Introduction
C++ is a powerful language with a limitless number of libraries. And as we all know, great power comes with great responsibility. At a time, almost every coder needs to take input from a file. A file is a perfect way to hold any data in the hardware.
This blog will discuss how to read file line by line using C++. Let's start.
Read File Line by Line using C++
Let's first decode the meaning of this name. The name itself says that reading a file line by line. We will do the same things using different methods. Now, there are many ways to do so. We will see some important and most-used methods.
Using the >> Operator
This (>>) operator is also known as the right shift operator. Here, we call this a stream input operator that will read the input from the text file.
Let's say we have a text file named "Ninja.txt", and the data inside the file looks like the below image.
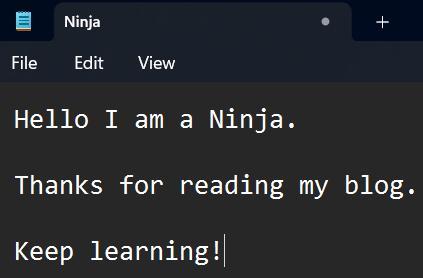
As you can see in the above image, three lines are separated by line breaks in the given text file. Let's try to read file line by line using C++. We will take a code example for a better understanding of this topic.
Implementation
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
int main (){
std::ifstream file;
file.open("Ninja.txt");
std::string str;
if ( file.is_open() ) {
while ( file.good() ) {
file >> str;
std::cout << str;
}
}
else {
std::cout << "Couldn't open file\n";
}
return 0;
}Output

Explanation
Our first step is to check whether the given file is open. If the file is open, put the file's content in the stream and print the data present in the stream on the output screen.
If you notice here, we are not getting any kind of space or line break after any words. The reason behind this is the >> operator. The >> operator simply removes all the whitespace or line breaks from the input file to the output screen.
Now the question is how we can resolve this issue. Let's move to the next heading for the answer.
Using get() Function
To resolve the above problem, we will use the get() method in place of the >> operator. The get() function reads only a single character at a time and is also a member of fstream class. The implementation using the get() is as follows.
Implementation
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
int main (){
std::ifstream file;
file.open("Ninja.txt");
if (file.is_open() ) {
char input;
while (file) {
input = file.get();
std::cout << input;
}
}
else {
std::cout << "Couldn't open file\n";
}
return 0;
}Output
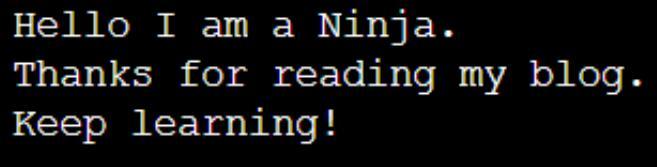
Explanation
As you can see, we have got our desired output along with the whitespaces and line breaks using the get() function. The get() function treats the whitespace as a character. That's why we are able to see them as well.
Using std:: getline() Function
In the next method, we will use the getline() method to read the file line by line. Initially, we will create an input stream and then open the file using the open() method. Before moving to the working example, we will see the syntax of getline() function.
Syntax
istream& getline (istream& is, string& str, char delim);Here,
-
Here, "is" is the object of the stream class. Along with this, "is" also tells the method about the stream from where it will read input.
-
str is simply a string that will store the input after the stream read it from the text file.
-
The delim is an optional argument in the getline() function syntax. It tells the stream when to stop reading the input. This argument takes a character as input, and as soon as the stream finds the character, it stops reading.
- Generally, the getline() function takes input until the file ends or encounters a new line (\n).
Implementation
Let's now discuss the working code example to read file line by line using C++.
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
int main () {
std::ifstream file;
file.open("Ninja.txt");
std::string str;
if ( file.is_open() ) {
while ( file.good() ) {
std::getline (file, str);
std::cout << str << '\n';
}
}
else {
std::cout << "Couldn't open file\n";
}
return 0;
}Output
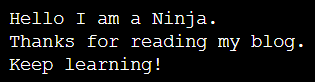
Explanation
In the above code,
-
We first opened the file named Ninja.txt.
-
After that, we created a string variable, str.
-
In the next step, we opened the file using the open() function. Here, we used the function getline() with the first two arguments, i.e., is & str (mentioned in syntax).
- After that, we printed the file that stream read as an input.
Also see, Abstract Data Types in C++




