Introduction
Kivy is an independent GUI tool in Python that can be used to create Android, IOS, Linux, and Windows applications. Kivy provides the functionality to write the code for once and run it on different platforms. Though, most applications built on kivy are Android applications we can use it for desktop applications as well.
Relative Layout is one of the many layout techniques that allow us to set the position of our children's elements. Relative makes use of the fact that the children always hold a relative position with respect to the parent. Thus, we can make our children positioned relative to the layout. Therefore, in this blog we will learn how we can create a relative layout.
Creating Relative Layout
The relative layout is similar to the FloatLayout with the only differences being that the positioning properties (x, y, center_x, right, y, center_y, and top) are relative to the Layout size and not the whole window size making it relative to the parent element. The window coordinate system defines the coordinate with (0,0) at the bottom left corner of the window. After that, we can define where the child needs to be placed in relation to the parent widget.
The available pos_hint keys are useful for aligning to edges or centering.
Example
pos_hint: {‘center_x’: .5, ‘center_y’: .5} would make sure that the widget is always aligned in the middle of the parent no matter the size of the window.
rellayout.py
#we import all the necessary imports
import kivy
from kivy.app import App
#here we need the relative layout import and the config to configure the graphics as resizable
from kivy.uix.relativelayout import RelativeLayout
from kivy.config import Config
Config.set('graphics', 'resizable', True)
#create a parent widget that will contain all the other children in relative layout
class RelLayout(RelativeLayout):
pass
#create the function that will be run along with the .kv file
class RelLayoutApp(App):
# defining build()
def build(self):
# returning the instance of root class
return RelLayout()
# run the app
if __name__ == "__main__":
RelLayoutApp().run() RelLayout.kv
Now we will create the .kv file for the above py file. This will contain first the button for our program. Next we define the Relative layout and give some examples.
<Button>:
font_size: 15
size_hint: 0.25, 0.25
<RelativeLayout>:
canvas:
Color:
rgb:0, 1, 1
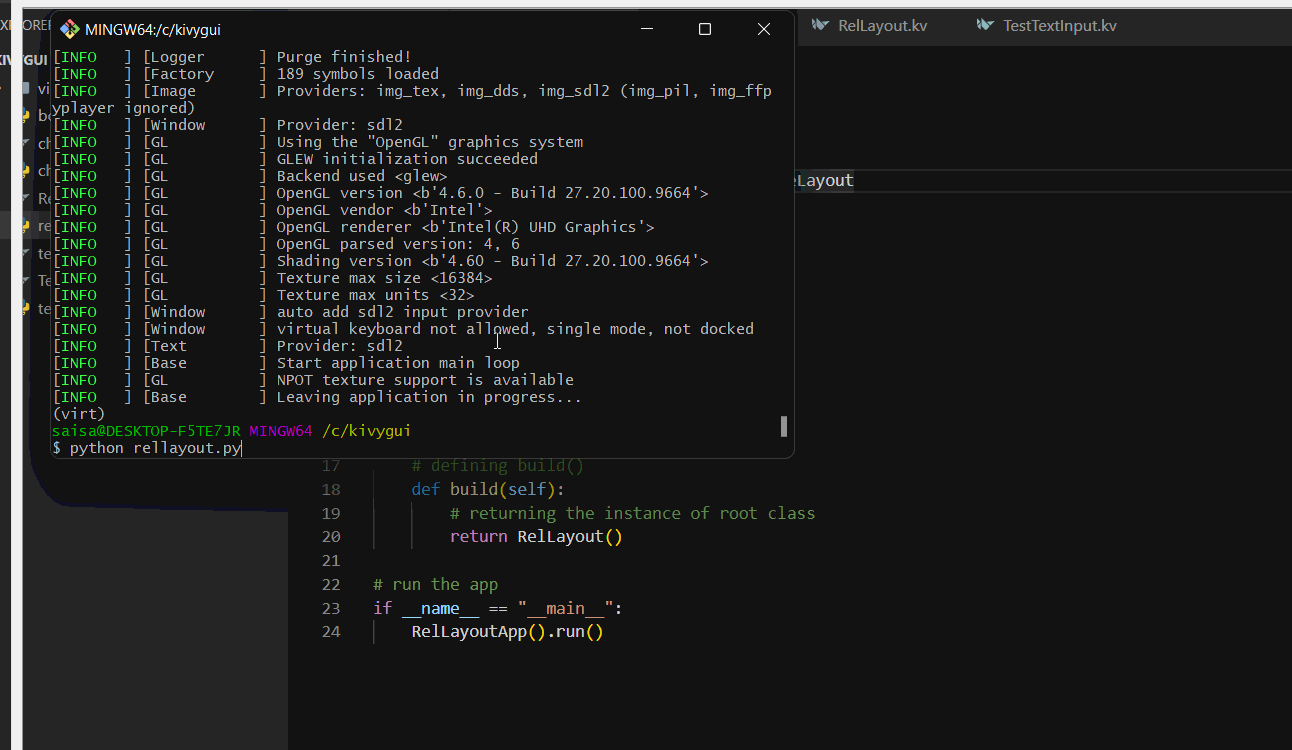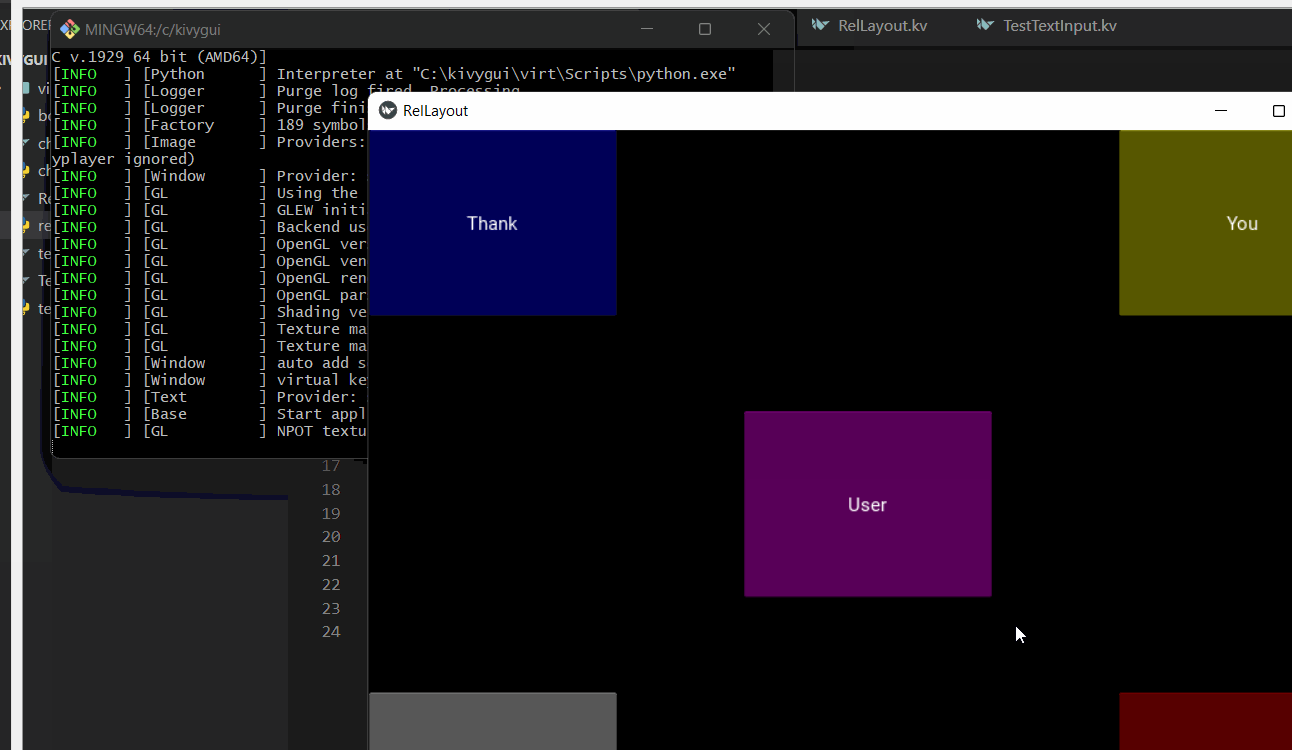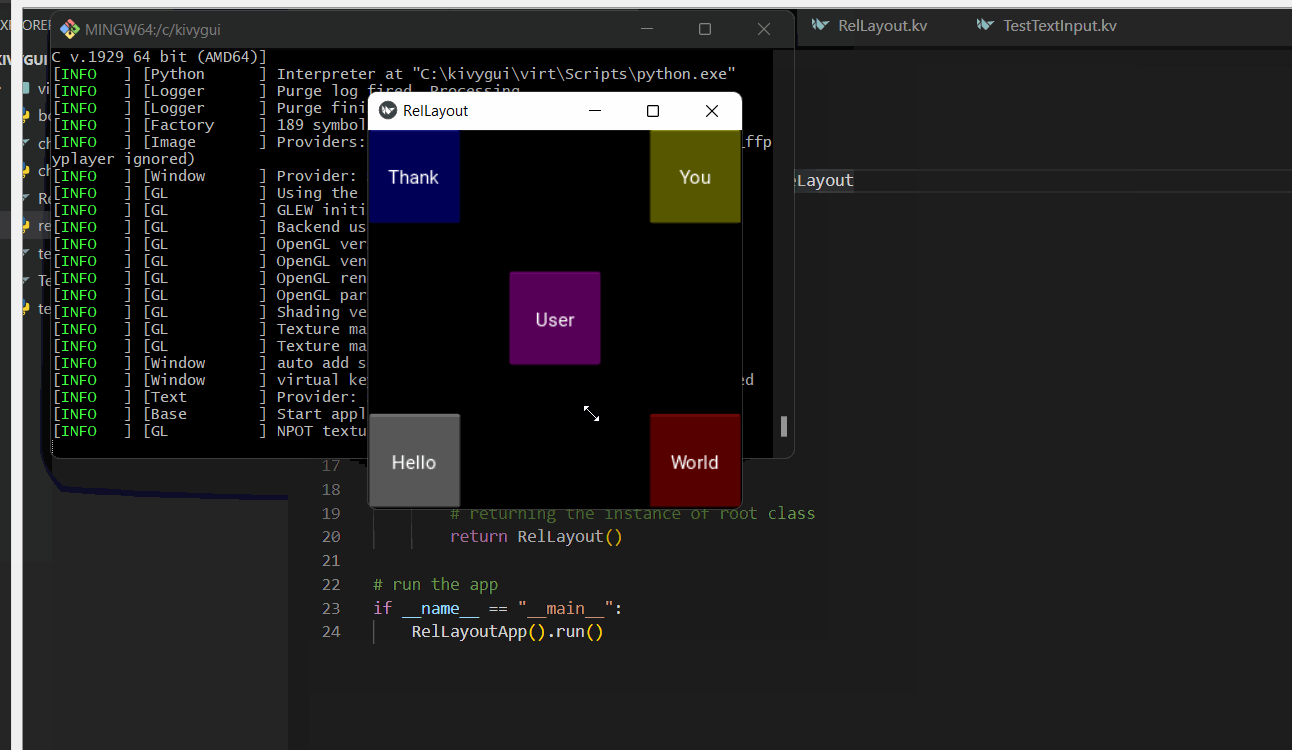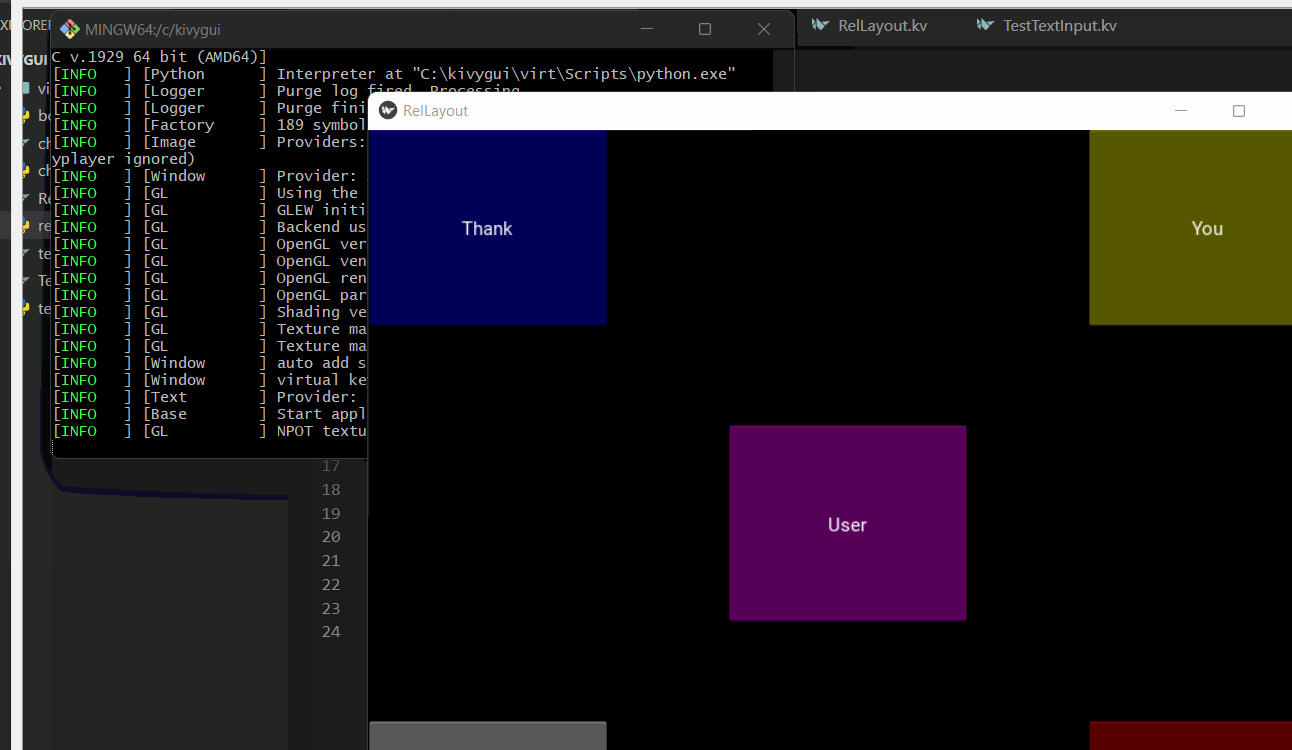
Button:
text:"Hello"
background_color: 0.1, 0.5, 0.6, 1
# relatively at 0 from x axis and 0 from y axis
pos_hint: {"x":0, "y":0}
Button:
text:"World"
background_color: 1, 0, 0, 1
pos_hint: {"right":1, "y":0}
Button:
text:"User"
background_color: 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 1
pos_hint: {"center_x":.5, "center_y":.5}
Button:
text:"Thank"
background_color: 0, 0, 1, 1
pos_hint: {"x":0, "top":1}
Button:
text:"You"
background_color: 0.8, 0.9, 0.2, 1
pos_hint: {"right":1, "top":1} Output