Introduction
Operating system software handles computer operations such as editing, input/output operation, resource allocation, file system manipulation, etc., and acts as a visual interface between user and hardware. There are different types of operating systems which are-
- Real-time operating system
- Time-sharing operating system
- Distributed operating system
- Network operating system
- Batch operating system
In this article, we are going to discuss about the Real Time Operating System in detail.

So, let’s get started:
Also see: Multiprogramming vs Multitasking and Open Source Operating System
What is a Real-Time Operating System?
A real-time operating system (RTOS) is a specially designed operating system used in computers with strict time limits for any work to be done. It is widely used in those systems where calculation results influence the process while executing.
In RTOS, the processing time required is calculated by ten incremental seconds. It is a time-limited system defined as fixed time constraints. In this type of system, processing should be done within the specified parameters. Otherwise, this will lead to system failure.
Examples of real-time operating systems: Flight traffic control systems, Command Control Systems, Heart pacemakers, Airlines Booking systems, Multimedia Network Systems, Medical Imaging Systems, Cell phone switching gadgets, Robots, etc.

Source:Intel
Next, let us discuss the components of an RTOS:
Also Read About, FCFS Scheduling Algorithm and Difference Between Bit and Byte
Components of Real-Time Operating System (RTOS)
RTOS is system software that controls computer hardware and software resources and provides essential services to computer programs. It acts as a link between the computer user and the computer hardware like any other operating system. We can perform computer programs efficiently and easily using the operating system. There are several different tasks performed within the system, and it responds appropriately to every task in short intervals. This makes real-time systems compatible with systems.
There are various components of Real-time operating systems which are given below-
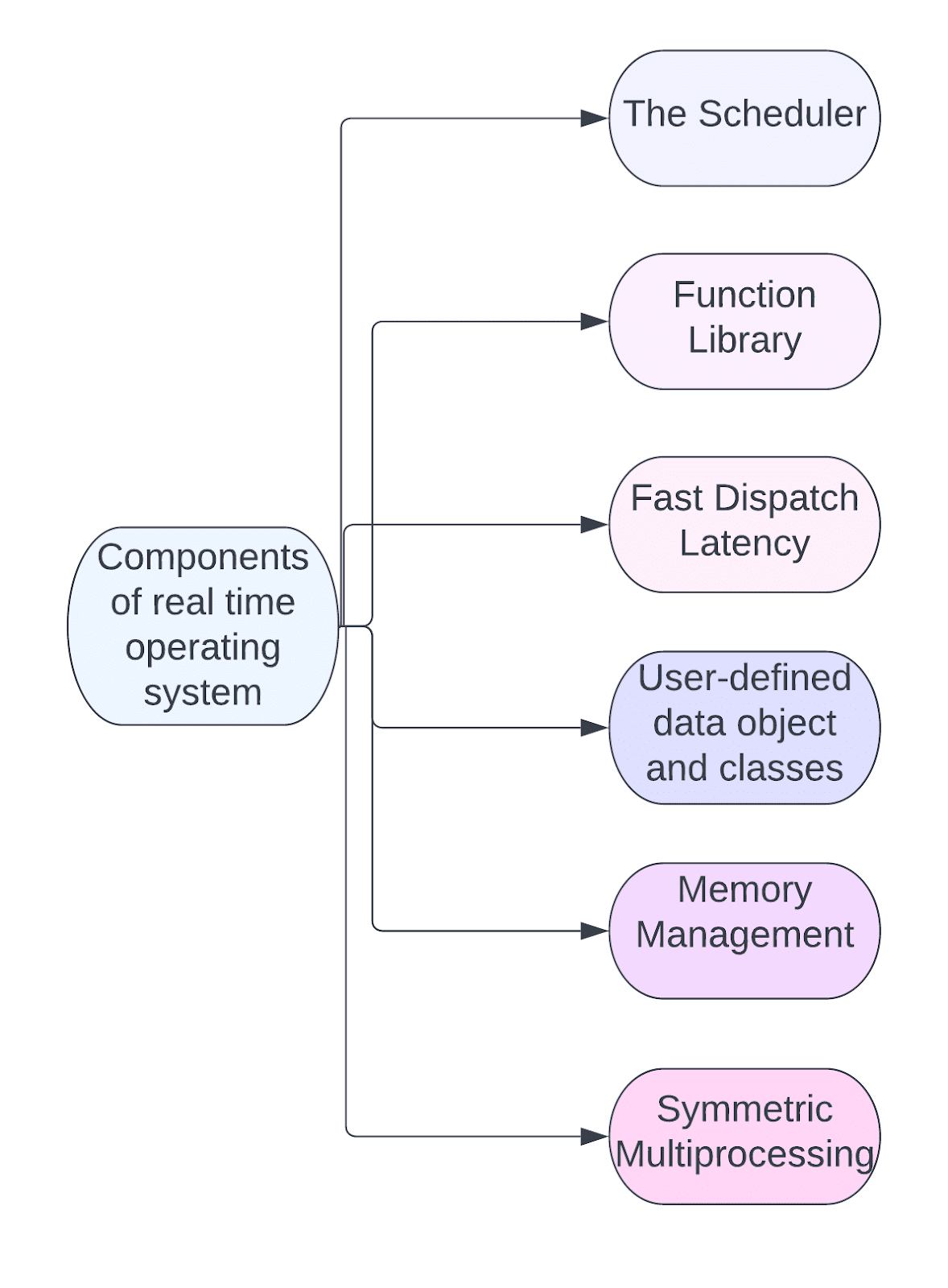
The Scheduler: This component of RTOS tells the order of the tasks in which it can be executed which are usually based on priorities.
Function Library: It is an important RTOS feature that serves as a visual connector that helps you to connect the kernel and application code. This application allows you to send requests to Kernel using the library so that the app can provide the results you want.
Fast dispatch latency: It is an interval between the termination of the task that can be identified by the OS and the actual time taken by the thread, which is in the ready queue, that has started processing.
User-defined data objects and classes: The RTOS system uses programming languages such as C or C ++, which must be configured according to their functionality or operation.
Memory Management: this feature is required in the system to allocate memory to every program, which is a very important part of RTOS.
Symmetric Multiprocessing (SMP): It is a number of different functions that can be managed by RTOS so that parallel processing can be done.
Must Read Multiprocessing Operating System






