Introduction
We'll take a quick look at the problem statement and discuss the level order tree traversal approach to solve the problem of printing the nodes between two given level numbers of a binary tree. Level Order traversal is one of the most famous binary tree traversal techniques which is also known as breadth-first traversal. There are different types of binary tree traversals - Inorder, Postorder, and Preorder. Please also have a look at this blog which explains the topic of Level Order Traversal in detail.
Problem Statement
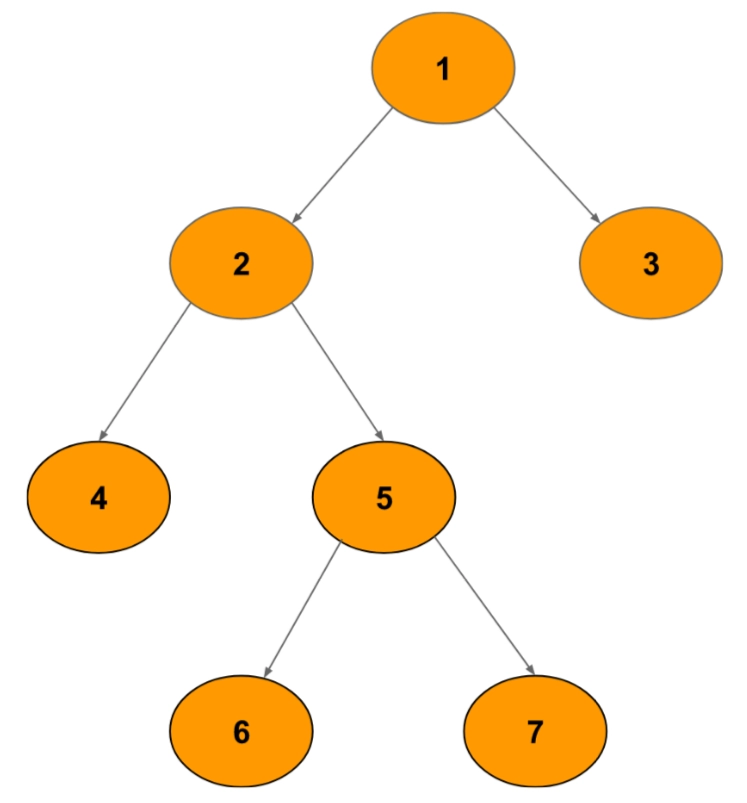
We are given a binary tree and two integers low and high, and we have to print the nodes from level low to level high (both inclusive).
Sample Examples
Input
Enter the low val: 2
Enter the high val: 3
Output
The nodes between given two levels is :
2 3
4 5
Explanation

For low=2 and high=3 , we get the nodes 2, 3 at level 2 and 4, 5 at level 3.
Approach
A straight approach would be to print all nodes of given levels one by one. Then call a recursive function using a loop from the upper level to the lower level in the tree. This algorithm is simple but more complex of order O(n^2), where n is the total number of nodes in the binary tree.
Using queue-based iterative level order traversal, we can print nodes in O(n) time. The goal is to perform a simple level order traversal using a queue. Add a marker node at the end of your inorder traversal. We raise the level number whenever we see a marker node. If the level number is between low and high, then print nodes.
Algorithm
-
Create a queue to store the tree node with level.
-
Push the root node into the queue with 1 as the level.
-
Do a level order traversal
-
Get the first element from the queue if it is in between low and high level and print it.
-
Push the left and right child of the node into the queue.
-
Keep repeating the above steps until our queue becomes empty.
-
Get the first element from the queue if it is in between low and high level and print it.
- Exit
Implementation in C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
int key;
struct Node* left;
struct Node* right;
};
//function to print node between low and high lvl
void lvl_order(Node* root, int low_val, int high_val)
{
queue <Node *> q;
int level = 1;
// position node to indicate end of level
Node *pos = new Node;
// push only first level node and pos node for end of lvl
q.push(root);
q.push(pos);
while (q.empty() == 0)
{
// Remove the front item from queue
Node *n = q.front();
q.pop();
// Check if end of lvl is reached
if (n == pos)
{
cout << endl;
level++; //increment lvl
//if the queue is empty or lvl exceeds then break
if (q.empty() == true || level > high_val) break;
// Enqueue the pos for end of next level
q.push(pos);
continue;
}
//if level is above low print
if (level >= low_val)
cout << n->key << " ";
// Enqueue the rest children
if (n->left != NULL)
q.push(n->left);
if (n->right != NULL)
q.push(n->right);
}
}
// allocates new node with data and NULL left,right pointers
Node* newNode(int key)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->key = key;
temp->left = NULL;
temp->right = NULL;
return (temp);
}
int main()
{
int low,high;
cout<<"Enter the low val: ";
cin>>low;
cout<<"Enter the high val: ";
cin>>high;
struct Node *root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
root->left->right->left = newNode(6);
root->left->right->right = newNode(7);
cout << "The nodes between given two levels is : ";
lvl_order(root, low, high);
return 0;
}
Input
Enter the low val: 2
Enter the high val: 3
Output
The nodes between given two levels is :
2 3
4 5Time Complexity
Time complexity is O(n), where n is the number of nodes in a binary tree.
Space Complexity
A queue is used to store the node with its level. So, the space complexity of our program is O(n).





