Introduction
One of the most vital topics to know if you want to get a job at a top product-based organization is data structure and algorithms. Having a thorough understanding of DSA requires the solutions of various coding problems. So, in this blog, we will discuss a coding problem where we have to print the level of all nodes in a binary tree. We will be using a queue data structure to solve the problem.
Problem Statement
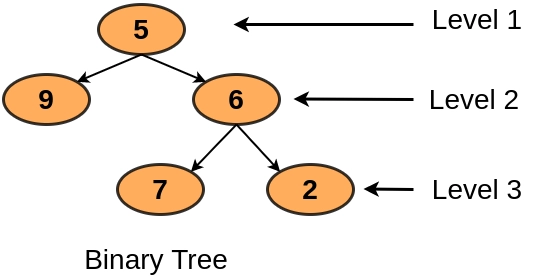
Given a binary tree, You have to print levels of all nodes in a binary tree. The level of a tree is explained in the image below:
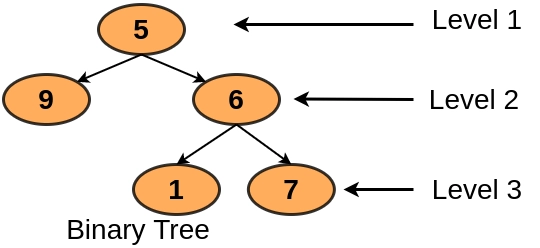
Sample Examples
Input
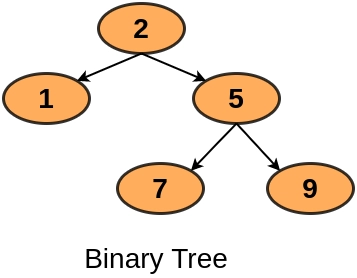
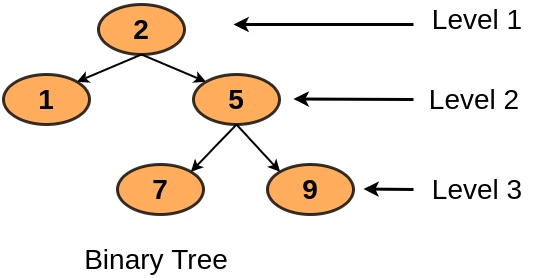
Output
Node 2, Level: 1
Node 1, Level: 2
Node 5, Level: 2
Node 7, Level: 3
Node 9, Level: 3
Explanation
Example 2
Input
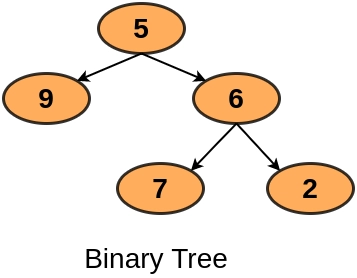
Output
Node 5, Level: 1
Node 9, Level: 2
Node 6, Level: 2
Node 7, Level: 3
Node 2, Level: 3
Explanation
Approach
We’ll create a queue to store the node and its level. Then we’ll do a level order traversal in which we’ll first print the level of the first element from the queue and then we’ll push the left and right children of that node into our queue. We'll keep on repeating this process until our queue becomes empty.
Algorithm
- Create a queue to store the tree node with level.
- Push the root node into the queue with 1 as the level.
-
Do a level order traversal
- Get the first element from the queue and print its level.
- Push the left and right child of the node into the queue.
- Keep repeating the above steps until our queue becomes empty.
- Exit
Implementation in C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// our node
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node(int data)
{
this->data = data;
left = nullptr;
right = nullptr;
}
};
void print_level(Node *root)
{
// if root node is null
// return
if (!root)
return;
// queue for storing tree node with level
queue<pair<Node *, int>> q;
// pushing root node
q.push({root, 1});
// storing node with level
pair<Node *, int> p;
// level order traversal
while (!q.empty())
{
p = q.front();
q.pop();
// printing the level of node
cout << "Node " << p.first->data << ", Level: " << p.second << "\n";
if (p.first->left)
q.push({p.first->left, p.second + 1});
if (p.first->right)
q.push({p.first->right, p.second + 1});
}
}
// main function
int main()
{
// root node
Node *root = NULL;
// Constructing binary tree
root = new Node(2);
root->left = new Node(1);
root->right = new Node(5);
root->right->left = new Node(7);
root->right->right = new Node(9);
// calling the function
print_level(root);
return 0;
}
Output
Node 2, Level: 1
Node 1, Level: 2
Node 5, Level: 2
Node 7, Level: 3
Node 9, Level: 3Time Complexity
Time complexity is O(n), where n is the number of nodes in a binary tree.
Space Complexity
A queue is used to store the node with its level. So, the space complexity of our program is O(n).





