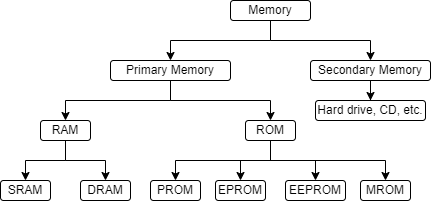
What is Secondary Memory?
Secondary memory is used for long-term storage. Unlike primary memory, it is not directly accessed by the CPU. It stores data, files, software, and the operating system even when the power is off.
This type of memory keeps your data safe until you choose to delete or update it. Before using this data, the computer moves it to primary memory.
Here are some common types of secondary memory:
- Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) – store large amounts of data permanently.
- Compact Discs (CDs) – store music, software, and files.
- Digital Versatile Discs (DVDs) – store videos or larger files than CDs.
- Floppy Disks – old storage devices with low capacity, now rarely used.
Secondary memory offers more space than primary memory, but it works slower. It is essential for saving your work and files over time.
RAM
RAM stands for Random Access Memory. It is a primary volatile memory and stores the data required by the CPU while executing a program. RAM is volatile memory meaning that the data is lost when the power is turned off. The data stored in RAM can be read and changed in any order. RAM can further be classified into SRAM (Static Random Access Memory) and DRAM (Dynamic Random Access Memory).
Types of RAM
- Static RAM (SRAM)
- Dynamic RAM (DRAM)
SRAM (Static RAM)
As suggested by the word static, Static-RAM holds the data as long as power is available. It uses latching circuitry (D Flip-Flops) to store every bit. It can store only a limited number of bits per chip, making it more expensive. SRAM is faster than DRAM, but it uses more power and generates more heat. SRAM is used in cache memory and CPU internal registers.
DRAM (Dynamic RAM (DRAM)
Dynamic-RAM requires a recharge every few milliseconds to maintain its data, hence the name dynamic. It stores each bit of data in a memory cell consisting of a capacitor and a transistor, based on MOS (Metal Oxide Semiconductor) technology. Due to this, it can store many bits per chip, making it inexpensive. It uses less power than SRAM and generates less heat. It is primarily used in main memory. The RAM in computers or the graphics memory on the graphics card, which we usually refer to, is DRAM.
Advantages and Disadvantages of RAM
Advantages of RAM
- Fast Data Access
RAM allows quick access to data, making it faster than other types of storage like hard disks. This speed helps improve the system’s overall performance.
- Supports Multitasking
More RAM lets the computer run multiple applications at the same time without slowing down. It helps in switching between apps smoothly.
- Temporary Storage for Active Tasks
RAM stores only the data currently in use. This temporary nature helps the system stay organized and responsive while working.
Disadvantages of RAM
- Volatile Memory
RAM loses all data when the computer is turned off. You cannot use it to save data permanently.
- Limited Storage
RAM has a smaller capacity compared to hard drives. If too many programs run at once, it can slow down or crash the system.
- Expensive Cost
RAM is more costly per GB than secondary storage. Increasing RAM in a system can raise the overall cost of the computer.
ROM (Read Only Memory)
ROM stands for Read-Only Memory. As the name implies, the contents stored on this memory can only be read and usually can not be changed. However, there are some types of ROM where modification is allowed. The manufacturer programs the ROM, after which the data and instructions can't be altered or modified. ROM is a non-volatile memory; therefore, it retains the data stored in it even after a power cut. It holds the crucial information essential to operate the system. For example- a program that is needed to boot the computer. It is used where the programming needs not to be changed like embedded systems, calculators, etc. ROM can further be classified into four types: PROM (Programmable ROM), EPROM (Erasable Programmable ROM), EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable ROM), and MROM (Mask ROM).
Types of ROM
- ROM (Read-Only Memory)
- PROM (Programmable ROM)
- EPROM (Erasable Programmable ROM)
- EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable ROM)
PROM (Programmable ROM)
PROM is a type of ROM where the user can program the ROM but only once in its lifetime. After it has been programmed, the data and instructions can't be changed by anyone.
Uses: Cell Phones and Video Game Consoles
EPROM (Erasable Programmable ROM)
EPROM can be programmed by the user more than once, unlike PROM, but to do so, the user needs to erase the previous data and instructions stored on it by exposing it to Ultraviolet light.
Uses: Intel 8048 micro-controller (to store programs)
EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable ROM)
EEPROM can also be reprogrammed multiple times. But here, it is erased and reprogrammed electrically without using Ultraviolet lights. It is also known as Flash EEPROM as it is similar to flash memory. It can be erased and reprogrammed continuously, up to 10000 times.
Uses: Computer (to store BIOS)
MROM (Masked ROM)
MROM chips are made of ICs (Integrated Circuits). It is programmed during the manufacturing process only and can't be reprogrammed later. However, if reprogramming is required, the process would be complex or slow.
Uses: It is the oldest type of ROM, and it's not used anywhere in today's world.
Read About - Shift Registers in Digital Electronics
Advantages and Disadvantages of ROM
Advantages of ROM
- Permanent Storage
ROM stores data permanently, even when the power is turned off. It helps in saving essential programs like system boot instructions.
- Data Security
Since users cannot easily modify the ROM, it offers better security for important data. This prevents accidental changes or deletions.
- Low Power Usage
ROM consumes very little power compared to other memory types. This makes it ideal for devices that need to stay powered for long hours.
Disadvantages of ROM
- Not Easily Upgradable
ROM cannot be updated or rewritten easily. You need special tools or chips to make changes.
- Slow Data Access
ROM is slower than RAM in reading and processing data. This makes it unsuitable for tasks that need fast performance.
- Limited Storage Capacity
ROM usually has smaller storage space. It can only store essential programs and is not ideal for large data.
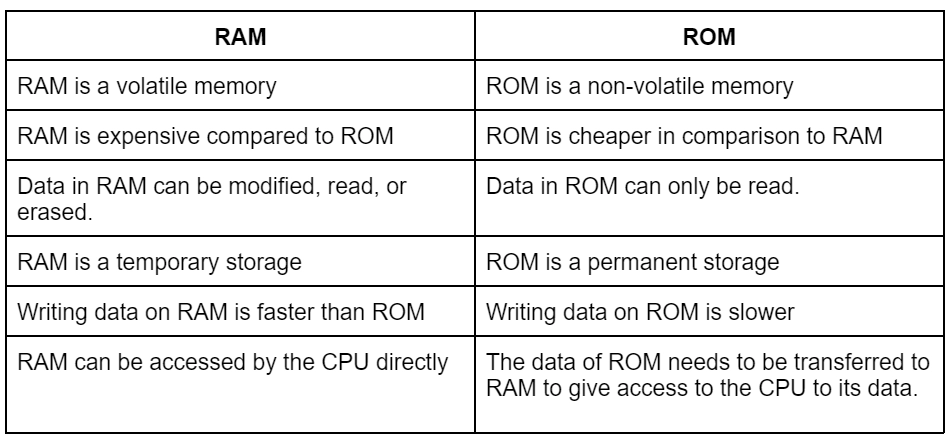
Differences between RAM and ROM
You can also read about the memory hierarchy Demultiplexer
Frequently Asked Questions
Is a hard disk a type of ROM?
No, hard disk is a type of secondary memory, and ROM is primary memory.
Which is the fastest memory?
Cache memory is the fastest.
Which memory is volatile?
RAM is a volatile memory.
Which memory is used primarily in the startup process of a computer?
ROM is used in the booting process of a computer.
Among RAM and HDD/SDD, which one is faster?
RAM is faster than HDD and SDD.
Conclusion
In this article, we have learned what RAM is and what ROM is. We also discussed different types of RAMs and ROMs and their real-life applications. I hope you have learned something from this article. Don't stop here; learn about the evolution of computers and the classification of computers to further increase your knowledge in Computer Architecture and Organization.
Happy Learning Ninja :)