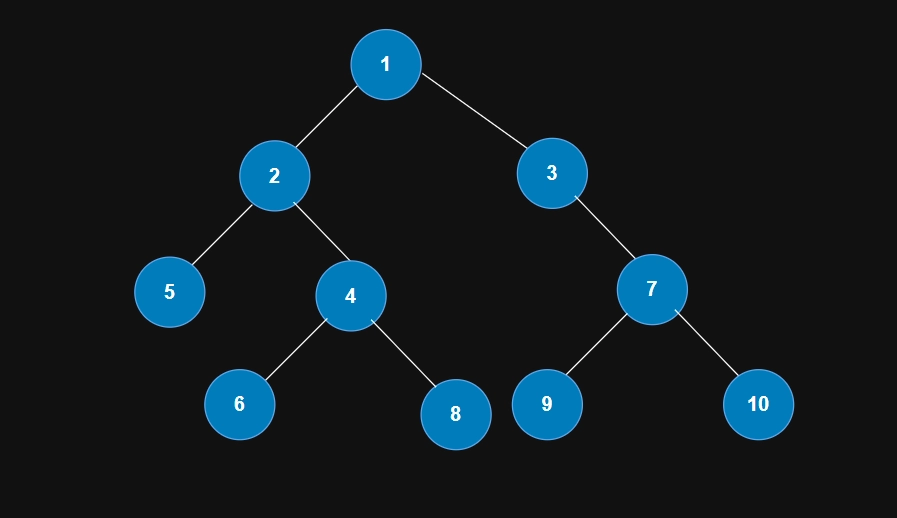
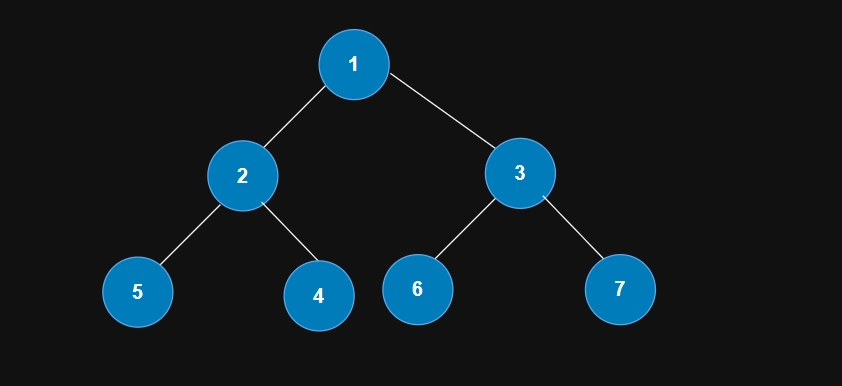
Approach
The approach for the above problem is quite simple and straightforward. We will check if the node is null or a leaf node. In the case of a leaf node, we will print it otherwise, if null, we will return from that point of the function. If either of the above two cases is not present, we will recursively call the method for the node's left and right children.
Algorithm
1. Start traversing the tree.
2. Determine whether or not the given node is null. Return from the function if it returns null.
3. Check if it's a leaf node. Print the data of the node if it is a leaf node.
4. If the node is not a leaf node in the previous step, verify if the node's left and right children exist. If yes, recursively call the function for the node's left and right children.
Implementation in C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// Declaring Binary Tree Node Structure
struct Node
{
int x;
struct Node *leftChild, *rightChild;
};
// function to print all of the leaf
// nodes in a left-to-right manner
void printNodes(Node *root)
{
// if the current node is a null, return from the function
if (!root)
return;
// if the current node is a leaf node, print its data
if (!root->leftChild && !root->rightChild)
{
cout << root->x << " ";
return;
}
// if left or right child exists, check for leaf
// recursively
if (root->leftChild)
printNodes(root->leftChild);
if (root->rightChild)
printNodes(root->rightChild);
}
// Utility functions
Node *newNode(int x)
{
Node *temp = new Node;
temp->x = x;
temp->leftChild = temp->rightChild = NULL;
return temp;
}
// Driver program
int main()
{
// create binary tree
Node *root = newNode(1);
root->leftChild = newNode(2);
root->rightChild = newNode(3);
root->leftChild->leftChild = newNode(11);
root->rightChild->leftChild = newNode(5);
root->rightChild->rightChild = newNode(8);
root->rightChild->leftChild->leftChild = newNode(12);
root->rightChild->leftChild->rightChild = newNode(13);
root->rightChild->rightChild->leftChild = newNode(4);
root->rightChild->rightChild->rightChild = newNode(6);
// printing leaf nodes
cout << "The leaf nodes in left to right manner are: " << endl;
printNodes(root);
return 0;
}

You can also try this code with Online C++ Compiler
Output
The leaf nodes in left to right manner are:
11 12 13 4 6
Time Complexity
The Time Complexity of the given approach is O(n), where n is the number of nodes as we traverse through each tree node only once.
Space Complexity
The program's auxiliary space is O(1) because no additional data structure is involved.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is tree called a non-linear data structure?
As it does not sequentially store data, a tree data structure is non-linear. Since the elements of a Tree are grouped at numerous levels, it is a hierarchical structure.
What is a node in a tree data structure?
A tree is constructed up of nodes, which are individual entities. Edges link nodes together. Each node has a value or piece of data and may or may not have a child node. The root refers to the tree's first node.
What is the degree of a tree?
The number of children of a node determines its degree. The maximum degree of any of a tree's nodes is its degree.
Conclusion
This article extensively discussed the problem of printing all the leaf nodes of a binary tree in a left-to-right manner and its time and space complexities.
Cheers, you have reached the end. Hope you liked the blog and it has added some knowledge to your life. Please look at these similar topics to learn more: Binary Tree, Binary Search Tree, Binary Tree to BST, and All Binary Trees.
Refer to our Coding Ninjas Studio Guided Path to learn Data Structures and Algorithms, Competitive Programming, JavaScript, System Design, and even more! You can also check out the mock test series and participate in the contests hosted by Coding Ninjas Studio! But say you're just starting and want to learn about questions posed by tech titans like Amazon, Microsoft, Uber, and so on. In such a case, for placement preparations, you can also look at the problems, interview experiences, and interview bundle.
Recommended Problems:
You should also consider our premium courses to offer your career advantage over others!
Please upvote our blogs if you find them useful and exciting!
Happy Coding!