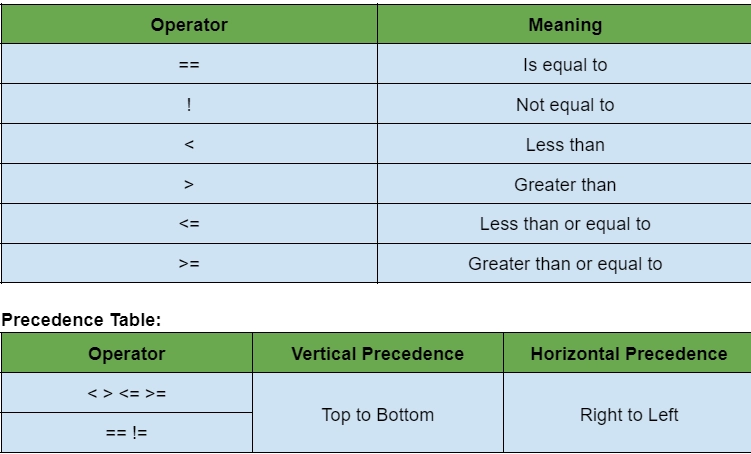
Example: In this example, we will discuss all the comparison operators.
Code:
// Is equal to
print(2 == 2)
// Not equal to
print(2 != 2)
// Greater than
print(4 > 1)
// Smaller than
print(3 < 1)
// Greater than or equal to
print(10 >= 10)
// Smaller than or equal to
print(12 <= 20)
Output:
true
false
true
false
true
trueLogical Operators
In swift, we use a logical operator to check if an expression is true or false. It is also used in decision flow control.
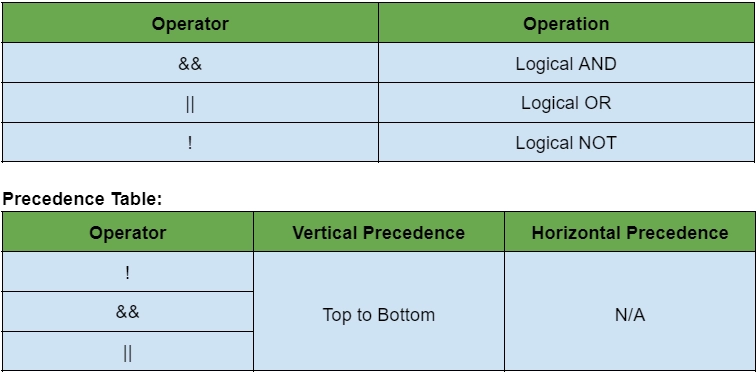
Example: In this example, we will discuss all the logical operators.
Code:
// Logical Not
print(!true)
// Logical OR
print(true || true)
print(false || false)
// Logical AND
print(true && true)
print(false && true)
Output:
false
true
false
true
falseBitwise Operators
In swift bitwise operator is used to perform operations on the bits. Types of bitwise operators are:
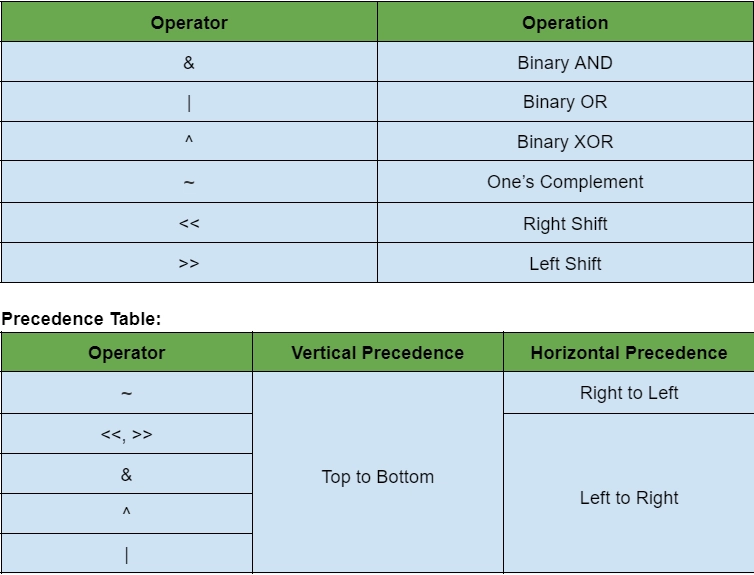
Example: In this example, we will discuss all the logical operators.
Code:
// Binary XOR
print(2 ^ 3)
// Binary AND
print(10 & 10)
// Binary OR
print(4 | 5)
// Left Shift
print(10<<2)
// Right Shift
print(12>>2)
Output:
1
10
5
40
3Range Operator
In swift, we use the range operator to show the range of values. Types of range operators are:
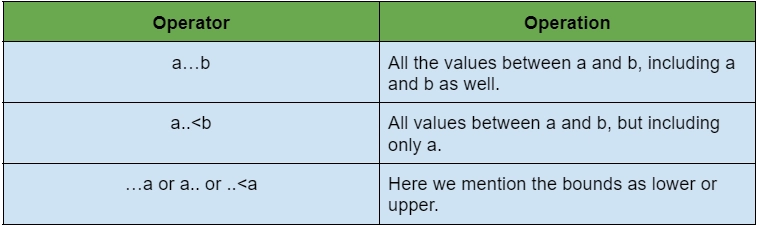
Example: In this example, we will discuss all the logical operators.
Code:
// Using a...b
print("Using a...b operator:")
for x in 1...5{
print(x)
}
// Using a..<b
print("Using a..<b operator:")
for x in 1..<5{
print(x)
}
// Using a... or ...a or ..<a
print("Using a... or ...a or ..<a operator:")
let range1 = ..<3
print(range1.contains(-3))
let range2 = 4...
print(range2.contains(10))
Output:
Using a...b operator:
1
2
3
4
5
Using a..<b operator:
1
2
3
4
Using a... or ...a or ..<a operator:
true
true
Read about Bitwise Operators in C here.






