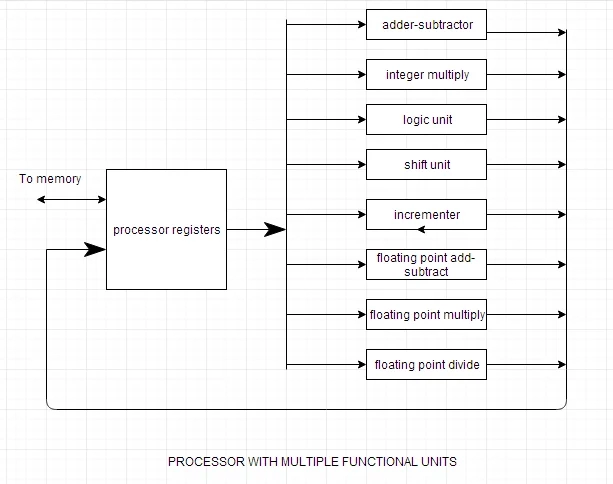
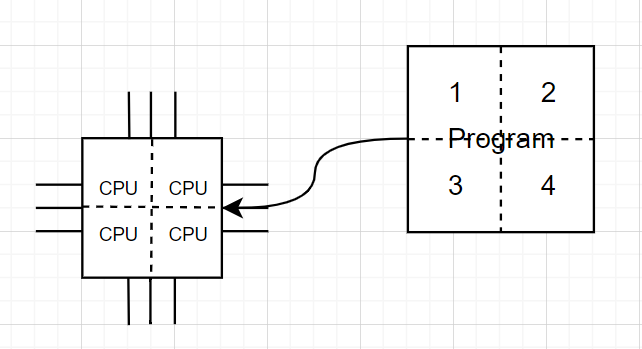
How Does Parallel Processing Work?
Parallel processing involves breaking down tasks into smaller subtasks that can be executed simultaneously by multiple processing units, increasing efficiency and reducing overall execution time.
Types of Parallel Processing
1. Task Parallelism
In task parallelism, different tasks or processes are executed concurrently, each handling a specific part of the overall workload.
2. Data Parallelism
Data parallelism involves splitting the data into smaller chunks and processing each chunk concurrently using multiple processing units.
Parallel Processing Examples
1. Image Processing
In image processing, tasks such as filtering, edge detection, and resizing can be performed concurrently on different regions of an image using task parallelism.
2. Matrix Multiplication
In data parallelism, matrix multiplication involves dividing matrices into smaller submatrices and computing their products simultaneously across multiple processing units.
Need of Parallel Processing
- Application demands: With increasing technology, modern applications require more computing cycles. Examples include videos, high graphic games, databases, science models, etc.
- Technology Trends: With the increasing number of transistors on a chip, clock rates are expected to go up but slowly.
- Economics: Instead of costly components used in traditional supercomputers, today's microprocessors offer high performance and have multiprocessor support.
Advantages of Parallel Processing
- It increases the speed and efficiency of computers. Sequential computing forces fast processors to do things inefficiently.
- Computers can be used to solve more complex and more extensive problems. A single web app may have to process millions of requests every second with so much data.
- For a system that has to support billions of operations (for example, bank software), parallel processing makes things cheaper.
- Parallel computing is more suited for hardware since serial computing wastes the computing power of processors.
Disadvantages of Parallel Processing
- Increases the cost of computers since more hardware is required.
- Multicore architectures consume higher power.
- Parallel architectures are difficult to achieve.
- A parallel computing system needs different code tweaking depending on the target architecture.
- It increases the overhead cost due to synchronization and data transfers.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is parallel processing?
Parallel processing divides a big task into smaller tasks and executes these smaller tasks concurrently to get the output. It increases the speed and efficiency of computers.
What is the use of parallel processing?
Parallel processing increases the speed and efficiency of computers. Computers can perform much more computations within the given time; thus, user experience is enhanced.
What is parallel processor in computer architecture?
A parallel processor in computer architecture refers to a system with multiple processing units that can execute instructions concurrently, enabling simultaneous execution of tasks and improving overall performance and efficiency.
What is parallel processing and pipelining in computer architecture?
Parallel processing involves breaking down tasks into smaller subtasks and executing them simultaneously by multiple processing units, while pipelining involves overlapping execution stages of instructions to improve throughput and reduce latency in a sequential manner.
What is parallelism and its types?
Parallelism refers to the ability of a system to execute multiple tasks concurrently, improving performance and efficiency. Types of parallelism include task parallelism, where different tasks are executed simultaneously, and data parallelism, where data is processed concurrently across multiple processing units.
Conclusion
In this article, we studied what parallel processing is. Parallel processing revolutionizes computing by harnessing the power of multiple processing units to execute tasks concurrently, thereby enhancing performance, efficiency, and scalability.
If you want to learn more about such topics, you can visit Coding Ninjas Studio.
Recommended Reading:
MVVM Architecture Android
Demand Paging in OS
If you think that this blog helped you share it with your friends!. To be more confident in data structures and algorithms, try out our DS and Algo Course.
Until then, All the best for your future endeavors, and Keep Coding.