
Introduction
Pretty Good Privacy or PGP was a popular program used to encrypt and decrypt email across the internet and authenticate our messages with digital signatures and encrypted stored files. It is an open-source and freely available software package for the security of emails.
The popularity of PGP is due to two given factors.
- The first one is that the system was initially available as freeware and spread quickly among users who wanted another level of security for their emails.
- The second is that both symmetric encryption and public-key encryption are used in PGP. So, it allows users who have never met to send encrypted messages to each other without exchanging private encryption keys.
(See Cryptography)
Recommended Topic, Basic Networking Commands
How does PGP work?
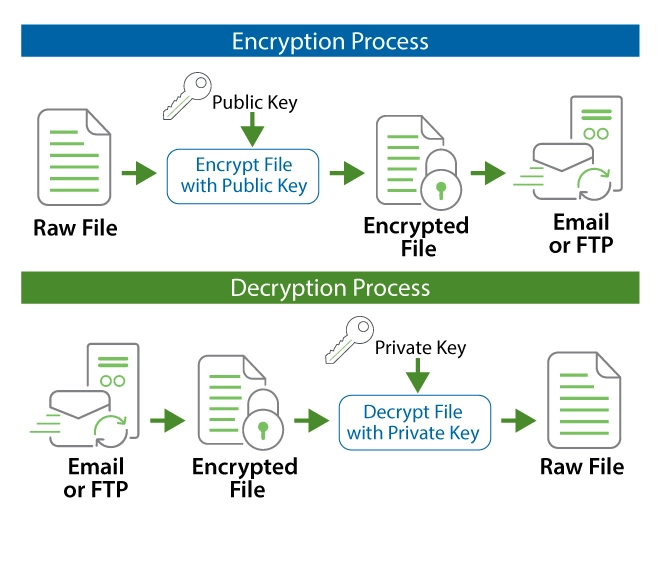
- PGP is a hybrid cryptosystem. It combines the best features of both conventional and public-key cryptography.
- When we encrypt plaintext with PGP, PGP first compresses the plaintext. Data compression can save modem transmission time and disk space and strengthen cryptographic security.
- Compression can reduce the patterns in plaintext, thereby greatly enhancing resistance to cryptanalysis. But the files that are too short to compress are not compressed.
- After that, PGP creates a session key, which is a one-time-only secret key. A key is a random number generated by the random movements of our mouse and the keystrokes we type. This session key uses a very secure, fast conventional encryption algorithm for plaintext; the encrypted text we got is called ciphertext.
- After the data is encrypted, the session key is encrypted to the recipient's public key. The public key-encrypted session key is transmitted along with the ciphertext to the recipient.
- Decryption works in reverse. The recipient's copy of PGP uses their private key to recover the temporary session key, which PGP uses to decrypt the conventionally-encrypted ciphertext later.
Advantages of PGP Encryption
- The combination of the two encryption methods combines the convenience of public-key encryption with the speed of conventional encryption.
- Conventional encryption is approximately 1,000 times faster than public-key encryption.
- Public key encryption provides a solution to key distribution and data transmission issues. Performance and key distribution will be improved without sacrificing security.
Disadvantages of PGP Encryption
- Complexity: PGP encryption is typically not user-friendly. Using PGP, encrypting data and files takes time and complicates message sending for users. Organizations should have to provide training to employees if they are implementing PGP.
- Key management: Users need to fully understand the functionality of the PGP system to ensure that they do not create holes in their security defenses. This can occur either through the incorrect usage of PGP or losing or corrupting keys. It puts their fellow users at risk in highly secure environments.
- Lack of anonymity: PGP will encrypt messages users send but do not anonymize them. It means that senders and recipients of emails sent through a PGP can be traced. The subject line of the message is also not encrypted.
- Compatibility: It is impossible to use PGP until both the sender and recipient use the same software version.
You can also read about the Layered Architecture in Computer Network.






