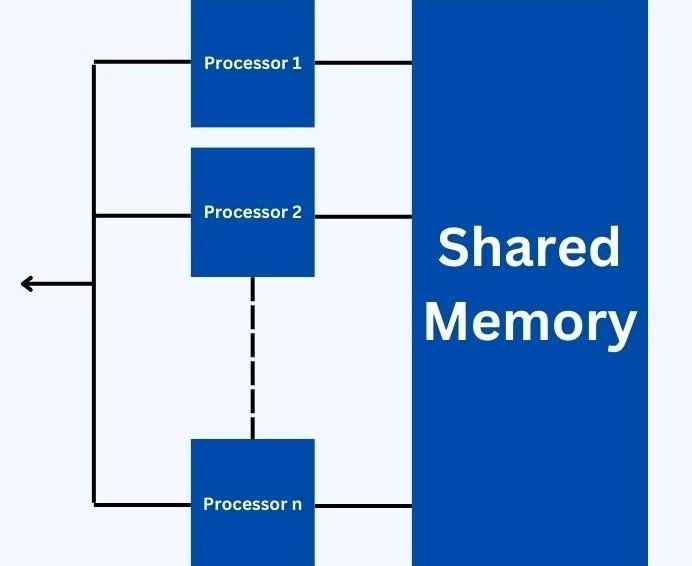
Working of a Parallel Operating System
The main task is broken down into smaller sub-tasks in a parallel operating system design. Then, each sub-task is assigned to a different system for processing. This way, the task is completed quickly since each instruction is further divided for various CPU components.
Usually, a single system transmits and processes instructions whenever a task is assigned to different components for simultaneous processing. In a parallel operating system, various systems achieve the same much quicker, and such a system can handle much more loads of work simultaneously.
Functions of Parallel Operating System
Let us see some main functions of a parallel operating system.
-
It has a multiprocessing environment for faster processing. At the same time, it implements security measures among the processors.
-
A parallel operating system design can handle much more work than a single system. Also, resources are shared effectively among different processors.
- Processes that may thread with each other are focused on so that there is no interference between simultaneous processes.
Types of Parallel Operating Systems
Mainly, parallel operating systems are categorized into two types:- type 1 and type 2. Let us study them one by one.
-
type-1:- This system runs directly on metal and acts as a native hypervisor. Systems that share physical hardware or virtual machines can be used in this type. The operating system does not provide any Input/Output emulations. For example, VMware uses the type-1 parallel operating system design.
- type-2:- This type is hosted on a hypervisor. But, it is executed when the hypervisor runs on conventional operating systems like Windows, Linux, etc.
Application of Parallel Operating System
Parallel operating systems are used in various applications to harness the power of multiple processors or cores for improved performance and efficiency. Applications include:
-
High-Performance Computing (HPC): Parallel OSs are essential for scientific simulations, weather modeling, and other data-intensive HPC tasks.
-
Data Centers and Cloud Computing: They enable efficient resource allocation and scalability in data centers and cloud environments.
-
Real-time Systems: Used in applications like autonomous vehicles and industrial automation where rapid response times are critical.
-
Database Management: Parallel databases benefit from the ability to distribute and process data across multiple nodes.
-
Scientific and Engineering Simulations: Parallel computing accelerates complex simulations in fields like physics and engineering.
-
Machine Learning and AI: Parallelism accelerates deep learning and training of complex neural networks.
Parallel operating systems facilitate better performance, scalability, and responsiveness in these and other compute-intensive applications.
Advantages of Parallel Operating Systems
Let us look at some benefits of parallel operating systems.
-
It helps reduce task completion time since multiple processes are run simultaneously.
-
It can solve large and complex operating system problems. It achieves this by sharing resources efficiently.
- It can allocate much more memory space and resources to processors than a single system making it faster.
Disadvantages of Parallel Operating System
Let us look at some limitations of using a parallel operating system.
-
The architecture of such systems is complex and requires a high power supply and high maintenance.
-
Such systems are costly since numerous processors require many resources. Also, coolers are used, which are expensive too.
Also see, Difference Between Bit and Byte
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a parallel operating system?
A parallel operating system is designed to manage and utilize multiple processors or processor cores for concurrent and efficient execution of tasks, enhancing system performance and responsiveness.
What is an example of a parallel operating system?
One example of a parallel operating system is IBM's AIX, which is designed for high-performance computing and supports parallel processing on systems with multiple processors or cores.
What is parallel system and time sharing operating system?
- A parallel system refers to a computer system with multiple processors working together to execute tasks concurrently, improving performance and throughput.
- A time-sharing operating system allows multiple users to access and use a single computer simultaneously, dividing CPU time for fair allocation among users and providing interactive computing.
What are the two types of parallelism in OS?
Two types of parallelism in operating systems are:
- Instruction-Level Parallelism (ILP): Concurrent execution of multiple instructions within a single process.
- Task-Level Parallelism (TLP): Concurrent execution of multiple processes or tasks.
Conclusion
Operating systems are essential for the working of any system. An operating system is a bridge between the user and the system. However, a single system or processor often takes a lot of time for some tasks. Here comes the role of parallel operating systems in play. It divides the tasks into smaller ones, and each system needs to get a specific task done so that simultaneously, the task gets completed quickly. Multiple applications can also be run using this without interference. This article studied Parallel Operating Systems and their functions, advantages, disadvantages, and applications.
We recommend you go through the following articles for more information:
You can also consider our System Design Course to give your career an edge over others.