Introduction
In this article, we are going to discuss how to drop a database in PostgreSQL. Before moving to how to drop a database, let’s see what PostgreSQL is?
PostgreSQL is a powerful, open-source object-relational database management system (ORDBMS). It is used to store data securely. Some features of PostgreSQL includes -
- It runs on all major operating systems like Windows, Linux, Unix, Mac OS etc.
- It supports text, image, sound, video and includes interfaces for many languages like C, C++, Java etc.
- It supports many SQL features like complex SQL queries, foreign keys, triggers, views, transactions, concurrency etc.
- In PostgreSQL, tables can be set to inherit their characteristics from a “parent table”.
- We can install several extensions to add additional functionality to PostgreSQL.
Since we got an insight into PostgreSQL, it’s time to get back to our topic.
How to drop a database in PostgreSQL?
A Database is usually dropped once it is no longer needed. We must be a superuser or the owner of the database for dropping a database in PostgreSQL.

Source: MEME
There are two ways to drop a database in PostgreSQL. These are-
- Using the DROP DATABASE command on PostgreSQL shell prompt.
- Using dropdb command on command prompt.
We will discuss both these ways one by one.
Using the DROP DATABASE command
We can simply drop a database using the DROP DATABASE command. We just need to open the PostgreSQL shell prompt and enter our password.
The syntax of the DROP DATABASE command is-
DROP DATABASE [IF EXISTS] database_name;where,
IF EXISTS: It is used to prevent PostgreSQL from throwing an error in case the database does not exist. Else PostgreSQL throws an error.
database_name: The name of the database to be dropped.
The DROP DATABASE command must be used with caution because once a database is deleted, it cannot be undone. This command deletes catalogue entries and data directory permanently.
Moreover, the DROP DATABASE command cannot be used if the database still has active connections.
- In that case, first, we should disconnect from that database, connect to another database and then drop that database.
-
Other way could be to terminate the active connections and then drop the database.
We will see both cases further in the article.
Now, let’s see an example to drop a database with no active connections.
Drop a database with no active connections
First, we will check the existing databases on our server. We can use the \l (backslash l) command.
Note: \l or \list is a psql tool that lists all the databases present in the current server.
postgres=# \lThe output of the above query will be-
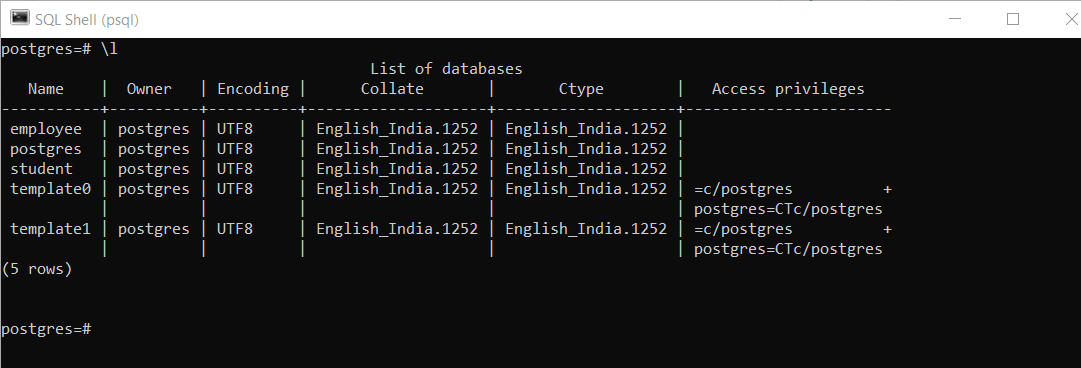
The owner of the employee database, i.e., postgres can only delete the employee database. Now let’s delete the database employee:
postgres=# DROP DATABASE employee;
postgres=#The database is deleted successfully.
Now, we will see how to drop a database with active connections.
Drop a database with active connections
For knowing how to drop a database with active connections, we need to connect with a database. So, let's connect with the student database using the \c (backslash c) command.
Note: A \c command is a psql tool used to switch the connection to a new database.
postgres=# \c student;The output of the above query will be-
You are now connected to database "student" as user "postgres".
student=# Now, we will try to drop the student database.
student=# DROP DATABASE student;The above statement does not execute and throws an error.
ERROR: cannot drop the currently open database
student=#This error occurred because the student database has an active connection. To check the active connections, we will execute the following command-
student=# SELECT * from pg_stat_activity WHERE datname = 'student';The output of the above query will be-
datid | datname | pid | usesysid | usename | application_name | client_addr|
16399 | student | 11784 | 10 | postgres | psql | ::1 |
(1 row)The student database has one connection from localhost; therefore, it is safe to terminate this connection and remove the database.
For terminating the connection, we will execute the following command-
student=# SELECT pg_terminate_backend (pg_stat_activity.pid) FROM pg_stat_activity WHERE pg_stat_activity.datname = 'student';Now, the connection is terminated and we can drop the student database.
student=# DROP DATABASE student;
student=#Database dropped successfully.
We have seen how to drop a database using the first way, i.e., using the DROP DATABASE command. Now, we will explore the second way, i.e., the dropdb command.
Using the dropdb command
If you don’t want to open the PostgreSQL shell prompt, you can also drop a database using the command prompt present in your system.
For doing this, first, open the command prompt. Go to the directory where PostgreSQL is installed. Then go to the bin directory.
The syntax of the dropdb command is-
dropdb [options] database_name;The dropdb command may contain two parameters defined below:
- options: These contain the command-line arguments which dropdb command accepts. These include-
S.No |
Command line argument |
Description |
| 1. | -e | Echo the commands that dropdb generates and sends to the server. |
| 2. | -h host | Specifies the hostname of the machine running the server. |
| 3. | -i | Issues a confirmation message before executing the command. |
| 4. | -p port | Specifies the TCP port on which the server is listening for connections. |
| 5. | -U username | Username to connect. |
| 6. | -V | Prints the dropdb version and exits. |
| 7. | -w | Never issue a password prompt. |
| 8. | -W | Asks dropdb to prompt for the user’s password before connecting to the database. |
| 9. | --help | Display help about dropdb command line argument and exit. |
| 10. | --if-exists | Do not throw an error if the database does not exist. |
| 11. | --maintenance-db=dbname | Specifies the database to connect to after dropping the target database. |
2. database_name: The name of the new database to be dropped.
Let’s run a query to understand the dropdb command.
First, we will check the existing databases on our server. We can use the \l (backslash l) command.
Note: \l or \list is a psql tool that lists all the databases present in the current server.
postgres=# \lThe output of the above query will be-
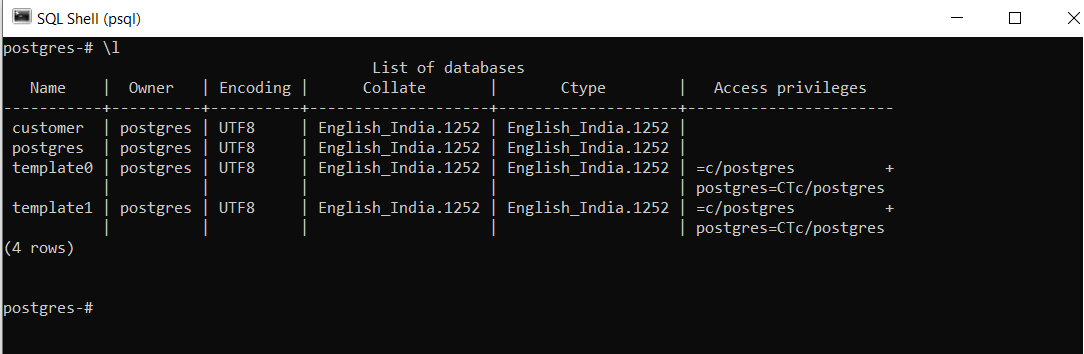
We will drop a database named customer using the following command.
dropdb -h localhost -p 5432 -U postgres customer
Password: *****As soon as you hit enter after writing the dropdb line, the command prompt will ask you to enter your PostgreSQL admin user password. Just type the password and hit enter.
The database is successfully deleted. Using the \l command on the PostgreSQL shell prompt, you can check this.
postgres=# \lThe output of the above query will be-

As you can see, the customer database is not present.
The difference between the DROP DATABASE command and dropdb command is -
- The DROP DATABASE command is a SQL command. In contrast, dropdb is a command-line wrapper around the SQL command DROP DATABASE.
- DROP DATABASE command can run from the PostgreSQL shell prompt, while the dropdb command can run from the command prompt.




