Solution
Recommended: Please try to solve it yourself first before moving on to the solution.
The idea is simple:
- We will first find the pointer to the last node of the Linked List.
- We can recursively sort the Linked List using pointers to the first and last nodes of a linked list, similar to the recursive method where we pass indexes of first and last array elements.
- A linked list's partition function is similar to that of an array's partition function. It will return a pointer to the pivot element instead of the index of the pivot element.
Below is the C++ implementation of QuickSort on a Doubly Linked List:
// QuickSort on a Doubly Linked List
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// a node of a doubly linked list.
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node *next;
Node *prev;
};
/* A helper function to swap elements. */
void swap ( int* x, int* y ) {
int temp = *x;
*x = *y;
*y = temp;
}
// A helper function to find the last node of the linked list.
Node *lastNode(Node *head)
{
Node *root = head;
while (root && root->next)
root = root->next;
return root;
}
//Consider the last element as pivot.
Node* partition(Node *start, Node *end)
{
// set pivot as end element.
int pivot = end->data;
// similar to i = l-1 for array implementation.
Node *i = start->prev;
for (Node *temp = start; temp != end; temp = temp->next)
{
if (temp->data <= pivot)
{
if ( i == NULL)
i = start;
else
i = i->next;
swap(&(i->data), &(temp->data));
}
}
if ( i == NULL)
i = start;
else
i = i->next;
swap(&(i->data), &(end->data));
return i;
}
// implementation of quicksort.
void _quickSort(Node *start, Node *end)
{
if (end != NULL && start != end && start != end->next)
{
Node *pivot = partition(start, end);
_quickSort(start, pivot->prev);
_quickSort(pivot->next, end);
}
}
void quickSort(Node *root)
{
Node *end = lastNode(root);
Node *head = root;
_quickSort(head, end);
}
// A helper function to print contents of arr.
void printList(Node *root)
{
while (root)
{
cout << root->data << " ";
root = root->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
//helper function to insert a node in the beginning.
void push(Node** head, int data)
{
Node* node = new Node;
node->data = data;
node->prev = NULL;
node->next = (*head);
if ((*head) != NULL)
(*head)->prev = node ;
(*head) = node;
}
/* Driver code */
int main()
{
Node *root = NULL;
push(&root, 2);
push(&root, 4);
push(&root, 8);
push(&root, 12);
push(&root, 15);
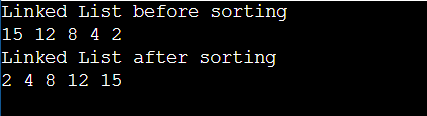
cout << "Linked List before sorting \n";
printList(root);
quickSort(root);
cout << "Linked List after sorting \n";
printList(root);
return 0;
}

You can also try this code with Online C++ Compiler
Output
Time Complexity
The above implementation is the same as QuickSort for arrays. Therefore time complexity is also the same as that of the time complexity of QuickSort for an array.
In the worst case, it takes O(n2) time, whereas, in the average and best cases, it takes O(NLogN). When the linked list is already sorted, the worst case occurs.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is a Doubly Linked List different than a Singly Linked List?
The nodes of Doubly Linked Lists have pointers to their previous nodes as well as their next nodes in them. Whereas the nodes of a singly Linked List only have pointers to the next node.
What is the worst-case time complexity of the QuickSort algorithm?
QuickSort algorithm has a worst-case time complexity of O(N*N) where N is the size of the data set and the next case time complexity is O(NlogN).
Conclusion
Here we saw how to implement QuickSort on a Doubly Linked List. Join this Master Class on DP by Coding Ninjas and become a Ninja coder.
Challenge: Can you implement random QuickSort for a linked list?
Random QuickSort is when we choose pivot randomly. We can only implement Quicksort for Linked List when we can choose a fixed point as the pivot (like the last element in the above implementation). Therefore, Random QuickSort cannot be implemented for Linked Lists.
Recommended Problems -
Recommended Articles
Do check out The Interview guide for Product Based Companies as well as some of the Popular Interview Problems from Top companies like Amazon, Adobe, Google, Uber, Microsoft, etc. on Coding Ninjas Studio.
Also check out some of the Guided Paths on topics such as Data Structure and Algorithms, Competitive Programming, Operating Systems, Computer Networks, DBMS, System Design, etc. as well as some Contests, Test Series, Interview Bundles, and some Interview Experiences curated by top Industry Experts only on Coding Ninjas Studio.
Happy Coding!